This code computes Goodness of Pronunciation (GOP) and extracts phone-level pronunciation feature for mispronunciations detection tasks, the reference: More...
Namespaces | |
| cu | |
| decoder | |
| differentiable_transform | |
| discriminative | |
| internal | |
| kws_internal | |
| nnet1 | |
| nnet2 | |
| nnet3 | |
| sparse_vector_utils | |
| unittest | |
Classes | |
| class | AccumAmDiagGmm |
| class | AccumDiagGmm |
| class | AccumFullGmm |
| Class for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model. More... | |
| class | AccumulateMultiThreadedClass |
| struct | AccumulateTreeStatsInfo |
| struct | AccumulateTreeStatsOptions |
| struct | ActivePath |
| class | AffineXformStats |
| class | AgglomerativeClusterer |
| The AgglomerativeClusterer class contains the necessary mechanisms for the actual clustering algorithm. More... | |
| struct | AhcCluster |
| AhcCluster is the cluster object for the agglomerative clustering. More... | |
| struct | AlignConfig |
| struct | AlignedTermsPair |
| class | AmDiagGmm |
| class | AmSgmm2 |
| Class for definition of the subspace Gmm acoustic model. More... | |
| class | ArbitraryResample |
| Class ArbitraryResample allows you to resample a signal (assumed zero outside the sample region, not periodic) at arbitrary specified time values, which don't have to be linearly spaced. More... | |
| class | ArcPosteriorComputer |
| class | ArpaFileParser |
| ArpaFileParser is an abstract base class for ARPA LM file conversion. More... | |
| struct | ArpaLine |
| class | ArpaLmCompiler |
| class | ArpaLmCompilerImpl |
| class | ArpaLmCompilerImplInterface |
| struct | ArpaParseOptions |
| Options that control ArpaFileParser. More... | |
| class | basic_filebuf |
| class | basic_pipebuf |
| class | BasicHolder |
| BasicHolder is valid for float, double, bool, and integer types. More... | |
| class | BasicPairVectorHolder |
| BasicPairVectorHolder is a Holder for a vector of pairs of a basic type, e.g. More... | |
| class | BasicVectorHolder |
| A Holder for a vector of basic types, e.g. More... | |
| class | BasicVectorVectorHolder |
| BasicVectorVectorHolder is a Holder for a vector of vector of a basic type, e.g. More... | |
| class | BasisFmllrAccus |
| Stats for fMLLR subspace estimation. More... | |
| class | BasisFmllrEstimate |
| Estimation functions for basis fMLLR. More... | |
| struct | BasisFmllrOptions |
| class | BiglmFasterDecoder |
| This is as FasterDecoder, but does online composition between HCLG and the "difference language model", which is a deterministic FST that represents the difference between the language model you want and the language model you compiled HCLG with. More... | |
| struct | BiglmFasterDecoderOptions |
| class | BottomUpClusterer |
| struct | ClatRescoreTuple |
| class | Clusterable |
| struct | ClusterKMeansOptions |
| class | CompactLatticeHolder |
| class | CompactLatticeToKwsProductFstMapper |
| struct | CompareFirstMemberOfPair |
| Comparator object for pairs that compares only the first pair. More... | |
| struct | ComparePosteriorByPdfs |
| struct | CompareReverseSecond |
| class | CompartmentalizedBottomUpClusterer |
| struct | CompBotClustElem |
| struct | ComposeLatticePrunedOptions |
| class | CompressedAffineXformStats |
| class | CompressedMatrix |
| class | ComputeNormalizersClass |
| class | ConfigLine |
| This class is responsible for parsing input like hi-there xx=yyy a=b c empty= f-oo=Append(bar, sss) ba_z=123 bing='a b c' baz="a b c d='a b' e" and giving you access to the fields, in this case. More... | |
| class | ConstantEventMap |
| class | ConstArpaLm |
| class | ConstArpaLmBuilder |
| class | ConstArpaLmDeterministicFst |
| This class wraps a ConstArpaLm format language model with the interface defined in DeterministicOnDemandFst. More... | |
| class | ConstIntegerSet |
| class | ContextDependency |
| class | ContextDependencyInterface |
| context-dep-itf.h provides a link between the tree-building code in ../tree/, and the FST code in ../fstext/ (particularly, ../fstext/context-dep.h). More... | |
| struct | CountStats |
| class | CovarianceStats |
| struct | CuAllocatorOptions |
| class | CuArray |
| Class CuArray represents a vector of an integer or struct of type T. More... | |
| class | CuArrayBase |
| Class CuArrayBase, CuSubArray and CuArray are analogues of classes CuVectorBase, CuSubVector and CuVector, except that they are intended to store things other than float/double: they are intended to store integers or small structs. More... | |
| class | CuBlockMatrix |
| The class CuBlockMatrix holds a vector of objects of type CuMatrix, say, M_1, M_2, . More... | |
| class | CuCompressedMatrix |
| Class CuCompressedMatrix, templated on an integer type (expected to be one of: int8, uint8, int16, uint16), this provides a way to approximate a CuMatrix in a more memory-efficient format. More... | |
| class | CuCompressedMatrixBase |
| Class CuCompressedMatrixBase is an abstract base class that allows you to compress a matrix of type CuMatrix<BaseFloat>. More... | |
| class | CuMatrix |
| This class represents a matrix that's stored on the GPU if we have one, and in memory if not. More... | |
| class | CuMatrixBase |
| Matrix for CUDA computing. More... | |
| class | CuPackedMatrix |
| Matrix for CUDA computing. More... | |
| class | CuRand |
| class | CuSparseMatrix |
| class | CuSpMatrix |
| class | CuSubArray |
| class | CuSubMatrix |
| This class is used for a piece of a CuMatrix. More... | |
| class | CuSubVector |
| class | CuTpMatrix |
| class | CuValue |
| The following class is used to simulate non-const references to Real, e.g. More... | |
| class | CuVector |
| class | CuVectorBase |
| Vector for CUDA computing. More... | |
| class | DecisionTreeSplitter |
| class | DecodableAmDiagGmm |
| class | DecodableAmDiagGmmRegtreeFmllr |
| class | DecodableAmDiagGmmRegtreeMllr |
| class | DecodableAmDiagGmmScaled |
| class | DecodableAmDiagGmmUnmapped |
| DecodableAmDiagGmmUnmapped is a decodable object that takes indices that correspond to pdf-id's plus one. More... | |
| class | DecodableAmSgmm2 |
| class | DecodableAmSgmm2Scaled |
| class | DecodableDiagGmmScaledOnline |
| class | DecodableInterface |
| DecodableInterface provides a link between the (acoustic-modeling and feature-processing) code and the decoder. More... | |
| class | DecodableMapped |
| class | DecodableMatrixMapped |
| This is like DecodableMatrixScaledMapped, but it doesn't support an acoustic scale, and it does support a frame offset, whereby you can state that the first row of 'likes' is actually the n'th row of the matrix of available log-likelihoods. More... | |
| class | DecodableMatrixMappedOffset |
| This decodable class returns log-likes stored in a matrix; it supports repeatedly writing to the matrix and setting a time-offset representing the frame-index of the first row of the matrix. More... | |
| class | DecodableMatrixScaled |
| class | DecodableMatrixScaledMapped |
| class | DecodableSum |
| class | DecodableSumScaled |
| class | DecodeUtteranceLatticeFasterClass |
| This class basically does the same job as the function DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster, but in a way that allows us to build a multi-threaded command line program more easily. More... | |
| class | DeltaFeatures |
| struct | DeltaFeaturesOptions |
| class | DeterminizeLatticeTask |
| class | DiagGmm |
| Definition for Gaussian Mixture Model with diagonal covariances. More... | |
| class | DiagGmmNormal |
| Definition for Gaussian Mixture Model with diagonal covariances in normal mode: where the parameters are stored as means and variances (instead of the exponential form that the DiagGmm class is stored as). More... | |
| struct | DummyOptions |
| struct | EbwAmSgmm2Options |
| This header implements a form of Extended Baum-Welch training for SGMMs. More... | |
| class | EbwAmSgmm2Updater |
| struct | EbwOptions |
| class | EbwUpdatePhoneVectorsClass |
| struct | EbwWeightOptions |
| class | EigenvalueDecomposition |
| struct | error_stats |
| class | EventMap |
| A class that is capable of representing a generic mapping from EventType (which is a vector of (key, value) pairs) to EventAnswerType which is just an integer. More... | |
| struct | EventMapVectorEqual |
| struct | EventMapVectorHash |
| class | ExampleClass |
| class | ExampleFeatureComputer |
| This class is only added for documentation, it is not intended to ever be used. More... | |
| struct | ExampleFeatureComputerOptions |
| This class is only added for documentation, it is not intended to ever be used. More... | |
| class | FasterDecoder |
| struct | FasterDecoderOptions |
| class | FbankComputer |
| Class for computing mel-filterbank features; see Computing MFCC features for more information. More... | |
| struct | FbankOptions |
| FbankOptions contains basic options for computing filterbank features. More... | |
| class | FeatureTransformEstimate |
| Class for computing a feature transform used for preconditioning of the training data in neural-networks. More... | |
| class | FeatureTransformEstimateMulti |
| struct | FeatureTransformEstimateOptions |
| struct | FeatureWindowFunction |
| class | FileInputImpl |
| class | FileOutputImpl |
| class | FmllrDiagGmmAccs |
| This does not work with multiple feature transforms. More... | |
| struct | FmllrOptions |
| class | FmllrRawAccs |
| struct | FmllrRawOptions |
| class | FmllrSgmm2Accs |
| Class for computing the accumulators needed for the maximum-likelihood estimate of FMLLR transforms for a subspace GMM acoustic model. More... | |
| class | Fmpe |
| struct | FmpeOptions |
| struct | FmpeStats |
| struct | FmpeUpdateOptions |
| struct | FrameExtractionOptions |
| class | FullGmm |
| Definition for Gaussian Mixture Model with full covariances. More... | |
| class | FullGmmNormal |
| Definition for Gaussian Mixture Model with full covariances in normal mode: where the parameters are stored as means and variances (instead of the exponential form that the FullGmm class is stored as). More... | |
| class | GaussClusterable |
| GaussClusterable wraps Gaussian statistics in a form accessible to generic clustering algorithms. More... | |
| struct | GaussInfo |
| class | GaussPostHolder |
| class | GeneralMatrix |
| This class is a wrapper that enables you to store a matrix in one of three forms: either as a Matrix<BaseFloat>, or a CompressedMatrix, or a SparseMatrix<BaseFloat>. More... | |
| class | GenericHolder |
| GenericHolder serves to document the requirements of the Holder interface; it's not intended to be used. More... | |
| class | HashList |
| struct | HmmCacheHash |
| class | HmmTopology |
| A class for storing topology information for phones. More... | |
| struct | HtkHeader |
| A structure containing the HTK header. More... | |
| class | HtkMatrixHolder |
| struct | HTransducerConfig |
| Configuration class for the GetHTransducer() function; see The HTransducerConfig configuration class for context. More... | |
| class | Input |
| class | InputImplBase |
| union | Int32AndFloat |
| struct | Int32IsZero |
| class | Interval |
| struct | IvectorEstimationOptions |
| class | IvectorExtractor |
| class | IvectorExtractorComputeDerivedVarsClass |
| struct | IvectorExtractorEstimationOptions |
| Options for training the IvectorExtractor, e.g. variance flooring. More... | |
| struct | IvectorExtractorOptions |
| class | IvectorExtractorStats |
| IvectorExtractorStats is a class used to update the parameters of the ivector extractor. More... | |
| struct | IvectorExtractorStatsOptions |
| Options for IvectorExtractorStats, which is used to update the parameters of IvectorExtractor. More... | |
| class | IvectorExtractorUpdateProjectionClass |
| class | IvectorExtractorUpdateWeightClass |
| class | IvectorExtractorUtteranceStats |
| These are the stats for a particular utterance, i.e. More... | |
| class | IvectorExtractTask |
| class | IvectorTask |
| class | KaldiFatalError |
| Kaldi fatal runtime error exception. More... | |
| class | KaldiObjectHolder |
| KaldiObjectHolder works for Kaldi objects that have the "standard" Read and Write functions, and a copy constructor. More... | |
| class | KaldiRnnlmWrapper |
| struct | KaldiRnnlmWrapperOpts |
| class | KwsAlignment |
| class | KwsProductFstToKwsLexicographicFstMapper |
| class | KwsTerm |
| class | KwsTermsAligner |
| struct | KwsTermsAlignerOptions |
| struct | LatticeArcRecord |
| This is used in CompactLatticeLimitDepth. More... | |
| class | LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder |
| This is as LatticeFasterDecoder, but does online composition between HCLG and the "difference language model", which is a deterministic FST that represents the difference between the language model you want and the language model you compiled HCLG with. More... | |
| struct | LatticeFasterDecoderConfig |
| class | LatticeFasterDecoderTpl |
| This is the "normal" lattice-generating decoder. More... | |
| class | LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl |
| LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl is as LatticeFasterDecoderTpl but also supports an efficient way to get the best path (see the function BestPathEnd()), which is useful in endpointing and in situations where you might want to frequently access the best path. More... | |
| class | LatticeHolder |
| struct | LatticeIncrementalDecoderConfig |
| The normal decoder, lattice-faster-decoder.h, sometimes has an issue when doing real-time applications with long utterances, that each time you get the lattice the lattice determinization can take a considerable amount of time; this introduces latency. More... | |
| class | LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl |
| This is an extention to the "normal" lattice-generating decoder. More... | |
| class | LatticeIncrementalDeterminizer |
| This class is used inside LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl; it handles some of the details of incremental determinization. More... | |
| class | LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl |
| LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl is as LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl but also supports an efficient way to get the best path (see the function BestPathEnd()), which is useful in endpointing and in situations where you might want to frequently access the best path. More... | |
| class | LatticeLexiconWordAligner |
| class | LatticePhoneAligner |
| class | LatticeReader |
| LatticeReader provides (static) functions for reading both Lattice and CompactLattice, in text form. More... | |
| class | LatticeSimpleDecoder |
| Simplest possible decoder, included largely for didactic purposes and as a means to debug more highly optimized decoders. More... | |
| struct | LatticeSimpleDecoderConfig |
| class | LatticeWordAligner |
| struct | LbfgsOptions |
| This is an implementation of L-BFGS. More... | |
| class | LdaEstimate |
| Class for computing linear discriminant analysis (LDA) transform. More... | |
| struct | LdaEstimateOptions |
| struct | LinearCgdOptions |
| class | LinearResample |
| LinearResample is a special case of ArbitraryResample, where we want to resample a signal at linearly spaced intervals (this means we want to upsample or downsample the signal). More... | |
| class | LinearVtln |
| class | LmState |
| class | LogisticRegression |
| struct | LogisticRegressionConfig |
| struct | LogMessageEnvelope |
| Log message severity and source location info. More... | |
| struct | MapDiagGmmOptions |
| Configuration variables for Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) update. More... | |
| struct | MapTransitionUpdateConfig |
| class | Matrix |
| A class for storing matrices. More... | |
| class | MatrixBase |
| Base class which provides matrix operations not involving resizing or allocation. More... | |
| class | MelBanks |
| struct | MelBanksOptions |
| class | MessageLogger |
| class | MfccComputer |
| struct | MfccOptions |
| MfccOptions contains basic options for computing MFCC features. More... | |
| class | MinimumBayesRisk |
| This class does the word-level Minimum Bayes Risk computation, and gives you either the 1-best MBR output together with the expected Bayes Risk, or a sausage-like structure. More... | |
| struct | MinimumBayesRiskOptions |
| The implementation of the Minimum Bayes Risk decoding method described in "Minimum Bayes Risk decoding and system combination based on a recursion for
edit distance", Haihua Xu, Daniel Povey, Lidia Mangu and Jie Zhu, Computer Speech and Language, 2011 This is a slightly more principled way to do Minimum Bayes Risk (MBR) decoding than the standard "Confusion Network" method. More... | |
| class | MleAmSgmm2Accs |
| Class for the accumulators associated with the phonetic-subspace model parameters. More... | |
| struct | MleAmSgmm2Options |
| Configuration variables needed in the SGMM estimation process. More... | |
| class | MleAmSgmm2Updater |
| struct | MleDiagGmmOptions |
| Configuration variables like variance floor, minimum occupancy, etc. More... | |
| struct | MleFullGmmOptions |
| Configuration variables like variance floor, minimum occupancy, etc. More... | |
| class | MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs |
| Class for the accumulators required to update the speaker vectors v_s. More... | |
| struct | MleTransitionUpdateConfig |
| class | MlltAccs |
| A class for estimating Maximum Likelihood Linear Transform, also known as global Semi-tied Covariance (STC), for GMMs. More... | |
| class | MultiThreadable |
| class | MultiThreader |
| class | MyTaskClass |
| class | MyThreadClass |
| struct | NccfInfo |
| struct | NGram |
| A parsed n-gram from ARPA LM file. More... | |
| class | NumberIstream |
| class | OfflineFeatureTpl |
| This templated class is intended for offline feature extraction, i.e. More... | |
| class | OffsetFileInputImpl |
| class | OnlineAppendFeature |
| This online-feature class implements combination of two feature streams (such as pitch, plp) into one stream. More... | |
| class | OnlineAudioSourceItf |
| class | OnlineBaseFeature |
| Add a virtual class for "source" features such as MFCC or PLP or pitch features. More... | |
| class | OnlineCacheFeature |
| This feature type can be used to cache its input, to avoid repetition of computation in a multi-pass decoding context. More... | |
| class | OnlineCacheInput |
| class | OnlineCmnInput |
| class | OnlineCmvn |
| This class does an online version of the cepstral mean and [optionally] variance, but note that this is not equivalent to the offline version. More... | |
| struct | OnlineCmvnOptions |
| struct | OnlineCmvnState |
| Struct OnlineCmvnState stores the state of CMVN adaptation between utterances (but not the state of the computation within an utterance). More... | |
| class | OnlineDecodableDiagGmmScaled |
| class | OnlineDeltaFeature |
| class | OnlineDeltaInput |
| struct | OnlineEndpointConfig |
| struct | OnlineEndpointRule |
| This header contains a simple facility for endpointing, that should be used in conjunction with the "online2" online decoding code; see ../online2bin/online2-wav-gmm-latgen-faster-endpoint.cc. More... | |
| class | OnlineFasterDecoder |
| struct | OnlineFasterDecoderOpts |
| class | OnlineFeatInputItf |
| class | OnlineFeatureInterface |
| OnlineFeatureInterface is an interface for online feature processing (it is also usable in the offline setting, but currently we're not using it for that). More... | |
| class | OnlineFeatureMatrix |
| struct | OnlineFeatureMatrixOptions |
| class | OnlineFeaturePipeline |
| OnlineFeaturePipeline is a class that's responsible for putting together the various stages of the feature-processing pipeline, in an online setting. More... | |
| struct | OnlineFeaturePipelineCommandLineConfig |
| This configuration class is to set up OnlineFeaturePipelineConfig, which in turn is the configuration class for OnlineFeaturePipeline. More... | |
| struct | OnlineFeaturePipelineConfig |
| This configuration class is responsible for storing the configuration options for OnlineFeaturePipeline, but it does not set them. More... | |
| class | OnlineFeInput |
| class | OnlineGenericBaseFeature |
| This is a templated class for online feature extraction; it's templated on a class like MfccComputer or PlpComputer that does the basic feature extraction. More... | |
| struct | OnlineGmmAdaptationState |
| struct | OnlineGmmDecodingAdaptationPolicyConfig |
| This configuration class controls when to re-estimate the basis-fMLLR during online decoding. More... | |
| struct | OnlineGmmDecodingConfig |
| class | OnlineGmmDecodingModels |
| This class is used to read, store and give access to the models used for 3 phases of decoding (first-pass with online-CMN features; the ML models used for estimating transforms; and the discriminatively trained models). More... | |
| class | OnlineIvectorEstimationStats |
| This class helps us to efficiently estimate iVectors in situations where the data is coming in frame by frame. More... | |
| struct | OnlineIvectorExtractionConfig |
| This class includes configuration variables relating to the online iVector extraction, but not including configuration for the "base feature", i.e. More... | |
| struct | OnlineIvectorExtractionInfo |
| This struct contains various things that are needed (as const references) by class OnlineIvectorExtractor. More... | |
| struct | OnlineIvectorExtractorAdaptationState |
| This class stores the adaptation state from the online iVector extractor, which can help you to initialize the adaptation state for the next utterance of the same speaker in a more informed way. More... | |
| class | OnlineIvectorFeature |
| OnlineIvectorFeature is an online feature-extraction class that's responsible for extracting iVectors from raw features such as MFCC, PLP or filterbank. More... | |
| class | OnlineLdaInput |
| class | OnlineMatrixFeature |
| This class takes a Matrix<BaseFloat> and wraps it as an OnlineFeatureInterface: this can be useful where some earlier stage of feature processing has been done offline but you want to use part of the online pipeline. More... | |
| class | OnlineMatrixInput |
| struct | OnlineNnet2DecodingConfig |
| struct | OnlineNnet2DecodingThreadedConfig |
| class | OnlineNnet2FeaturePipeline |
| OnlineNnet2FeaturePipeline is a class that's responsible for putting together the various parts of the feature-processing pipeline for neural networks, in an online setting. More... | |
| struct | OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineConfig |
| This configuration class is to set up OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineInfo, which in turn is the configuration class for OnlineNnet2FeaturePipeline. More... | |
| struct | OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineInfo |
| This class is responsible for storing configuration variables, objects and options for OnlineNnet2FeaturePipeline (including the actual LDA and CMVN-stats matrices, and the iVector extractor, which is a member of ivector_extractor_info. More... | |
| class | OnlinePaSource |
| class | OnlinePitchFeature |
| class | OnlinePitchFeatureImpl |
| class | OnlineProcessPitch |
| This online-feature class implements post processing of pitch features. More... | |
| class | OnlineSilenceWeighting |
| struct | OnlineSilenceWeightingConfig |
| class | OnlineSpeexDecoder |
| class | OnlineSpeexEncoder |
| class | OnlineSpliceFrames |
| struct | OnlineSpliceOptions |
| class | OnlineTcpVectorSource |
| class | OnlineTimer |
| class OnlineTimer is used to test real-time decoding algorithms and evaluate how long the decoding of a particular utterance would take. More... | |
| class | OnlineTimingStats |
| class OnlineTimingStats stores statistics from timing of online decoding, which will enable the Print() function to print out the average real-time factor and average delay per utterance. More... | |
| class | OnlineTransform |
| This online-feature class implements any affine or linear transform. More... | |
| class | OnlineUdpInput |
| class | OnlineVectorSource |
| class | OptimizableInterface |
| OptimizableInterface provides a virtual class for optimizable objects. More... | |
| class | OptimizeLbfgs |
| class | OptionsItf |
| class | OtherReal |
| This class provides a way for switching between double and float types. More... | |
| class | OtherReal< double > |
| A specialized class for switching from double to float. More... | |
| class | OtherReal< float > |
| A specialized class for switching from float to double. More... | |
| class | Output |
| class | OutputImplBase |
| class | PackedMatrix |
| Packed matrix: base class for triangular and symmetric matrices. More... | |
| struct | PairHasher |
| A hashing function-object for pairs of ints. More... | |
| class | ParseOptions |
| The class ParseOptions is for parsing command-line options; see Parsing command-line options for more documentation. More... | |
| struct | PhoneAlignLatticeOptions |
| class | PipeInputImpl |
| class | PipeOutputImpl |
| struct | PitchExtractionOptions |
| class | PitchFrameInfo |
| class | PitchInterpolator |
| struct | PitchInterpolatorOptions |
| struct | PitchInterpolatorStats |
| class | Plda |
| struct | PldaConfig |
| struct | PldaEstimationConfig |
| class | PldaEstimator |
| class | PldaStats |
| class | PldaUnsupervisedAdaptor |
| This class takes unlabeled iVectors from the domain of interest and uses their mean and variance to adapt your PLDA matrices to a new domain. More... | |
| struct | PldaUnsupervisedAdaptorConfig |
| class | PlpComputer |
| This is the new-style interface to the PLP computation. More... | |
| struct | PlpOptions |
| PlpOptions contains basic options for computing PLP features. More... | |
| class | PosteriorHolder |
| struct | ProcessPitchOptions |
| class | Profiler |
| class | ProfileStats |
| class | PrunedCompactLatticeComposer |
| PrunedCompactLatticeComposer implements an algorithm for pruned composition. More... | |
| class | Questions |
| This class defines, for each EventKeyType, a set of initial questions that it tries and also a number of iterations for which to refine the questions to increase likelihood. More... | |
| struct | QuestionsForKey |
| QuestionsForKey is a class used to define the questions for a key, and also options that allow us to refine the question during tree-building (i.e. More... | |
| class | RandomAccessTableReader |
| Allows random access to a collection of objects in an archive or script file; see The Table concept. More... | |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderArchiveImplBase |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderDSortedArchiveImpl |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderImplBase |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderMapped |
| This class is for when you are reading something in random access, but it may actually be stored per-speaker (or something similar) but the keys you're using are per utterance. More... | |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderScriptImpl |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderSortedArchiveImpl |
| class | RandomAccessTableReaderUnsortedArchiveImpl |
| struct | RandomState |
| struct | RecognizedWord |
| class | RecyclingVector |
| This class serves as a storage for feature vectors with an option to limit the memory usage by removing old elements. More... | |
| class | RefineClusterer |
| struct | RefineClustersOptions |
| class | RegressionTree |
| A regression tree is a clustering of Gaussian densities in an acoustic model, such that the group of Gaussians at each node of the tree are transformed by the same transform. More... | |
| class | RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm |
| An FMLLR (feature-space MLLR) transformation, also called CMLLR (constrained MLLR) is an affine transformation of the feature vectors. More... | |
| class | RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs |
| Class for computing the accumulators needed for the maximum-likelihood estimate of FMLLR transforms for an acoustic model that uses diagonal Gaussian mixture models as emission densities. More... | |
| struct | RegtreeFmllrOptions |
| Configuration variables for FMLLR transforms. More... | |
| class | RegtreeMllrDiagGmm |
| An MLLR mean transformation is an affine transformation of Gaussian means. More... | |
| class | RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs |
| Class for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of an acoustic model that uses diagonal Gaussian mixture models as emission densities. More... | |
| struct | RegtreeMllrOptions |
| Configuration variables for FMLLR transforms. More... | |
| class | RnnlmDeterministicFst |
| struct | RspecifierOptions |
| class | ScalarClusterable |
| ScalarClusterable clusters scalars with x^2 loss. More... | |
| class | Semaphore |
| class | SequentialTableReader |
| A templated class for reading objects sequentially from an archive or script file; see The Table concept. More... | |
| class | SequentialTableReaderArchiveImpl |
| class | SequentialTableReaderBackgroundImpl |
| class | SequentialTableReaderImplBase |
| class | SequentialTableReaderScriptImpl |
| struct | Sgmm2FmllrConfig |
| Configuration variables needed in the estimation of FMLLR for SGMMs. More... | |
| class | Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams |
| Global adaptation parameters. More... | |
| class | Sgmm2GauPost |
| indexed by time. More... | |
| struct | Sgmm2GauPostElement |
| This is the entry for a single time. More... | |
| struct | Sgmm2GselectConfig |
| struct | Sgmm2LikelihoodCache |
| Sgmm2LikelihoodCache caches SGMM likelihoods at two levels: the final pdf likelihoods, and the sub-state level likelihoods, which means that with the SCTM system we can avoid redundant computation. More... | |
| struct | Sgmm2PerFrameDerivedVars |
| Holds the per-frame precomputed quantities x(t), x_{i}(t), z_{i}(t), and n_{i}(t) (cf. More... | |
| class | Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars |
| class | Sgmm2Project |
| struct | Sgmm2SplitSubstatesConfig |
| class | ShiftedDeltaFeatures |
| struct | ShiftedDeltaFeaturesOptions |
| class | SimpleDecoder |
| Simplest possible decoder, included largely for didactic purposes and as a means to debug more highly optimized decoders. More... | |
| class | SimpleOptions |
| The class SimpleOptions is an implementation of OptionsItf that allows setting and getting option values programmatically, i.e., via getter and setter methods. More... | |
| class | SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder |
| You will instantiate this class when you want to decode a single utterance using the online-decoding setup. More... | |
| class | SingleUtteranceNnet2Decoder |
| You will instantiate this class when you want to decode a single utterance using the online-decoding setup for neural nets. More... | |
| class | SingleUtteranceNnet2DecoderThreaded |
| You will instantiate this class when you want to decode a single utterance using the online-decoding setup for neural nets. More... | |
| class | SingleUtteranceNnet3DecoderTpl |
| You will instantiate this class when you want to decode a single utterance using the online-decoding setup for neural nets. More... | |
| class | SingleUtteranceNnet3IncrementalDecoderTpl |
| You will instantiate this class when you want to decode a single utterance using the online-decoding setup for neural nets. More... | |
| struct | SlidingWindowCmnOptions |
| struct | SolverOptions |
| This class describes the options for maximizing various quadratic objective functions. More... | |
| class | SparseMatrix |
| class | SparseVector |
| class | SpectrogramComputer |
| Class for computing spectrogram features. More... | |
| struct | SpectrogramOptions |
| SpectrogramOptions contains basic options for computing spectrogram features. More... | |
| struct | SpeexOptions |
| class | SphinxMatrixHolder |
| A class for reading/writing Sphinx format matrices. More... | |
| class | SplitEventMap |
| class | SplitRadixComplexFft |
| class | SplitRadixRealFft |
| class | SpMatrix |
| Packed symetric matrix class. More... | |
| class | StandardInputImpl |
| class | StandardOutputImpl |
| struct | StringHasher |
| A hashing function object for strings. More... | |
| class | SubMatrix |
| Sub-matrix representation. More... | |
| class | SubVector |
| Represents a non-allocating general vector which can be defined as a sub-vector of higher-level vector [or as the row of a matrix]. More... | |
| class | TableEventMap |
| class | TableWriter |
| A templated class for writing objects to an archive or script file; see The Table concept. More... | |
| class | TableWriterArchiveImpl |
| class | TableWriterBothImpl |
| class | TableWriterImplBase |
| class | TableWriterScriptImpl |
| class | TaskSequencer |
| struct | TaskSequencerConfig |
| class | TcpServer |
| class | ThreadSynchronizer |
| class ThreadSynchronizer acts to guard an arbitrary type of buffer between a producing and a consuming thread (note: it's all symmetric between the two thread types). More... | |
| class | TidToTstateMapper |
| class | Timer |
| class | TokenHolder |
| class | TokenVectorHolder |
| class | TpMatrix |
| Packed symetric matrix class. More... | |
| class | TrainingGraphCompiler |
| struct | TrainingGraphCompilerOptions |
| class | TransitionModel |
| class | TreeClusterer |
| struct | TreeClusterOptions |
| class | TreeRenderer |
| class | TwvMetrics |
| struct | TwvMetricsOptions |
| class | TwvMetricsStats |
| struct | UbmClusteringOptions |
| class | UpdatePhoneVectorsClass |
| class | UpdateWClass |
| struct | VadEnergyOptions |
| class | Vector |
| A class representing a vector. More... | |
| class | VectorBase |
| Provides a vector abstraction class. More... | |
| class | VectorClusterable |
| VectorClusterable wraps vectors in a form accessible to generic clustering algorithms. More... | |
| class | VectorFstToKwsLexicographicFstMapper |
| struct | VectorHasher |
| A hashing function-object for vectors. More... | |
| class | WaveData |
| This class's purpose is to read in Wave files. More... | |
| struct | WaveHeaderReadGofer |
| class | WaveHolder |
| class | WaveInfo |
| This class reads and hold wave file header information. More... | |
| class | WaveInfoHolder |
| class | WordAlignedLatticeTester |
| class | WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo |
| This class extracts some information from the lexicon and stores it in a suitable form for the word-alignment code to use. More... | |
| struct | WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts |
| struct | WordBoundaryInfo |
| struct | WordBoundaryInfoNewOpts |
| struct | WordBoundaryInfoOpts |
| struct | WspecifierOptions |
Functions | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | WriteBasicType (std::ostream &os, bool binary, T t) |
| WriteBasicType is the name of the write function for bool, integer types, and floating-point types. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | ReadBasicType (std::istream &is, bool binary, T *t) |
| ReadBasicType is the name of the read function for bool, integer types, and floating-point types. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | WriteIntegerPairVector (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const std::vector< std::pair< T, T > > &v) |
| Function for writing STL vectors of pairs of integer types. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | ReadIntegerPairVector (std::istream &is, bool binary, std::vector< std::pair< T, T > > *v) |
| Function for reading STL vector of pairs of integer types. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | WriteIntegerVector (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const std::vector< T > &v) |
| Function for writing STL vectors of integer types. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | ReadIntegerVector (std::istream &is, bool binary, std::vector< T > *v) |
| Function for reading STL vector of integer types. More... | |
| void | InitKaldiOutputStream (std::ostream &os, bool binary) |
| InitKaldiOutputStream initializes an opened stream for writing by writing an optional binary header and modifying the floating-point precision; it will typically not be called by users directly. More... | |
| bool | InitKaldiInputStream (std::istream &is, bool *binary) |
| Initialize an opened stream for reading by detecting the binary header and. More... | |
| void | UnitTestIo (bool binary) |
| template<> | |
| void | WriteBasicType< bool > (std::ostream &os, bool binary, bool b) |
| template<> | |
| void | ReadBasicType< bool > (std::istream &is, bool binary, bool *b) |
| template<> | |
| void | WriteBasicType< float > (std::ostream &os, bool binary, float f) |
| template<> | |
| void | WriteBasicType< double > (std::ostream &os, bool binary, double f) |
| template<> | |
| void | ReadBasicType< float > (std::istream &is, bool binary, float *f) |
| template<> | |
| void | ReadBasicType< double > (std::istream &is, bool binary, double *d) |
| void | CheckToken (const char *token) |
| void | WriteToken (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const char *token) |
| The WriteToken functions are for writing nonempty sequences of non-space characters. More... | |
| int | Peek (std::istream &is, bool binary) |
| Peek consumes whitespace (if binary == false) and then returns the peek() value of the stream. More... | |
| void | WriteToken (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const std::string &token) |
| void | ReadToken (std::istream &is, bool binary, std::string *token) |
| ReadToken gets the next token and puts it in str (exception on failure). More... | |
| int | PeekToken (std::istream &is, bool binary) |
| PeekToken will return the first character of the next token, or -1 if end of file. More... | |
| void | ExpectToken (std::istream &is, bool binary, const char *token) |
| ExpectToken tries to read in the given token, and throws an exception on failure. More... | |
| void | ExpectToken (std::istream &is, bool binary, const std::string &token) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | ReadBasicType (std::istream &is, bool binary, T *t, bool add) |
| void | ExpectPretty (std::istream &is, bool binary, const char *token) |
| ExpectPretty attempts to read the text in "token", but only in non-binary mode. More... | |
| void | ExpectPretty (std::istream &is, bool binary, const std::string &token) |
| void | MyFunction2 () |
| void | MyFunction1 () |
| void | UnitTestError () |
| void | VerifySymbolRange (const std::string &trace, const bool want_found, const std::string &want_symbol) |
| void | TestLocateSymbolRange () |
| void | SetProgramName (const char *basename) |
| Called by ParseOptions to set base name (no directory) of the executing program. More... | |
| static const char * | GetShortFileName (const char *path) |
| static std::string | KaldiGetStackTrace () |
| void | KaldiAssertFailure_ (const char *func, const char *file, int32 line, const char *cond_str) |
| LogHandler | SetLogHandler (LogHandler) |
| Set logging handler. More... | |
| int32 | GetVerboseLevel () |
| Get verbosity level, usually set via command line '–verbose=' switch. More... | |
| void | SetVerboseLevel (int32 i) |
| This should be rarely used, except by programs using Kaldi as library; command-line programs set the verbose level automatically from ParseOptions. More... | |
| template<class I > | |
| void | UnitTestGcdLcmTpl () |
| void | UnitTestRoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo () |
| void | UnitTestDivideRoundingDown () |
| void | UnitTestGcdLcm () |
| void | UnitTestRand () |
| void | UnitTestLogAddSub () |
| void | UnitTestDefines () |
| void | UnitTestAssertFunc () |
| template<class I > | |
| void | UnitTestFactorizeTpl () |
| void | UnitTestFactorize () |
| void | UnitTestApproxEqual () |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | UnitTestExpSpeed () |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | UnitTestLogSpeed () |
| int32 | RoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo (int32 n) |
| int | Rand (struct RandomState *state) |
| bool | WithProb (BaseFloat prob, struct RandomState *state) |
| int32 | RandInt (int32 min_val, int32 max_val, struct RandomState *state) |
| int32 | RandPoisson (float lambda, struct RandomState *state) |
| void | RandGauss2 (float *a, float *b, RandomState *state) |
| void | RandGauss2 (double *a, double *b, RandomState *state) |
| double | Exp (double x) |
| float | Exp (float x) |
| double | Log (double x) |
| float | Log (float x) |
| double | Log1p (double x) |
| float | Log1p (float x) |
| float | RandUniform (struct RandomState *state=NULL) |
| Returns a random number strictly between 0 and 1. More... | |
| float | RandGauss (struct RandomState *state=NULL) |
| template<class Float > | |
| Float | RandPrune (Float post, BaseFloat prune_thresh, struct RandomState *state=NULL) |
| double | LogAdd (double x, double y) |
| float | LogAdd (float x, float y) |
| double | LogSub (double x, double y) |
| float | LogSub (float x, float y) |
| static bool | ApproxEqual (float a, float b, float relative_tolerance=0.001) |
| return abs(a - b) <= relative_tolerance * (abs(a)+abs(b)). More... | |
| static void | AssertEqual (float a, float b, float relative_tolerance=0.001) |
| assert abs(a - b) <= relative_tolerance * (abs(a)+abs(b)) More... | |
| static int32 | DivideRoundingDown (int32 a, int32 b) |
| Returns a / b, rounding towards negative infinity in all cases. More... | |
| template<class I > | |
| I | Gcd (I m, I n) |
| template<class I > | |
| I | Lcm (I m, I n) |
| Returns the least common multiple of two integers. More... | |
| template<class I > | |
| void | Factorize (I m, std::vector< I > *factors) |
| double | Hypot (double x, double y) |
| float | Hypot (float x, float y) |
| std::string | CharToString (const char &c) |
| void | Sleep (float seconds) |
| int | MachineIsLittleEndian () |
| void | TimerTest () |
| void | cblas_Xcopy (const int N, const float *X, const int incX, float *Y, const int incY) |
| void | cblas_Xcopy (const int N, const double *X, const int incX, double *Y, const int incY) |
| float | cblas_Xasum (const int N, const float *X, const int incX) |
| double | cblas_Xasum (const int N, const double *X, const int incX) |
| void | cblas_Xrot (const int N, float *X, const int incX, float *Y, const int incY, const float c, const float s) |
| void | cblas_Xrot (const int N, double *X, const int incX, double *Y, const int incY, const double c, const double s) |
| float | cblas_Xdot (const int N, const float *const X, const int incX, const float *const Y, const int incY) |
| double | cblas_Xdot (const int N, const double *const X, const int incX, const double *const Y, const int incY) |
| void | cblas_Xaxpy (const int N, const float alpha, const float *X, const int incX, float *Y, const int incY) |
| void | cblas_Xaxpy (const int N, const double alpha, const double *X, const int incX, double *Y, const int incY) |
| void | cblas_Xscal (const int N, const float alpha, float *data, const int inc) |
| void | cblas_Xscal (const int N, const double alpha, double *data, const int inc) |
| void | cblas_Xspmv (const float alpha, const int num_rows, const float *Mdata, const float *v, const int v_inc, const float beta, float *y, const int y_inc) |
| void | cblas_Xspmv (const double alpha, const int num_rows, const double *Mdata, const double *v, const int v_inc, const double beta, double *y, const int y_inc) |
| void | cblas_Xtpmv (MatrixTransposeType trans, const float *Mdata, const int num_rows, float *y, const int y_inc) |
| void | cblas_Xtpmv (MatrixTransposeType trans, const double *Mdata, const int num_rows, double *y, const int y_inc) |
| void | cblas_Xtpsv (MatrixTransposeType trans, const float *Mdata, const int num_rows, float *y, const int y_inc) |
| void | cblas_Xtpsv (MatrixTransposeType trans, const double *Mdata, const int num_rows, double *y, const int y_inc) |
| void | cblas_Xspmv (MatrixIndexT dim, float alpha, const float *Mdata, const float *ydata, MatrixIndexT ystride, float beta, float *xdata, MatrixIndexT xstride) |
| void | cblas_Xspmv (MatrixIndexT dim, double alpha, const double *Mdata, const double *ydata, MatrixIndexT ystride, double beta, double *xdata, MatrixIndexT xstride) |
| void | cblas_Xspr2 (MatrixIndexT dim, float alpha, const float *Xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, const float *Ydata, MatrixIndexT incY, float *Adata) |
| void | cblas_Xspr2 (MatrixIndexT dim, double alpha, const double *Xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, const double *Ydata, MatrixIndexT incY, double *Adata) |
| void | cblas_Xspr (MatrixIndexT dim, float alpha, const float *Xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, float *Adata) |
| void | cblas_Xspr (MatrixIndexT dim, double alpha, const double *Xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, double *Adata) |
| void | cblas_Xgemv (MatrixTransposeType trans, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, float alpha, const float *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride, const float *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, float beta, float *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY) |
| void | cblas_Xgemv (MatrixTransposeType trans, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, double alpha, const double *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride, const double *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, double beta, double *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY) |
| void | cblas_Xgbmv (MatrixTransposeType trans, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, MatrixIndexT num_below, MatrixIndexT num_above, float alpha, const float *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride, const float *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, float beta, float *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY) |
| void | cblas_Xgbmv (MatrixTransposeType trans, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, MatrixIndexT num_below, MatrixIndexT num_above, double alpha, const double *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride, const double *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, double beta, double *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | Xgemv_sparsevec (MatrixTransposeType trans, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, Real alpha, const Real *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride, const Real *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, Real beta, Real *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY) |
| void | cblas_Xgemm (const float alpha, MatrixTransposeType transA, const float *Adata, MatrixIndexT a_num_rows, MatrixIndexT a_num_cols, MatrixIndexT a_stride, MatrixTransposeType transB, const float *Bdata, MatrixIndexT b_stride, const float beta, float *Mdata, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, MatrixIndexT stride) |
| void | cblas_Xgemm (const double alpha, MatrixTransposeType transA, const double *Adata, MatrixIndexT a_num_rows, MatrixIndexT a_num_cols, MatrixIndexT a_stride, MatrixTransposeType transB, const double *Bdata, MatrixIndexT b_stride, const double beta, double *Mdata, MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, MatrixIndexT stride) |
| void | cblas_Xsymm (const float alpha, MatrixIndexT sz, const float *Adata, MatrixIndexT a_stride, const float *Bdata, MatrixIndexT b_stride, const float beta, float *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride) |
| void | cblas_Xsymm (const double alpha, MatrixIndexT sz, const double *Adata, MatrixIndexT a_stride, const double *Bdata, MatrixIndexT b_stride, const double beta, double *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride) |
| void | cblas_Xger (MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, float alpha, const float *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, const float *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY, float *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride) |
| void | cblas_Xger (MatrixIndexT num_rows, MatrixIndexT num_cols, double alpha, const double *xdata, MatrixIndexT incX, const double *ydata, MatrixIndexT incY, double *Mdata, MatrixIndexT stride) |
| void | cblas_Xsyrk (const MatrixTransposeType trans, const MatrixIndexT dim_c, const MatrixIndexT other_dim_a, const float alpha, const float *A, const MatrixIndexT a_stride, const float beta, float *C, const MatrixIndexT c_stride) |
| void | cblas_Xsyrk (const MatrixTransposeType trans, const MatrixIndexT dim_c, const MatrixIndexT other_dim_a, const double alpha, const double *A, const MatrixIndexT a_stride, const double beta, double *C, const MatrixIndexT c_stride) |
| void | cblas_Xsbmv1 (const MatrixIndexT dim, const double *A, const double alpha, const double *x, const double beta, double *y) |
| matrix-vector multiply using a banded matrix; we always call this with b = 1 meaning we're multiplying by a diagonal matrix. More... | |
| void | cblas_Xsbmv1 (const MatrixIndexT dim, const float *A, const float alpha, const float *x, const float beta, float *y) |
| void | mul_elements (const MatrixIndexT dim, const double *a, double *b) |
| This is not really a wrapper for CBLAS as CBLAS does not have this; in future we could extend this somehow. More... | |
| void | mul_elements (const MatrixIndexT dim, const float *a, float *b) |
| void | clapack_Xtptri (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, float *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xtptri (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, double *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xgetrf2 (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, KaldiBlasInt *num_cols, float *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *stride, KaldiBlasInt *pivot, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xgetrf2 (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, KaldiBlasInt *num_cols, double *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *stride, KaldiBlasInt *pivot, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xgetri2 (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, float *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *stride, KaldiBlasInt *pivot, float *p_work, KaldiBlasInt *l_work, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xgetri2 (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, double *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *stride, KaldiBlasInt *pivot, double *p_work, KaldiBlasInt *l_work, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xgesvd (char *v, char *u, KaldiBlasInt *num_cols, KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, float *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *stride, float *sv, float *Vdata, KaldiBlasInt *vstride, float *Udata, KaldiBlasInt *ustride, float *p_work, KaldiBlasInt *l_work, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xgesvd (char *v, char *u, KaldiBlasInt *num_cols, KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, double *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *stride, double *sv, double *Vdata, KaldiBlasInt *vstride, double *Udata, KaldiBlasInt *ustride, double *p_work, KaldiBlasInt *l_work, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xsptri (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, float *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *ipiv, float *work, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xsptri (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, double *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *ipiv, double *work, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xsptrf (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, float *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *ipiv, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| void | clapack_Xsptrf (KaldiBlasInt *num_rows, double *Mdata, KaldiBlasInt *ipiv, KaldiBlasInt *result) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< Real > &M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &is, Matrix< Real > &M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &is, MatrixBase< Real > &M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ReadHtk (std::istream &is, Matrix< Real > *M_ptr, HtkHeader *header_ptr) |
| Extension of the HTK header. More... | |
| template bool | ReadHtk (std::istream &is, Matrix< float > *M, HtkHeader *header_ptr) |
| template bool | ReadHtk (std::istream &is, Matrix< double > *M, HtkHeader *header_ptr) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | WriteHtk (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< Real > &M, HtkHeader htk_hdr) |
| template bool | WriteHtk (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< float > &M, HtkHeader htk_hdr) |
| template bool | WriteHtk (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< double > &M, HtkHeader htk_hdr) |
| template<class Real > | |
| bool | WriteSphinx (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< Real > &M) |
| template bool | WriteSphinx (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< float > &M) |
| template bool | WriteSphinx (std::ostream &os, const MatrixBase< double > &M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatMatMat (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const MatrixBase< Real > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const MatrixBase< Real > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC) |
| Returns tr(A B C) More... | |
| template float | TraceMatMatMat (const MatrixBase< float > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const MatrixBase< float > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const MatrixBase< float > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC) |
| template double | TraceMatMatMat (const MatrixBase< double > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const MatrixBase< double > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const MatrixBase< double > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatMatMatMat (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const MatrixBase< Real > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const MatrixBase< Real > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC, const MatrixBase< Real > &D, MatrixTransposeType transD) |
| Returns tr(A B C D) More... | |
| template float | TraceMatMatMatMat (const MatrixBase< float > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const MatrixBase< float > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const MatrixBase< float > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC, const MatrixBase< float > &D, MatrixTransposeType transD) |
| template double | TraceMatMatMatMat (const MatrixBase< double > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const MatrixBase< double > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const MatrixBase< double > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC, const MatrixBase< double > &D, MatrixTransposeType transD) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | SortSvd (VectorBase< Real > *s, MatrixBase< Real > *U, MatrixBase< Real > *Vt=NULL, bool sort_on_absolute_value=true) |
| Function to ensure that SVD is sorted. More... | |
| template void | SortSvd (VectorBase< float > *s, MatrixBase< float > *U, MatrixBase< float > *Vt, bool) |
| template void | SortSvd (VectorBase< double > *s, MatrixBase< double > *U, MatrixBase< double > *Vt, bool) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CreateEigenvalueMatrix (const VectorBase< Real > &real, const VectorBase< Real > &imag, MatrixBase< Real > *D) |
| Creates the eigenvalue matrix D that is part of the decomposition used Matrix::Eig. More... | |
| template void | CreateEigenvalueMatrix (const VectorBase< float > &re, const VectorBase< float > &im, MatrixBase< float > *D) |
| template void | CreateEigenvalueMatrix (const VectorBase< double > &re, const VectorBase< double > &im, MatrixBase< double > *D) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | AttemptComplexPower (Real *x_re, Real *x_im, Real power) |
| The following function is used in Matrix::Power, and separately tested, so we declare it here mainly for the testing code to see. More... | |
| template bool | AttemptComplexPower (float *x_re, float *x_im, float power) |
| template bool | AttemptComplexPower (double *x_re, double *x_im, double power) |
| template float | TraceMatMat (const MatrixBase< float > &A, const MatrixBase< float > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template double | TraceMatMat (const MatrixBase< double > &A, const MatrixBase< double > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ApproxEqual (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, const MatrixBase< Real > &B, Real tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AssertEqual (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, const MatrixBase< Real > &B, float tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| double | TraceMat (const MatrixBase< Real > &A) |
| Returns trace of matrix. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | SameDim (const MatrixBase< Real > &M, const MatrixBase< Real > &N) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const VectorBase< Real > &rv) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &in, VectorBase< Real > &v) |
| Input from a C++ stream. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &in, Vector< Real > &v) |
| Input from a C++ stream. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | VecVec (const VectorBase< Real > &v1, const VectorBase< Real > &v2) |
| Returns dot product between v1 and v2. More... | |
| template float | VecVec (const VectorBase< float > &a, const VectorBase< float > &b) |
| template double | VecVec (const VectorBase< double > &a, const VectorBase< double > &b) |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| Real | VecVec (const VectorBase< Real > &ra, const VectorBase< OtherReal > &rb) |
| template float | VecVec (const VectorBase< float > &ra, const VectorBase< double > &rb) |
| template double | VecVec (const VectorBase< double > &ra, const VectorBase< float > &rb) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | VecMatVec (const VectorBase< Real > &v1, const MatrixBase< Real > &M, const VectorBase< Real > &v2) |
Returns 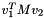 . More... . More... | |
| template float | VecMatVec (const VectorBase< float > &v1, const MatrixBase< float > &M, const VectorBase< float > &v2) |
| template double | VecMatVec (const VectorBase< double > &v1, const MatrixBase< double > &M, const VectorBase< double > &v2) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ApproxEqual (const VectorBase< Real > &a, const VectorBase< Real > &b, Real tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AssertEqual (VectorBase< Real > &a, VectorBase< Real > &b, float tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComplexMul (const Real &a_re, const Real &a_im, Real *b_re, Real *b_im) |
| ComplexMul implements, inline, the complex multiplication b *= a. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComplexAddProduct (const Real &a_re, const Real &a_im, const Real &b_re, const Real &b_im, Real *c_re, Real *c_im) |
| ComplexMul implements, inline, the complex operation c += (a * b). More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComplexImExp (Real x, Real *a_re, Real *a_im) |
| ComplexImExp implements a <– exp(i x), inline. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComplexFt (const VectorBase< Real > &in, VectorBase< Real > *out, bool forward) |
| ComplexFt is the same as ComplexFft but it implements the Fourier transform in an inefficient way. More... | |
| template void | ComplexFt (const VectorBase< float > &in, VectorBase< float > *out, bool forward) |
| template void | ComplexFt (const VectorBase< double > &in, VectorBase< double > *out, bool forward) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComplexFftRecursive (Real *data, int nffts, int N, const int *factor_begin, const int *factor_end, bool forward, Vector< Real > *tmp_vec) |
| ComplexFftRecursive is a recursive function that computes the complex FFT of size N. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComplexFft (VectorBase< Real > *v, bool forward, Vector< Real > *tmp_work=NULL) |
| The function ComplexFft does an Fft on the vector argument v. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | RealFftInefficient (VectorBase< Real > *v, bool forward) |
| Inefficient version of Fourier transform, for testing purposes. More... | |
| template void | RealFftInefficient (VectorBase< float > *v, bool forward) |
| template void | RealFftInefficient (VectorBase< double > *v, bool forward) |
| template void | ComplexFft (VectorBase< float > *v, bool forward, Vector< float > *tmp_in) |
| template void | ComplexFft (VectorBase< double > *v, bool forward, Vector< double > *tmp_in) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | RealFft (VectorBase< Real > *v, bool forward) |
| RealFft is a fourier transform of real inputs. More... | |
| template void | RealFft (VectorBase< float > *v, bool forward) |
| template void | RealFft (VectorBase< double > *v, bool forward) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComputeDctMatrix (Matrix< Real > *M) |
| ComputeDctMatrix computes a matrix corresponding to the DCT, such that M * v equals the DCT of vector v. More... | |
| template void | ComputeDctMatrix (Matrix< float > *M) |
| template void | ComputeDctMatrix (Matrix< double > *M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | ComputePca (const MatrixBase< Real > &X, MatrixBase< Real > *U, MatrixBase< Real > *A, bool print_eigs=false, bool exact=true) |
| ComputePCA does a PCA computation, using either outer products or inner products, whichever is more efficient. More... | |
| template void | ComputePca (const MatrixBase< float > &X, MatrixBase< float > *U, MatrixBase< float > *A, bool print_eigs, bool exact) |
| template void | ComputePca (const MatrixBase< double > &X, MatrixBase< double > *U, MatrixBase< double > *A, bool print_eigs, bool exact) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AddOuterProductPlusMinus (Real alpha, const VectorBase< Real > &a, const VectorBase< Real > &b, MatrixBase< Real > *plus, MatrixBase< Real > *minus) |
| template void | AddOuterProductPlusMinus< float > (float alpha, const VectorBase< float > &a, const VectorBase< float > &b, MatrixBase< float > *plus, MatrixBase< float > *minus) |
| template void | AddOuterProductPlusMinus< double > (double alpha, const VectorBase< double > &a, const VectorBase< double > &b, MatrixBase< double > *plus, MatrixBase< double > *minus) |
| template<typename Real1 , typename Real2 > | |
| void | AssertSameDim (const MatrixBase< Real1 > &mat1, const MatrixBase< Real2 > &mat2) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::string | NameOf () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | CsvResult (std::string test, int dim, BaseFloat measure, std::string units) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRealFftSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSplitRadixRealFftSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvdSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMatMatSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddRowSumMatSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddColSumMatSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddVecToRowsSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddVecToColsSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | MatrixUnitSpeedTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | RandPosdefSpMatrix (MatrixIndexT dim, SpMatrix< Real > *matrix) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | InitRandNonsingular (MatrixBase< Real > *M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | InitRandNonsingular (SpMatrix< Real > *M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | CholeskyUnitTestTr () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | SlowMatMul () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddToDiagMatrix () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddDiagVecMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMatDiagVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMatMatElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddSp () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| static void | UnitTestSpAddDiagVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSpAddVecVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopyRowsAndCols () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSpliceRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRemoveRow () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSubvector () |
| static int32 | DoubleFactorial (int32 i) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSetRandn () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSetRandUniform () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSimpleForVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestVectorMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestVectorMin () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestReplaceValue () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestNorm () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopyRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopyToRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddToRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopyCols () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSimpleForMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRow () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAxpy () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopySp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestPower () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestPowerAbs () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestHeaviside () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddOuterProductPlusMinus () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSger () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestDeterminant () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestDeterminantSign () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSpVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTraceProduct () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvd () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvdBad () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvdZero () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvdNodestroy () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvdJustvec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestEigSymmetric () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestEig () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestEigSp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static Real | NonOrthogonality (const MatrixBase< Real > &M, MatrixTransposeType transM) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static Real | NonDiagonalness (const SpMatrix< Real > &S) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static Real | NonUnitness (const SpMatrix< Real > &S) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTridiagonalize () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTridiagonalizeAndQr () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMmul () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMmulSym () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddVecVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestVecmul () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestInverse () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMulElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestDotprod () |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | PlaceNansInGaps (Matrix< Real > *mat) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestResizeCopyDataDifferentStrideType () |
| Make sure that when Resize() is called with resize_type = kCopyData and a stride_type different from this's stride_type, the resized matrix is equivalent to the original matrix (modulo the stride). More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestResize () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTp2Sp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTp2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddDiagMat2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddDiagMatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestOrthogonalizeRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTransposeScatter () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRankNUpdate () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSpInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTpInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestLimitCondInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestFloorChol () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestFloorUnit () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestFloorCeiling () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMat2Vec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestLimitCond () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTanh () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSigmoid () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSoftHinge () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSimple () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestIo () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestIoCross () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestHtkIo () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRange () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestScale () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMul () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestApplyExpSpecial () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestInnerProd () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddToDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestScaleDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSetDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTraceSpSpLower () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMatSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMat2Sp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMatSelf () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMat2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSymAddMat2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSolve () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMax2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMaxAbsEig () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestLbfgs () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestLinearCgd () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMaxMin () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static bool | approx_equal (Real a, Real b) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTrace () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestComplexFt () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestDct () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestComplexFft () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSplitRadixComplexFft () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTranspose () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddVecToRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddVec2Sp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddVecToCols () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestComplexFft2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSplitRadixComplexFft2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRealFft () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSplitRadixRealFft () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRealFftSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSplitRadixRealFftSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestComplexPower () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestNonsymmetricPower () |
| void | UnitTestAddVecCross () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestPca (bool full_test) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestPca2 (bool full_test) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSvdSpeed () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCompressedMatrix2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCompressedMatrix () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestGeneralMatrix () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestExtractCompressedMatrix () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTridiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestRandCategorical () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestAddMatMatNans () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTopEigs () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTriVecSolver () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | MatrixUnitTest (bool full_test) |
| template<class Real > | |
| int32 | LinearCgd (const LinearCgdOptions &opts, const SpMatrix< Real > &A, const VectorBase< Real > &b, VectorBase< Real > *x) |
| template int32 | LinearCgd< float > (const LinearCgdOptions &opts, const SpMatrix< float > &A, const VectorBase< float > &b, VectorBase< float > *x) |
| template int32 | LinearCgd< double > (const LinearCgdOptions &opts, const SpMatrix< double > &A, const VectorBase< double > &b, VectorBase< double > *x) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const PackedMatrix< Real > &M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &is, PackedMatrix< Real > &M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | HouseBackward (MatrixIndexT dim, const Real *x, Real *v, Real *beta) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | Givens (Real a, Real b, Real *c, Real *s) |
| Create Givens rotations, as in Golub and Van Loan 3rd ed., page 216. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | QrStep (MatrixIndexT n, Real *diag, Real *off_diag, MatrixBase< Real > *Q) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | QrInternal (MatrixIndexT n, Real *diag, Real *off_diag, MatrixBase< Real > *Q) |
| template<> | |
| double | SolveQuadraticProblem (const SpMatrix< double > &H, const VectorBase< double > &g, const SolverOptions &opts, VectorBase< double > *x) |
| template<> | |
| float | SolveQuadraticProblem (const SpMatrix< float > &H, const VectorBase< float > &g, const SolverOptions &opts, VectorBase< float > *x) |
| double | TraceSpSp (const SpMatrix< double > &A, const SpMatrix< double > &B) |
| float | TraceSpSp (const SpMatrix< float > &A, const SpMatrix< float > &B) |
| Returns tr(A B). More... | |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| Real | TraceSpSp (const SpMatrix< Real > &A, const SpMatrix< OtherReal > &B) |
| Returns tr(A B). More... | |
| template float | TraceSpSp< float, double > (const SpMatrix< float > &A, const SpMatrix< double > &B) |
| template double | TraceSpSp< double, float > (const SpMatrix< double > &A, const SpMatrix< float > &B) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceSpMat (const SpMatrix< Real > &A, const MatrixBase< Real > &B) |
| Returns tr(A B). More... | |
| template float | TraceSpMat (const SpMatrix< float > &A, const MatrixBase< float > &B) |
| template double | TraceSpMat (const SpMatrix< double > &A, const MatrixBase< double > &B) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatSpMat (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const SpMatrix< Real > &B, const MatrixBase< Real > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC) |
| Returns tr(A B C) (A and C may be transposed as specified by transA and transC). More... | |
| template float | TraceMatSpMat (const MatrixBase< float > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const SpMatrix< float > &B, const MatrixBase< float > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC) |
| template double | TraceMatSpMat (const MatrixBase< double > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const SpMatrix< double > &B, const MatrixBase< double > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatSpMatSp (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const SpMatrix< Real > &B, const MatrixBase< Real > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC, const SpMatrix< Real > &D) |
| Returns tr (A B C D) (A and C may be transposed as specified by transA and transB). More... | |
| template float | TraceMatSpMatSp (const MatrixBase< float > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const SpMatrix< float > &B, const MatrixBase< float > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC, const SpMatrix< float > &D) |
| template double | TraceMatSpMatSp (const MatrixBase< double > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const SpMatrix< double > &B, const MatrixBase< double > &C, MatrixTransposeType transC, const SpMatrix< double > &D) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem (const SpMatrix< Real > &Q, const MatrixBase< Real > &Y, const SpMatrix< Real > &P, const SolverOptions &opts, MatrixBase< Real > *M) |
| Maximizes the auxiliary function :
Like a numerically stable version of | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem (const MatrixBase< Real > &G, const SpMatrix< Real > &P1, const SpMatrix< Real > &P2, const SpMatrix< Real > &Q1, const SpMatrix< Real > &Q2, const SolverOptions &opts, MatrixBase< Real > *M) |
| Maximizes the auxiliary function :
Encountered in matrix update with a prior. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | VecSpVec (const VectorBase< Real > &v1, const SpMatrix< Real > &M, const VectorBase< Real > &v2) |
| Computes v1^T * M * v2. More... | |
| template float | VecSpVec (const VectorBase< float > &v1, const SpMatrix< float > &M, const VectorBase< float > &v2) |
| template double | VecSpVec (const VectorBase< double > &v1, const SpMatrix< double > &M, const VectorBase< double > &v2) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceSpSpLower (const SpMatrix< Real > &A, const SpMatrix< Real > &B) |
| template double | TraceSpSpLower (const SpMatrix< double > &A, const SpMatrix< double > &B) |
| template float | TraceSpSpLower (const SpMatrix< float > &A, const SpMatrix< float > &B) |
| template float | SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem (const SpMatrix< float > &Q, const MatrixBase< float > &Y, const SpMatrix< float > &SigmaInv, const SolverOptions &opts, MatrixBase< float > *M) |
| template double | SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem (const SpMatrix< double > &Q, const MatrixBase< double > &Y, const SpMatrix< double > &SigmaInv, const SolverOptions &opts, MatrixBase< double > *M) |
| template float | SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem (const MatrixBase< float > &G, const SpMatrix< float > &P1, const SpMatrix< float > &P2, const SpMatrix< float > &Q1, const SpMatrix< float > &Q2, const SolverOptions &opts, MatrixBase< float > *M) |
| template double | SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem (const MatrixBase< double > &G, const SpMatrix< double > &P1, const SpMatrix< double > &P2, const SpMatrix< double > &Q1, const SpMatrix< double > &Q2, const SolverOptions &opts, MatrixBase< double > *M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ApproxEqual (const SpMatrix< Real > &A, const SpMatrix< Real > &B, Real tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AssertEqual (const SpMatrix< Real > &A, const SpMatrix< Real > &B, Real tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | SolveQuadraticProblem (const SpMatrix< Real > &H, const VectorBase< Real > &g, const SolverOptions &opts, VectorBase< Real > *x) |
| Maximizes the auxiliary function
using a numerically stable method. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseVectorSum () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseVectorAddToVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseVectorMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseVectorVecSvec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseMatrixSum () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseMatrixAddToMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseMatrixConstructor () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestMatrixAddMatSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestMatrixAddSmatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | SparseMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | VecSvec (const VectorBase< Real > &vec, const SparseVector< Real > &svec) |
| template float | VecSvec (const VectorBase< float > &vec, const SparseVector< float > &svec) |
| template double | VecSvec (const VectorBase< double > &vec, const SparseVector< double > &svec) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatSmat (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, const SparseMatrix< Real > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template float | TraceMatSmat (const MatrixBase< float > &A, const SparseMatrix< float > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template double | TraceMatSmat (const MatrixBase< double > &A, const SparseMatrix< double > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| void | AppendGeneralMatrixRows (const std::vector< const GeneralMatrix * > &src, GeneralMatrix *mat) |
| Appends all the matrix rows of a list of GeneralMatrixes, to get a single GeneralMatrix. More... | |
| void | FilterCompressedMatrixRows (const CompressedMatrix &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out) |
| Outputs a Matrix<Real> containing only the rows r of "in" such that keep_rows[r] == true. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | FilterMatrixRows (const Matrix< Real > &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, Matrix< Real > *out) |
| Outputs a Matrix<Real> containing only the rows r of "in" such that keep_keep_rows[r] == true. More... | |
| template void | FilterMatrixRows (const Matrix< float > &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, Matrix< float > *out) |
| template void | FilterMatrixRows (const Matrix< double > &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, Matrix< double > *out) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | FilterSparseMatrixRows (const SparseMatrix< Real > &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, SparseMatrix< Real > *out) |
| Outputs a SparseMatrix<Real> containing only the rows r of "in" such that keep_rows[r] == true. More... | |
| template void | FilterSparseMatrixRows (const SparseMatrix< float > &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, SparseMatrix< float > *out) |
| template void | FilterSparseMatrixRows (const SparseMatrix< double > &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, SparseMatrix< double > *out) |
| void | FilterGeneralMatrixRows (const GeneralMatrix &in, const std::vector< bool > &keep_rows, GeneralMatrix *out) |
| Outputs a GeneralMatrix containing only the rows r of "in" such that keep_rows[r] == true. More... | |
| void | ExtractRowRangeWithPadding (const GeneralMatrix &in, int32 row_offset, int32 num_rows, GeneralMatrix *out) |
| This function extracts a row-range of a GeneralMatrix and writes as a GeneralMatrix containing the same type of underlying matrix. More... | |
| template<class CharT , class Traits > | |
| void | swap (basic_filebuf< CharT, Traits > &x, basic_filebuf< CharT, Traits > &y) |
| template<class Int > | |
| void | TestSetOfNumbers (bool binary) |
| template<class T > | |
| int32 | LevenshteinEditDistance (const std::vector< T > &a, const std::vector< T > &b) |
| template<class T > | |
| int32 | LevenshteinEditDistance (const std::vector< T > &ref, const std::vector< T > &hyp, int32 *ins, int32 *del, int32 *sub) |
| template<class T > | |
| int32 | LevenshteinAlignment (const std::vector< T > &a, const std::vector< T > &b, T eps_symbol, std::vector< std::pair< T, T > > *output) |
| void | TestEditDistance () |
| void | TestEditDistanceString () |
| void | TestEditDistance2 () |
| void | TestEditDistance2String () |
| void | TestLevenshteinAlignment () |
| template<class Int , class T > | |
| void | TestHashList () |
| static bool | prefixp (const std::string &pfx, const std::string &str) |
| static std::string | cygprefix ("/cygdrive/") |
| static std::string | MapCygwinPathNoTmp (const std::string &filename) |
| std::string | MapCygwinPath (const std::string &filename) |
| static FILE * | CygwinCompatPopen (const char *command, const char *mode) |
| bool | ParseMatrixRangeSpecifier (const std::string &range, const int rows, const int cols, std::vector< int32 > *row_range, std::vector< int32 > *col_range) |
| bool | ExtractObjectRange (const GeneralMatrix &input, const std::string &range, GeneralMatrix *output) |
| GeneralMatrix is always of type BaseFloat. More... | |
| template<class Real > | |
| bool | ExtractObjectRange (const CompressedMatrix &input, const std::string &range, Matrix< Real > *output) |
| CompressedMatrix is always of the type BaseFloat but it is more efficient to provide template as it uses CompressedMatrix's own conversion to Matrix<Real> More... | |
| template bool | ExtractObjectRange (const CompressedMatrix &, const std::string &, Matrix< float > *) |
| template bool | ExtractObjectRange (const CompressedMatrix &, const std::string &, Matrix< double > *) |
| template<class Real > | |
| bool | ExtractObjectRange (const Matrix< Real > &input, const std::string &range, Matrix< Real > *output) |
| The template is specialized with a version that actually does something, for types Matrix<float> and Matrix<double>. More... | |
| template bool | ExtractObjectRange (const Matrix< double > &, const std::string &, Matrix< double > *) |
| template bool | ExtractObjectRange (const Matrix< float > &, const std::string &, Matrix< float > *) |
| template<class Real > | |
| bool | ExtractObjectRange (const Vector< Real > &input, const std::string &range, Vector< Real > *output) |
| The template is specialized types Vector<float> and Vector<double>. More... | |
| template bool | ExtractObjectRange (const Vector< double > &, const std::string &, Vector< double > *) |
| template bool | ExtractObjectRange (const Vector< float > &, const std::string &, Vector< float > *) |
| bool | ExtractRangeSpecifier (const std::string &rxfilename_with_range, std::string *data_rxfilename, std::string *range) |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | ExtractObjectRange (const T &input, const std::string &range, T *output) |
| This templated function exists so that we can write .scp files with 'object ranges' specified: the canonical example is a [first:last] range of rows of a matrix, or [first-row:last-row,first-column,last-column] of a matrix. More... | |
| void | UnitTestClassifyRxfilename () |
| void | UnitTestClassifyWxfilename () |
| void | UnitTestIoNew (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestIoPipe (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestIoStandard () |
| void | UnitTestNativeFilename () |
| std::string | PrintableRxfilename (const std::string &rxfilename) |
| PrintableRxfilename turns the rxfilename into a more human-readable form for error reporting, i.e. More... | |
| std::string | PrintableWxfilename (const std::string &wxfilename) |
| PrintableWxfilename turns the wxfilename into a more human-readable form for error reporting, i.e. More... | |
| OutputType | ClassifyWxfilename (const std::string &wxfilename) |
| ClassifyWxfilename interprets filenames as follows: More... | |
| InputType | ClassifyRxfilename (const std::string &rxfilename) |
| ClassifyRxfilenames interprets filenames for reading as follows: More... | |
| template<> | |
| void | ReadKaldiObject (const std::string &filename, Matrix< float > *m) |
| template<> | |
| void | ReadKaldiObject (const std::string &filename, Matrix< double > *m) |
| template<class C > | |
| void | ReadKaldiObject (const std::string &filename, C *c) |
| template<class C > | |
| void | WriteKaldiObject (const C &c, const std::string &filename, bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestReadScriptFile () |
| void | UnitTestClassifyWspecifier () |
| void | UnitTestClassifyRspecifier () |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialInt32 (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialBool (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialDouble (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleBoth (bool binary, bool read_scp) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorBoth (bool binary, bool read_scp) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialInt32PairVectorBoth (bool binary, bool read_scp) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorVectorBoth (bool binary, bool read_scp) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialInt32Script (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleMatrixBoth (bool binary, bool read_scp) |
| void | UnitTestTableSequentialBaseFloatVectorBoth (bool binary, bool read_scp) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | RandomizeVector (std::vector< T > *v) |
| void | UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble (bool binary, bool read_scp, bool sorted, bool called_sorted, bool once) |
| void | UnitTestRangesMatrix (bool binary) |
| void | UnitTestTableRandomBothDoubleMatrix (bool binary, bool read_scp, bool sorted, bool called_sorted, bool once) |
| bool | ReadScriptFile (const std::string &rxfilename, bool warn, std::vector< std::pair< std::string, std::string > > *script_out) |
| bool | ReadScriptFile (std::istream &is, bool warn, std::vector< std::pair< std::string, std::string > > *script_out) |
| bool | WriteScriptFile (std::ostream &os, const std::vector< std::pair< std::string, std::string > > &script) |
| bool | WriteScriptFile (const std::string &wxfilename, const std::vector< std::pair< std::string, std::string > > &script) |
| WspecifierType | ClassifyWspecifier (const std::string &wspecifier, std::string *archive_wxfilename, std::string *script_wxfilename, WspecifierOptions *opts) |
| RspecifierType | ClassifyRspecifier (const std::string &rspecifier, std::string *rxfilename, RspecifierOptions *opts) |
| void | TestThreads () |
| void | TestTaskSequencer () |
| template<class C > | |
| void | RunMultiThreaded (const C &c_in) |
| Here, class C should inherit from MultiThreadable. More... | |
| void | UnitTestParseOptions () |
| static bool | MustBeQuoted (const std::string &str, ShellType st) |
| static std::string | QuoteAndEscape (const std::string &str, ShellType st) |
| template<class C > | |
| void | ReadConfigFromFile (const std::string &config_filename, C *c) |
| This template is provided for convenience in reading config classes from files; this is not the standard way to read configuration options, but may occasionally be needed. More... | |
| template<class C1 , class C2 > | |
| void | ReadConfigsFromFile (const std::string &conf, C1 *c1, C2 *c2) |
| This variant of the template ReadConfigFromFile is for if you need to read two config classes from the same file. More... | |
| bool | WriteIntegerVectorSimple (const std::string &wxfilename, const std::vector< int32 > &v) |
| WriteToList attempts to write this list of integers, one per line, to the given file, in text format. More... | |
| bool | ReadIntegerVectorSimple (const std::string &rxfilename, std::vector< int32 > *v) |
| ReadFromList attempts to read this list of integers, one per line, from the given file, in text format. More... | |
| bool | WriteIntegerVectorVectorSimple (const std::string &wxfilename, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &list) |
| bool | ReadIntegerVectorVectorSimple (const std::string &rxfilename, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *list) |
| void | UnitTestSimpleOptions () |
| template<typename T > | |
| static bool | SetOptionImpl (const std::string &key, const T &value, std::map< std::string, T *> &some_map) |
| template<typename T > | |
| static bool | GetOptionImpl (const std::string &key, T *value, std::map< std::string, T *> &some_map) |
| static void | TestIsSorted () |
| static void | TestIsSortedAndUniq () |
| static void | TestUniq () |
| static void | TestSortAndUniq () |
| void | TestCopySetToVector () |
| void | TestCopyMapToVector () |
| void | TestCopyMapKeysToVector () |
| void | TestCopyMapValuesToVector () |
| void | TestCopyMapKeysToSet () |
| void | TestCopyMapValuesToSet () |
| void | TestContainsNullPointers () |
| void | TestReverseVector () |
| void | TestMergePairVectorSumming () |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | SortAndUniq (std::vector< T > *vec) |
| Sorts and uniq's (removes duplicates) from a vector. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | IsSorted (const std::vector< T > &vec) |
| Returns true if the vector is sorted. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | IsSortedAndUniq (const std::vector< T > &vec) |
| Returns true if the vector is sorted and contains each element only once. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | Uniq (std::vector< T > *vec) |
| Removes duplicate elements from a sorted list. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CopySetToVector (const std::set< T > &s, std::vector< T > *v) |
| Copies the elements of a set to a vector. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CopySetToVector (const unordered_set< T > &s, std::vector< T > *v) |
| template<class A , class B > | |
| void | CopyMapToVector (const std::map< A, B > &m, std::vector< std::pair< A, B > > *v) |
| Copies the (key, value) pairs in a map to a vector of pairs. More... | |
| template<class A , class B > | |
| void | CopyMapKeysToVector (const std::map< A, B > &m, std::vector< A > *v) |
| Copies the keys in a map to a vector. More... | |
| template<class A , class B > | |
| void | CopyMapValuesToVector (const std::map< A, B > &m, std::vector< B > *v) |
| Copies the values in a map to a vector. More... | |
| template<class A , class B > | |
| void | CopyMapKeysToSet (const std::map< A, B > &m, std::set< A > *s) |
| Copies the keys in a map to a set. More... | |
| template<class A , class B > | |
| void | CopyMapValuesToSet (const std::map< A, B > &m, std::set< B > *s) |
| Copies the values in a map to a set. More... | |
| template<class A > | |
| void | CopyVectorToSet (const std::vector< A > &v, std::set< A > *s) |
| Copies the contents of a vector to a set. More... | |
| template<class A > | |
| void | DeletePointers (std::vector< A *> *v) |
| Deletes any non-NULL pointers in the vector v, and sets the corresponding entries of v to NULL. More... | |
| template<class A > | |
| bool | ContainsNullPointers (const std::vector< A *> &v) |
| Returns true if the vector of pointers contains NULL pointers. More... | |
| template<typename A , typename B > | |
| void | CopyVectorToVector (const std::vector< A > &vec_in, std::vector< B > *vec_out) |
| Copies the contents a vector of one type to a vector of another type. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | ReverseVector (std::vector< T > *vec) |
| Reverses the contents of a vector. More... | |
| template<typename I , typename F > | |
| void | MergePairVectorSumming (std::vector< std::pair< I, F > > *vec) |
| For a vector of pair<I, F> where I is an integer and F a floating-point or integer type, this function sorts a vector of type vector<pair<I, F> > on the I value and then merges elements with equal I values, summing these over the F component and then removing any F component with zero value. More... | |
| char | GetRandChar () |
| char | GetRandDelim () |
| void | TestSplitStringToVector () |
| void | TestSplitStringToIntegers () |
| void | TestSplitStringToFloats () |
| void | TestConvertStringToInteger () |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | TestConvertStringToReal () |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | TestNan () |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | TestInf () |
| std::string | TrimTmp (std::string s) |
| void | TestTrim () |
| void | TestSplitStringOnFirstSpace () |
| void | TestIsToken () |
| void | TestIsLine () |
| void | TestStringsApproxEqual () |
| void | UnitTestConfigLineParse () |
| void | UnitTestReadConfig () |
| template<class F > | |
| bool | SplitStringToFloats (const std::string &full, const char *delim, bool omit_empty_strings, std::vector< F > *out) |
| template bool | SplitStringToFloats (const std::string &full, const char *delim, bool omit_empty_strings, std::vector< float > *out) |
| template bool | SplitStringToFloats (const std::string &full, const char *delim, bool omit_empty_strings, std::vector< double > *out) |
| void | SplitStringToVector (const std::string &full, const char *delim, bool omit_empty_strings, std::vector< std::string > *out) |
| Split a string using any of the single character delimiters. More... | |
| void | JoinVectorToString (const std::vector< std::string > &vec_in, const char *delim, bool omit_empty_strings, std::string *str_out) |
| Joins the elements of a vector of strings into a single string using "delim" as the delimiter. More... | |
| void | Trim (std::string *str) |
| Removes the beginning and trailing whitespaces from a string. More... | |
| bool | IsToken (const std::string &token) |
| Returns true if "token" is nonempty, and all characters are printable and whitespace-free. More... | |
| void | SplitStringOnFirstSpace (const std::string &line, std::string *first, std::string *rest) |
| Removes leading and trailing white space from the string, then splits on the first section of whitespace found (if present), putting the part before the whitespace in "first" and the rest in "rest". More... | |
| bool | IsLine (const std::string &line) |
| Returns true if "line" is free of characters and unprintable characters, and does not contain leading or trailing whitespace. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | ConvertStringToReal (const std::string &str, T *out) |
| ConvertStringToReal converts a string into either float or double and returns false if there was any kind of problem (i.e. More... | |
| template bool | ConvertStringToReal (const std::string &str, float *out) |
| template bool | ConvertStringToReal (const std::string &str, double *out) |
| bool | StringsApproxEqualInternal (const char *a, const char *b, int32 decimal_places_tolerance, int32 places_into_number) |
| bool | StringsApproxEqual (const std::string &a, const std::string &b, int32 decimal_places_check=2) |
| This function returns true when two text strings are approximately equal, and false when they are not. More... | |
| void | ExpectOneOrTwoTokens (std::istream &is, bool binary, const std::string &token1, const std::string &token2) |
| This function is like ExpectToken but for two tokens, and it will either accept token1 and then token2, or just token2. More... | |
| bool | IsValidName (const std::string &name) |
| Returns true if 'name' would be a valid name for a component or node in a nnet3Nnet. More... | |
| void | ReadConfigLines (std::istream &is, std::vector< std::string > *lines) |
| This function reads in a config file and *appends* its contents to a vector of lines; it is responsible for removing comments (anything after '#') and stripping out any lines that contain only whitespace after comment removal. More... | |
| void | ParseConfigLines (const std::vector< std::string > &lines, std::vector< ConfigLine > *config_lines) |
| This function converts config-lines from a simple sequence of strings as output by ReadConfigLines(), into a sequence of first-tokens and name-value pairs. More... | |
| template<class I > | |
| bool | SplitStringToIntegers (const std::string &full, const char *delim, bool omit_empty_strings, std::vector< I > *out) |
| Split a string (e.g. More... | |
| template<class Int > | |
| bool | ConvertStringToInteger (const std::string &str, Int *out) |
| Converts a string into an integer via strtoll and returns false if there was any kind of problem (i.e. More... | |
| void | UnitTestOnlineCmvn () |
| void | ComputePowerSpectrum (VectorBase< BaseFloat > *waveform) |
| void | ComputeDeltas (const DeltaFeaturesOptions &delta_opts, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input_features, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output_features) |
| void | ComputeShiftedDeltas (const ShiftedDeltaFeaturesOptions &delta_opts, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input_features, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output_features) |
| void | InitIdftBases (int32 n_bases, int32 dimension, Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat_out) |
| void | SpliceFrames (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input_features, int32 left_context, int32 right_context, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output_features) |
| void | ReverseFrames (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input_features, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output_features) |
| void | SlidingWindowCmnInternal (const SlidingWindowCmnOptions &opts, const MatrixBase< double > &input, MatrixBase< double > *output) |
| void | SlidingWindowCmn (const SlidingWindowCmnOptions &opts, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *output) |
| Applies sliding-window cepstral mean and/or variance normalization. More... | |
| int64 | FirstSampleOfFrame (int32 frame, const FrameExtractionOptions &opts) |
| int32 | NumFrames (int64 num_samples, const FrameExtractionOptions &opts, bool flush=true) |
| This function returns the number of frames that we can extract from a wave file with the given number of samples in it (assumed to have the same sampling rate as specified in 'opts'). More... | |
| void | Dither (VectorBase< BaseFloat > *waveform, BaseFloat dither_value) |
| void | Preemphasize (VectorBase< BaseFloat > *waveform, BaseFloat preemph_coeff) |
| void | ProcessWindow (const FrameExtractionOptions &opts, const FeatureWindowFunction &window_function, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *window, BaseFloat *log_energy_pre_window=NULL) |
| This function does all the windowing steps after actually extracting the windowed signal: depending on the configuration, it does dithering, dc offset removal, preemphasis, and multiplication by the windowing function. More... | |
| void | ExtractWindow (int64 sample_offset, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, int32 f, const FrameExtractionOptions &opts, const FeatureWindowFunction &window_function, Vector< BaseFloat > *window, BaseFloat *log_energy_pre_window) |
| void | ComputeLifterCoeffs (BaseFloat Q, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *coeffs) |
| BaseFloat | Durbin (int n, const BaseFloat *pAC, BaseFloat *pLP, BaseFloat *pTmp) |
| void | Lpc2Cepstrum (int n, const BaseFloat *pLPC, BaseFloat *pCepst) |
| void | GetEqualLoudnessVector (const MelBanks &mel_banks, Vector< BaseFloat > *ans) |
| BaseFloat | ComputeLpc (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &autocorr_in, Vector< BaseFloat > *lpc_out) |
| void | GetOutput (OnlineFeatureInterface *a, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output) |
| bool | RandomSplit (int32 wav_dim, std::vector< int32 > *piece_dim, int32 num_pieces, int32 trials=5) |
| void | TestOnlineMatrixCacheFeature () |
| void | TestOnlineDeltaFeature () |
| void | TestOnlineSpliceFrames () |
| void | TestOnlineMfcc () |
| void | TestOnlinePlp () |
| void | TestOnlineTransform () |
| void | TestOnlineAppendFeature () |
| void | TestRecyclingVector () |
| std::string | ConvertIntToString (const int &number) |
| bool | DirExist (const std::string &dirname) |
| static void | UnitTestSimple () |
| static void | UnitTestSnipEdges () |
| static void | UnitTestPieces () |
| static void | UnitTestDelay () |
| static void | UnitTestSearch () |
| static void | UnitTestComputeGPE () |
| static void | UnitTestKeele () |
| static void | UnitTestPenaltyFactor () |
| static void | UnitTestKeeleNccfBallast () |
| static void | UnitTestPitchExtractionSpeed () |
| static void | UnitTestPitchExtractorCompareKeele () |
| void | UnitTestDiffSampleRate () |
| void | UnitTestProcess () |
| static void | UnitTestFeatNoKeele () |
| static void | UnitTestFeatWithKeele () |
| BaseFloat | NccfToPovFeature (BaseFloat n) |
| This function processes the NCCF n to a POV feature f by applying the formula f = (1.0001 - n)^0.15 - 1.0 This is a nonlinear function designed to make the output reasonably Gaussian distributed. More... | |
| BaseFloat | NccfToPov (BaseFloat n) |
| This function processes the NCCF n to a reasonably accurate probability of voicing p by applying the formula: More... | |
| void | ComputeCorrelation (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, int32 first_lag, int32 last_lag, int32 nccf_window_size, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *inner_prod, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *norm_prod) |
| This function computes some dot products that are required while computing the NCCF. More... | |
| void | ComputeNccf (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &inner_prod, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &norm_prod, BaseFloat nccf_ballast, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *nccf_vec) |
| Computes the NCCF as a fraction of the numerator term (a dot product between two vectors) and a denominator term which equals sqrt(e1*e2 + nccf_ballast) where e1 and e2 are both dot-products of bits of the wave with themselves, and e1*e2 is supplied as "norm_prod". More... | |
| void | SelectLags (const PitchExtractionOptions &opts, Vector< BaseFloat > *lags) |
| This function selects the lags at which we measure the NCCF: we need to select lags from 1/max_f0 to 1/min_f0, in a geometric progression with ratio 1 + d. More... | |
| void | ComputeLocalCost (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &nccf_pitch, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &lags, const PitchExtractionOptions &opts, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *local_cost) |
| This function computes the local-cost for the Viterbi computation, see eq. More... | |
| void | ComputeKaldiPitchFirstPass (const PitchExtractionOptions &opts, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output) |
| This function is called from ComputeKaldiPitch when the user specifies opts.simulate_first_pass_online == true. More... | |
| void | ComputeKaldiPitch (const PitchExtractionOptions &opts, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output) |
| This function extracts (pitch, NCCF) per frame, using the pitch extraction method described in "A Pitch Extraction Algorithm Tuned for Automatic Speech
Recognition", Pegah Ghahremani, Bagher BabaAli, Daniel Povey, Korbinian Riedhammer, Jan Trmal and Sanjeev Khudanpur, ICASSP 2014. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AppendVector (const VectorBase< Real > &src, Vector< Real > *dst) |
| void | ProcessPitch (const ProcessPitchOptions &opts, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output) |
| This function processes the raw (NCCF, pitch) quantities computed by ComputeKaldiPitch, and processes them into features. More... | |
| void | ComputeAndProcessKaldiPitch (const PitchExtractionOptions &pitch_opts, const ProcessPitchOptions &process_opts, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output) |
| This function combines ComputeKaldiPitch and ProcessPitch. More... | |
| void | ResampleWaveform (BaseFloat orig_freq, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, BaseFloat new_freq, Vector< BaseFloat > *new_wave) |
| Downsample or upsample a waveform. More... | |
| void | DownsampleWaveForm (BaseFloat orig_freq, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &wave, BaseFloat new_freq, Vector< BaseFloat > *new_wave) |
| This function is deprecated. More... | |
| void | UnitTestFFTbasedBlockConvolution () |
| void | UnitTestFFTbasedConvolution () |
| void | ElementwiseProductOfFft (const Vector< BaseFloat > &a, Vector< BaseFloat > *b) |
| void | ConvolveSignals (const Vector< BaseFloat > &filter, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal) |
| void | FFTbasedConvolveSignals (const Vector< BaseFloat > &filter, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal) |
| void | FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals (const Vector< BaseFloat > &filter, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal) |
| static void | WriteUint32 (std::ostream &os, int32 i) |
| static void | WriteUint16 (std::ostream &os, int16 i) |
| void | TestGenRandStats () |
| void | TestBuildTree () |
| void | TestTrivialTree () |
| void | TestPossibleValues () |
| void | TestConvertStats () |
| void | TestSplitStatsByKey () |
| void | TestFindAllKeys () |
| void | TestDoTableSplit () |
| void | TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap () |
| void | TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap2 () |
| void | TestClusterEventMap () |
| void | TestClusterEventMapRestricted () |
| void | TestShareEventMapLeaves () |
| void | TestQuestionsInitRand () |
| void | TestSplitDecisionTree () |
| void | TestBuildTreeStatsIo (bool binary) |
| void | WriteBuildTreeStats (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats) |
| Writes BuildTreeStats object. This works even if pointers are NULL. More... | |
| void | ReadBuildTreeStats (std::istream &is, bool binary, const Clusterable &example, BuildTreeStatsType *stats) |
| Reads BuildTreeStats object. More... | |
| bool | PossibleValues (EventKeyType key, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, std::vector< EventValueType > *ans) |
| Convenience function e.g. More... | |
| static void | GetEventKeys (const EventType &vec, std::vector< EventKeyType > *keys) |
| void | FindAllKeys (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, AllKeysType keys_type, std::vector< EventKeyType > *keys) |
| FindAllKeys puts in *keys the (sorted, unique) list of all key identities in the stats. More... | |
| EventMap * | DoTableSplit (const EventMap &orig, EventKeyType key, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int32 *num_leaves) |
| DoTableSplit does a complete split on this key (e.g. More... | |
| EventMap * | DoTableSplitMultiple (const EventMap &orig, const std::vector< EventKeyType > &keys, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int32 *num_leaves) |
| DoTableSplitMultiple does a complete split on all the keys, in order from keys[0], keys[1] and so on. More... | |
| void | SplitStatsByMap (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in, const EventMap &e, std::vector< BuildTreeStatsType > *stats_out) |
| Splits stats according to the EventMap, indexing them at output by the leaf type. More... | |
| void | SplitStatsByKey (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in, EventKeyType key, std::vector< BuildTreeStatsType > *stats_out) |
| SplitStatsByKey splits stats up according to the value of a particular key, which must be always defined and nonnegative. More... | |
| void | FilterStatsByKey (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in, EventKeyType key, std::vector< EventValueType > &values, bool include_if_present, BuildTreeStatsType *stats_out) |
| FilterStatsByKey filters the stats according the value of a specified key. More... | |
| Clusterable * | SumStats (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in) |
| Sums stats, or returns NULL stats_in has no non-NULL stats. More... | |
| BaseFloat | SumNormalizer (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in) |
| Sums the normalizer [typically, data-count] over the stats. More... | |
| BaseFloat | SumObjf (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in) |
| Sums the objective function over the stats. More... | |
| void | SumStatsVec (const std::vector< BuildTreeStatsType > &stats_in, std::vector< Clusterable * > *stats_out) |
| Sum a vector of stats. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ObjfGivenMap (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats_in, const EventMap &e) |
| Cluster the stats given the event map return the total objf given those clusters. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ComputeInitialSplit (const std::vector< Clusterable *> &summed_stats, const Questions &q_opts, EventKeyType key, std::vector< EventValueType > *yes_set) |
| BaseFloat | FindBestSplitForKey (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, const Questions &qcfg, EventKeyType key, std::vector< EventValueType > *yes_set) |
| FindBestSplitForKey is a function used in DoDecisionTreeSplit. More... | |
| EventMap * | SplitDecisionTree (const EventMap &orig, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, Questions &qcfg, BaseFloat thresh, int32 max_leaves, int32 *num_leaves, BaseFloat *objf_impr_out, BaseFloat *smallest_split_change_out) |
| Does a decision-tree split at the leaves of an EventMap. More... | |
| int | ClusterEventMapGetMapping (const EventMap &e_in, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, BaseFloat thresh, std::vector< EventMap * > *mapping) |
| "ClusterEventMapGetMapping" clusters the leaves of the EventMap, with "thresh" a delta-likelihood threshold to control how many leaves we combine (might be the same as the delta-like threshold used in splitting. More... | |
| EventMap * | RenumberEventMap (const EventMap &e_in, int32 *num_leaves) |
| RenumberEventMap [intended to be used after calling ClusterEventMap] renumbers an EventMap so its leaves are consecutive. More... | |
| EventMap * | MapEventMapLeaves (const EventMap &e_in, const std::vector< int32 > &mapping) |
| This function remaps the event-map leaves using this mapping, indexed by the number at leaf. More... | |
| EventMap * | ClusterEventMap (const EventMap &e_in, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, BaseFloat thresh, int32 *num_removed) |
| This is as ClusterEventMapGetMapping but a more convenient interface that exposes less of the internals. More... | |
| EventMap * | ShareEventMapLeaves (const EventMap &e_in, EventKeyType key, std::vector< std::vector< EventValueType > > &values, int32 *num_leaves) |
| ShareEventMapLeaves performs a quite specific function that allows us to generate trees where, for a certain list of phones, and for all states in the phone, all the pdf's are shared. More... | |
| void | DeleteBuildTreeStats (BuildTreeStatsType *stats) |
| This frees the Clusterable* pointers in "stats", where non-NULL, and sets them to NULL. More... | |
| EventMap * | GetToLengthMap (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int32 P, const std::vector< EventValueType > *phones, int32 default_length) |
| static int32 | ClusterEventMapRestrictedHelper (const EventMap &e_in, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, BaseFloat thresh, std::vector< EventKeyType > keys, std::vector< EventMap *> *leaf_mapping) |
| EventMap * | ClusterEventMapRestrictedByKeys (const EventMap &e_in, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, BaseFloat thresh, const std::vector< EventKeyType > &keys, int32 *num_removed) |
| This is as ClusterEventMap, but first splits the stats on the keys specified in "keys" (e.g. More... | |
| EventMap * | ClusterEventMapRestrictedByMap (const EventMap &e_in, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, BaseFloat thresh, const EventMap &e_restrict, int32 *num_removed) |
| This version of ClusterEventMapRestricted restricts the clustering to only allow things that "e_restrict" maps to the same value to be clustered together. More... | |
| EventMap * | ClusterEventMapToNClustersRestrictedByMap (const EventMap &e_in, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int32 num_clusters, const EventMap &e_restrict, int32 *num_removed) |
| This version of ClusterEventMapRestrictedByMap clusters to get a specific number of clusters as specified by 'num_clusters'. More... | |
| EventMap * | GetStubMap (int32 P, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > &phone2num_pdf_classes, const std::vector< bool > &share_roots, int32 *num_leaves) |
| GetStubMap is used in tree-building functions to get the initial to-states map, before the decision-tree-building process. More... | |
| bool | ConvertStats (int32 oldN, int32 oldP, int32 newN, int32 newP, BuildTreeStatsType *stats) |
| Converts stats from a given context-window (N) and central-position (P) to a different N and P, by possibly reducing context. More... | |
| EventMap * | TrivialTree (int32 *num_leaves) |
| Returns a tree with just one node. More... | |
| void | CreateRandomQuestions (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int32 num_quest, Questions *cfg_out) |
| CreateRandomQuestions will initialize a Questions randomly, in a reasonable way [for testing purposes, or when hand-designed questions are not available]. More... | |
| void | GenRandStats (int32 dim, int32 num_stats, int32 N, int32 P, const std::vector< int32 > &phone_ids, const std::vector< int32 > &hmm_lengths, const std::vector< bool > &is_ctx_dep, bool ensure_all_phones_covered, BuildTreeStatsType *stats_out) |
| GenRandStats generates random statistics of the form used by BuildTree. More... | |
| EventMap * | BuildTree (Questions &qopts, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > &phone2num_pdf_classes, const std::vector< bool > &share_roots, const std::vector< bool > &do_split, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, BaseFloat thresh, int32 max_leaves, BaseFloat cluster_thresh, int32 P, bool round_num_leaves=true) |
| BuildTree is the normal way to build a set of decision trees. More... | |
| static void | ComputeTreeMapping (const EventMap &small_tree, const EventMap &big_tree, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, std::vector< int32 > *leaf_map) |
| EventMap * | BuildTreeTwoLevel (Questions &qopts, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > &phone2num_pdf_classes, const std::vector< bool > &share_roots, const std::vector< bool > &do_split, const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int32 max_leaves_first, int32 max_leaves_second, bool cluster_leaves, int32 P, std::vector< int32 > *leaf_map) |
| BuildTreeTwoLevel builds a two-level tree, useful for example in building tied mixture systems with multiple codebooks. More... | |
| void | ReadSymbolTableAsIntegers (std::string filename, bool include_eps, std::vector< int32 > *syms) |
| included here because it's used in some tree-building calling code. More... | |
| static void | RemoveDuplicates (std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *vecs) |
| static void | ObtainSetsOfPhones (const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > &assignments, const std::vector< int32 > &clust_assignments, int32 num_leaves, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *sets_out) |
| ObtainSetsOfPhones is called by AutomaticallyObtainQuestions. More... | |
| void | AutomaticallyObtainQuestions (BuildTreeStatsType &stats, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets_in, const std::vector< int32 > &all_pdf_classes_in, int32 P, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *questions_out) |
| Outputs sets of phones that are reasonable for questions to ask in the tree-building algorithm. More... | |
| void | KMeansClusterPhones (BuildTreeStatsType &stats, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets_in, const std::vector< int32 > &all_pdf_classes_in, int32 P, int32 num_classes, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *sets_out) |
| This function clusters the phones (or some initially specified sets of phones) into sets of phones, using a k-means algorithm. More... | |
| void | ReadRootsFile (std::istream &is, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *phone_sets, std::vector< bool > *is_shared_root, std::vector< bool > *is_split_root) |
| Reads the roots file (throws on error). More... | |
| static void | TestClusterUtils () |
| static void | TestClusterUtilsVector () |
| static void | TestObjfPlus () |
| static void | TestObjfMinus () |
| static void | TestDistance () |
| static void | TestSumObjfAndSumNormalizer () |
| static void | TestSum () |
| static void | TestEnsureClusterableVectorNotNull () |
| static void | TestAddToClusters () |
| static void | TestAddToClustersOptimized () |
| static void | TestClusterBottomUp () |
| static void | TestRefineClusters () |
| static void | TestClusterKMeans () |
| static void | TestClusterKMeansVector () |
| static void | TestTreeCluster () |
| static void | TestClusterTopDown () |
| BaseFloat | SumClusterableObjf (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &vec) |
| Returns the total objective function after adding up all the statistics in the vector (pointers may be NULL). More... | |
| BaseFloat | SumClusterableNormalizer (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &vec) |
| Returns the total normalizer (usually count) of the cluster (pointers may be NULL). More... | |
| Clusterable * | SumClusterable (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &vec) |
| Sums stats (ptrs may be NULL). Returns NULL if no non-NULL stats present. More... | |
| void | EnsureClusterableVectorNotNull (std::vector< Clusterable * > *stats) |
| Fills in any (NULL) holes in "stats" vector, with empty stats, because certain algorithms require non-NULL stats. More... | |
| void | AddToClusters (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &stats, const std::vector< int32 > &assignments, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters) |
| Given stats and a vector "assignments" of the same size (that maps to cluster indices), sums the stats up into "clusters." It will add to any stats already present in "clusters" (although typically "clusters" will be empty when called), and it will extend with NULL pointers for any unseen indices. More... | |
| void | AddToClustersOptimized (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &stats, const std::vector< int32 > &assignments, const Clusterable &total, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters) |
| AddToClustersOptimized does the same as AddToClusters (it sums up the stats within each cluster, except it uses the sum of all the stats ("total") to optimize the computation for speed, if possible. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ClusterBottomUp (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &points, BaseFloat thresh, int32 min_clust, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters_out, std::vector< int32 > *assignments_out) |
| A bottom-up clustering algorithm. More... | |
| bool | operator> (const CompBotClustElem &a, const CompBotClustElem &b) |
| BaseFloat | ClusterBottomUpCompartmentalized (const std::vector< std::vector< Clusterable * > > &points, BaseFloat thresh, int32 min_clust, std::vector< std::vector< Clusterable * > > *clusters_out, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *assignments_out) |
| This is a bottom-up clustering where the points are pre-clustered in a set of compartments, such that only points in the same compartment are clustered together. More... | |
| BaseFloat | RefineClusters (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &points, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters, std::vector< int32 > *assignments, RefineClustersOptions cfg=RefineClustersOptions()) |
| RefineClusters is mainly used internally by other clustering algorithms. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ClusterKMeansOnce (const std::vector< Clusterable *> &points, int32 num_clust, std::vector< Clusterable *> *clusters_out, std::vector< int32 > *assignments_out, ClusterKMeansOptions &cfg) |
| ClusterKMeansOnce is called internally by ClusterKMeans; it is equivalent to calling ClusterKMeans with cfg.num_tries == 1. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ClusterKMeans (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &points, int32 num_clust, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters_out, std::vector< int32 > *assignments_out, ClusterKMeansOptions cfg=ClusterKMeansOptions()) |
| ClusterKMeans is a K-means-like clustering algorithm. More... | |
| BaseFloat | TreeCluster (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &points, int32 max_clust, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters_out, std::vector< int32 > *assignments_out, std::vector< int32 > *clust_assignments_out, int32 *num_leaves_out, TreeClusterOptions cfg=TreeClusterOptions()) |
| TreeCluster is a top-down clustering algorithm, using a binary tree (not necessarily balanced). More... | |
| BaseFloat | ClusterTopDown (const std::vector< Clusterable * > &points, int32 max_clust, std::vector< Clusterable * > *clusters_out, std::vector< int32 > *assignments_out, TreeClusterOptions cfg=TreeClusterOptions()) |
| A clustering algorithm that internally uses TreeCluster, but does not give you the information about the structure of the tree. More... | |
| void | TestContextDep () |
| void | TestMonophoneContextDependency () |
| void | TestGenRandContextDependency () |
| ContextDependency * | GenRandContextDependency (const std::vector< int32 > &phones, bool ensure_all_covered, std::vector< int32 > *num_pdf_classes) |
| GenRandContextDependency is mainly of use for debugging. More... | |
| ContextDependency * | GenRandContextDependencyLarge (const std::vector< int32 > &phones, int N, int P, bool ensure_all_covered, std::vector< int32 > *num_pdf_classes) |
| GenRandContextDependencyLarge is like GenRandContextDependency but generates a larger tree with specified N and P for use in "one-time" larger-scale tests. More... | |
| ContextDependency * | MonophoneContextDependency (const std::vector< int32 > &phones, const std::vector< int32 > &phone2num_pdf_classes) |
| ContextDependency * | MonophoneContextDependencyShared (const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > &phone2num_pdf_classes) |
| void | TestEventMap () |
| void | TestEventTypeIo (bool binary) |
| EventMap * | RandomEventMap (const std::vector< EventKeyType > &keys) |
| void | TestEventMapIo (bool binary) |
| void | TestEventMapPrune () |
| void | TestEventMapMapValues () |
| void | WriteEventType (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const EventType &evec) |
| void | ReadEventType (std::istream &is, bool binary, EventType *evec) |
| std::string | EventTypeToString (const EventType &evec) |
| static bool | IsLeafNode (const EventMap *e) |
| static bool | GetTreeStructureInternal (const EventMap &map, std::vector< const EventMap *> *nonleaf_nodes, std::map< const EventMap *, const EventMap *> *nonleaf_parents, std::vector< const EventMap *> *leaf_parents) |
| bool | GetTreeStructure (const EventMap &map, int32 *num_leaves, std::vector< int32 > *parents) |
| This function gets the tree structure of the EventMap "map" in a convenient form. More... | |
| std::pair< EventKeyType, EventValueType > | MakeEventPair (EventKeyType k, EventValueType v) |
| void | ClusterGaussiansToUbm (const AmDiagGmm &am, const Vector< BaseFloat > &state_occs, UbmClusteringOptions opts, DiagGmm *ubm_out) |
| Clusters the Gaussians in an acoustic model to a single GMM with specified number of components. More... | |
| void | InitRandomGmm (DiagGmm *gmm_in) |
| void | UnitTestDiagGmmGenerate () |
| void | UnitTestDiagGmm () |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const kaldi::DiagGmm &gmm) |
| ostream operator that calls DiagGMM::Write() More... | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &is, kaldi::DiagGmm &gmm) |
| istream operator that calls DiagGMM::Read() More... | |
| void | UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm () |
| static bool | EBWUpdateGaussian (BaseFloat D, GmmFlagsType flags, const VectorBase< double > &orig_mean, const VectorBase< double > &orig_var, const VectorBase< double > &x_stats, const VectorBase< double > &x2_stats, double occ, VectorBase< double > *mean, VectorBase< double > *var, double *auxf_impr) |
| void | UpdateEbwDiagGmm (const AccumDiagGmm &num_stats, const AccumDiagGmm &den_stats, GmmFlagsType flags, const EbwOptions &opts, DiagGmm *gmm, BaseFloat *auxf_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out, int32 *num_floored_out) |
| void | UpdateEbwWeightsDiagGmm (const AccumDiagGmm &num_stats, const AccumDiagGmm &den_stats, const EbwWeightOptions &opts, DiagGmm *gmm, BaseFloat *auxf_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out) |
| void | UpdateEbwAmDiagGmm (const AccumAmDiagGmm &num_stats, const AccumAmDiagGmm &den_stats, GmmFlagsType flags, const EbwOptions &opts, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm, BaseFloat *auxf_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out, int32 *num_floored_out) |
| void | UpdateEbwWeightsAmDiagGmm (const AccumAmDiagGmm &num_stats, const AccumAmDiagGmm &den_stats, const EbwWeightOptions &opts, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm, BaseFloat *auxf_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out) |
| void | IsmoothStatsDiagGmm (const AccumDiagGmm &src_stats, double tau, AccumDiagGmm *dst_stats) |
| I-Smooth the stats. src_stats and dst_stats do not have to be different. More... | |
| void | DiagGmmToStats (const DiagGmm &gmm, GmmFlagsType flags, double state_occ, AccumDiagGmm *dst_stats) |
| Creates stats from the GMM. Resizes them as needed. More... | |
| void | IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmm (const AccumAmDiagGmm &src_stats, double tau, AccumAmDiagGmm *dst_stats) |
| Smooth "dst_stats" with "src_stats". More... | |
| void | IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmmFromModel (const AmDiagGmm &src_model, double tau, AccumAmDiagGmm *dst_stats) |
| This version of the I-smoothing function takes a model as input. More... | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &rOut, const kaldi::FullGmm &gmm) |
| ostream operator that calls FullGmm::Write() More... | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &rIn, kaldi::FullGmm &gmm) |
| istream operator that calls FullGmm::Read() More... | |
| void | GetSingleStatsDerivative (double ml_count, double ml_x_stats, double ml_x2_stats, double disc_count, double disc_x_stats, double disc_x2_stats, double model_mean, double model_var, BaseFloat min_variance, double *ml_x_stats_deriv, double *ml_x2_stats_deriv) |
| void | GetStatsDerivative (const DiagGmm &gmm, const AccumDiagGmm &num_acc, const AccumDiagGmm &den_acc, const AccumDiagGmm &ml_acc, BaseFloat min_variance, BaseFloat min_gaussian_occupancy, AccumDiagGmm *out_accs) |
| void | GetStatsDerivative (const AmDiagGmm &gmm, const AccumAmDiagGmm &num_accs, const AccumAmDiagGmm &den_accs, const AccumAmDiagGmm &ml_accs, BaseFloat min_variance, BaseFloat min_gaussian_occupancy, AccumAmDiagGmm *out_accs) |
| void | DoRescalingUpdate (const AccumDiagGmm &old_ml_acc, const AccumDiagGmm &new_ml_acc, BaseFloat min_variance, BaseFloat min_gaussian_occupancy, DiagGmm *gmm, double *tot_count, double *tot_divergence) |
| void | DoRescalingUpdate (const AccumAmDiagGmm &old_ml_accs, const AccumAmDiagGmm &new_ml_accs, BaseFloat min_variance, BaseFloat min_gaussian_occupancy, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm) |
| void | ResizeModel (int32 dim, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm) |
| void | MleAmDiagGmmUpdate (const MleDiagGmmOptions &config, const AccumAmDiagGmm &amdiaggmm_acc, GmmFlagsType flags, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm, BaseFloat *obj_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out) |
| for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of an acoustic model that uses diagonal Gaussian mixture models as emission densities. More... | |
| void | MapAmDiagGmmUpdate (const MapDiagGmmOptions &config, const AccumAmDiagGmm &diag_gmm_acc, GmmFlagsType flags, AmDiagGmm *gmm, BaseFloat *obj_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out) |
| Maximum A Posteriori update. More... | |
| BaseFloat | MlObjective (const DiagGmm &gmm, const AccumDiagGmm &diaggmm_acc) |
| Calc using the DiagGMM exponential form. More... | |
| void | MleDiagGmmUpdate (const MleDiagGmmOptions &config, const AccumDiagGmm &diag_gmm_acc, GmmFlagsType flags, DiagGmm *gmm, BaseFloat *obj_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out, int32 *floored_elements_out=NULL, int32 *floored_gauss_out=NULL, int32 *removed_gauss_out=NULL) |
| for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model. More... | |
| void | MapDiagGmmUpdate (const MapDiagGmmOptions &config, const AccumDiagGmm &diag_gmm_acc, GmmFlagsType flags, DiagGmm *gmm, BaseFloat *obj_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out) |
| Maximum A Posteriori estimation of the model. More... | |
| GmmFlagsType | AugmentGmmFlags (GmmFlagsType f) |
| Returns "augmented" version of flags: e.g. More... | |
| BaseFloat | MlObjective (const FullGmm &gmm, const AccumFullGmm &fullgmm_acc) |
| Calc using the DiagGMM exponential form. More... | |
| void | MleFullGmmUpdate (const MleFullGmmOptions &config, const AccumFullGmm &fullgmm_acc, GmmFlagsType flags, FullGmm *gmm, BaseFloat *obj_change_out, BaseFloat *count_out) |
| for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model. More... | |
| GmmFlagsType | StringToGmmFlags (std::string str) |
| Convert string which is some subset of "mSwa" to flags. More... | |
| std::string | GmmFlagsToString (GmmFlagsType gmm_flags) |
| Convert GMM flags to string. More... | |
| SgmmUpdateFlagsType | StringToSgmmUpdateFlags (std::string str) |
| SgmmUpdateFlagsType | StringToSgmmWriteFlags (std::string str) |
| void | GetSplitTargets (const Vector< BaseFloat > &state_occs, int32 target_components, BaseFloat power, BaseFloat min_count, std::vector< int32 > *targets) |
| Get Gaussian-mixture or substate-mixture splitting targets, according to a power rule (e.g. More... | |
| static BaseFloat | CalBasisFmllrStepSize (const AffineXformStats &spk_stats, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &spk_stats_tmp_K, const std::vector< SpMatrix< BaseFloat > > &spk_stats_tmp_G, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &delta, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &A, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &S, int32 max_iters) |
| This function takes the step direction (delta) of fMLLR matrix as argument, and optimize step size using Newton's method. More... | |
| void | InitCmvnStats (int32 dim, Matrix< double > *stats) |
| This function initializes the matrix to dimension 2 by (dim+1); 1st "dim" elements of 1st row are mean stats, 1st "dim" elements of 2nd row are var stats, last element of 1st row is count, last element of 2nd row is zero. More... | |
| void | AccCmvnStats (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &feat, BaseFloat weight, MatrixBase< double > *stats) |
| Accumulation from a single frame (weighted). More... | |
| void | AccCmvnStats (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &feats, const VectorBase< BaseFloat > *weights, MatrixBase< double > *stats) |
| Accumulation from a feature file (possibly weighted– useful in excluding silence). More... | |
| void | ApplyCmvn (const MatrixBase< double > &stats, bool norm_vars, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *feats) |
| Apply cepstral mean and variance normalization to a matrix of features. More... | |
| void | ApplyCmvnReverse (const MatrixBase< double > &stats, bool norm_vars, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *feats) |
| This is as ApplyCmvn, but does so in the reverse sense, i.e. More... | |
| void | FakeStatsForSomeDims (const std::vector< int32 > &dims, MatrixBase< double > *stats) |
| Modify the stats so that for some dimensions (specified in "dims"), we replace them with "fake" stats that have zero mean and unit variance; this is done to disable CMVN for those dimensions. More... | |
| static void | ComputeGconsts (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &weights, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &means, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &inv_vars, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *gconsts_out) |
| void | UnitTestFmllrDiagGmm () |
| void | UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmDiagonal () |
| void | UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmOffset () |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &in_xform, const AffineXformStats &stats, std::string fmllr_type, int32 num_iters, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *out_xform) |
| This function internally calls ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm{Full, Diagonal, Offset}, depending on "fmllr_type". More... | |
| void | FmllrInnerUpdate (SpMatrix< double > &inv_G, VectorBase< double > &k, double beta, int32 row, MatrixBase< double > *transform) |
| This function does one row of the inner-loop fMLLR transform update. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &in_xform, const AffineXformStats &stats, int32 num_iters, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *out_xform) |
| Updates the FMLLR matrix using Mark Gales' row-by-row update. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &in_xform, const AffineXformStats &stats, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *out_xform) |
| This does diagonal fMLLR (i.e. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmOffset (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &in_xform, const AffineXformStats &stats, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *out_xform) |
| This does offset-only fMLLR, i.e. it only estimates an offset. More... | |
| void | ApplyFeatureTransformToStats (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &xform, AffineXformStats *stats) |
| This function applies a feature-level transform to stats (useful for certain techniques based on fMLLR). More... | |
| void | ApplyModelTransformToStats (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &xform, AffineXformStats *stats) |
| ApplyModelTransformToStats takes a transform "xform", which must be diagonal (i.e. More... | |
| float | FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm (const MatrixBase< float > &xform, const AffineXformStats &stats) |
| Returns the (diagonal-GMM) FMLLR auxiliary function value given the transform and the stats. More... | |
| double | FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm (const MatrixBase< double > &xform, const AffineXformStats &stats) |
| BaseFloat | FmllrAuxfGradient (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &xform, const AffineXformStats &stats, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *grad_out) |
| Returns the (diagonal-GMM) FMLLR auxiliary function value given the transform and the stats. More... | |
| void | InitFmllr (int32 dim, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out_fmllr) |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrDiagGmm (const FmllrDiagGmmAccs &accs, const FmllrOptions &opts, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out_fmllr, BaseFloat *logdet) |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrLogDet (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &fmllr_mat) |
| BaseFloat | ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal2 (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &in_xform, const AffineXformStats &stats, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *out_xform) |
| void | UnitTestFmllrRaw (bool use_offset) |
| void | GetFeatDeriv (const DiagGmm &gmm, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, Matrix< BaseFloat > *deriv) |
| BaseFloat | GetGmmLike (const DiagGmm &gmm, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats) |
| void | TestFmpe () |
| BaseFloat | ComputeAmGmmFeatureDeriv (const AmDiagGmm &am_gmm, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const Posterior &posterior, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &features, Matrix< BaseFloat > *direct_deriv, const AccumAmDiagGmm *model_diff=NULL, Matrix< BaseFloat > *indirect_deriv=NULL) |
| Computes derivatives of the likelihood of these states (weighted), w.r.t. More... | |
| static bool | GetActiveParents (int32 node, const vector< int32 > &parents, const vector< bool > &is_active, vector< int32 > *active_parents_out) |
| static void | RandFullCova (Matrix< BaseFloat > *matrix) |
| static void | generate_features (cova_type covariance_type, size_t n_gaussians, size_t dim, Matrix< BaseFloat > &trans_mat, size_t frames_per_gaussian, std::vector< Vector< BaseFloat > *> &train_feats, std::vector< Vector< BaseFloat > *> &adapt_feats) |
| void | UnitTestRegtreeFmllrDiagGmm (cova_type feature_type, size_t max_bclass) |
| static void | ComputeMllrMatrix (const Matrix< double > &K, const vector< SpMatrix< double > > &G, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out) |
| static BaseFloat | MllrAuxFunction (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &xform, const AffineXformStats &stats) |
| bool | ComposeTransforms (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &a, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &b, bool b_is_affine, Matrix< BaseFloat > *c) |
| void | ApplyAffineTransform (const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &xform, VectorBase< BaseFloat > *vec) |
| Applies the affine transform 'xform' to the vector 'vec' and overwrites the contents of 'vec'. More... | |
| TransitionModel * | GenRandTransitionModel (ContextDependency **ctx_dep_out) |
| HmmTopology | GetDefaultTopology (const std::vector< int32 > &phones) |
| This function returns a HmmTopology object giving a normal 3-state topology, covering all phones in the list "phones". More... | |
| HmmTopology | GenRandTopology (const std::vector< int32 > &phones, const std::vector< int32 > &num_pdf_classes) |
| This method of generating an arbitrary HmmTopology object allows you to specify the number of pdf-classes for each phone separately. More... | |
| HmmTopology | GenRandTopology () |
| This version of GenRandTopology() generates the phone list and number of pdf classes randomly. More... | |
| void | GeneratePathThroughHmm (const HmmTopology &topology, bool reorder, int32 phone, std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > *path) |
| This function generates a random path through the HMM for the given phone. More... | |
| void | GenerateRandomAlignment (const ContextDependencyInterface &ctx_dep, const TransitionModel &trans_model, bool reorder, const std::vector< int32 > &phone_sequence, std::vector< int32 > *alignment) |
| For use in test code, this function generates an alignment (a sequence of transition-ids) corresponding to a given phone sequence. More... | |
| void | TestHmmTopology () |
| void | TestConvertPhnxToProns () |
| void | TestAccumulateTreeStatsOptions () |
| void | TestSplitToPhones () |
| void | TestConvertAlignment () |
| fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | GetHmmAsFsa (std::vector< int32 > context_window, const ContextDependencyInterface &ctx_dep, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const HTransducerConfig &config, HmmCacheType *cache=NULL) |
| Called by GetHTransducer() and probably will not need to be called directly; it creates and returns the FST corresponding to the phone. More... | |
| fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | GetHmmAsFsaSimple (std::vector< int32 > context_window, const ContextDependencyInterface &ctx_dep, const TransitionModel &trans_model, BaseFloat prob_scale) |
| Included mainly as a form of documentation, not used in any other code currently. More... | |
| static fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | MakeTrivialAcceptor (int32 label) |
| This utility function, used in GetHTransducer(), creates an FSA (finite state acceptor, i.e. More... | |
| fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | GetHTransducer (const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &ilabel_info, const ContextDependencyInterface &ctx_dep, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const HTransducerConfig &config, std::vector< int32 > *disambig_syms_left) |
| Returns the H tranducer; result owned by caller. More... | |
| void | GetIlabelMapping (const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &ilabel_info_old, const ContextDependencyInterface &ctx_dep, const TransitionModel &trans_model, std::vector< int32 > *old2new_map) |
| GetIlabelMapping produces a mapping that's similar to HTK's logical-to-physical model mapping (i.e. More... | |
| fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | GetPdfToTransitionIdTransducer (const TransitionModel &trans_model) |
| Returns a transducer from pdfs plus one (input) to transition-ids (output). More... | |
| static void | AddSelfLoopsReorder (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &disambig_syms, BaseFloat self_loop_scale, bool check_no_self_loops, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| static void | AddSelfLoopsNoReorder (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &disambig_syms, BaseFloat self_loop_scale, bool check_no_self_loops, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| void | AddSelfLoops (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &disambig_syms, BaseFloat self_loop_scale, bool reorder, bool check_no_self_loops, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| For context, see AddSelfLoops(). More... | |
| static bool | IsReordered (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &alignment) |
| static bool | SplitToPhonesInternal (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &alignment, bool reordered, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *split_output) |
| bool | SplitToPhones (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &alignment, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *split_alignment) |
| SplitToPhones splits up the TransitionIds in "alignment" into their individual phones (one vector per instance of a phone). More... | |
| static void | ConvertAlignmentForPhone (const TransitionModel &old_trans_model, const TransitionModel &new_trans_model, const ContextDependencyInterface &new_ctx_dep, const std::vector< int32 > &old_phone_alignment, const std::vector< int32 > &new_phone_window, bool old_is_reordered, bool new_is_reordered, std::vector< int32 > *new_phone_alignment) |
| This function is used internally inside ConvertAlignment; it converts the alignment for a single phone. More... | |
| static bool | ComputeNewPhoneLengths (const HmmTopology &topology, const std::vector< int32 > &mapped_phones, const std::vector< int32 > &old_lengths, int32 conversion_shift, int32 subsample_factor, std::vector< int32 > *new_lengths) |
| This function, called from ConvertAlignmentInternal(), works out suitable new lengths of phones in the case where subsample_factor != 1. More... | |
| static bool | ConvertAlignmentInternal (const TransitionModel &old_trans_model, const TransitionModel &new_trans_model, const ContextDependencyInterface &new_ctx_dep, const std::vector< int32 > &old_alignment, int32 conversion_shift, int32 subsample_factor, bool new_is_reordered, const std::vector< int32 > *phone_map, std::vector< int32 > *new_alignment) |
| This function is the same as 'ConvertAligment', but instead of the 'repeat_frames' option it supports the 'conversion_shift' option; see the documentation of ComputeNewPhoneLengths() for what 'conversion_shift' is for. More... | |
| bool | ConvertAlignment (const TransitionModel &old_trans_model, const TransitionModel &new_trans_model, const ContextDependencyInterface &new_ctx_dep, const std::vector< int32 > &old_alignment, int32 subsample_factor, bool repeat_frames, bool reorder, const std::vector< int32 > *phone_map, std::vector< int32 > *new_alignment) |
| ConvertAlignment converts an alignment that was created using one model, to another model. More... | |
| static BaseFloat | GetScaledTransitionLogProb (const TransitionModel &trans_model, int32 trans_id, BaseFloat transition_scale, BaseFloat self_loop_scale) |
| void | AddTransitionProbs (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &disambig_syms, BaseFloat transition_scale, BaseFloat self_loop_scale, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| Adds transition-probs, with the supplied scales (see Scaling of transition and acoustic probabilities), to the graph. More... | |
| void | AddTransitionProbs (const TransitionModel &trans_model, BaseFloat transition_scale, BaseFloat self_loop_scale, Lattice *lat) |
| This is as AddSelfLoops(), but operates on a Lattice, where it affects the graph part of the weight (the first element of the pair). More... | |
| bool | ConvertPhnxToProns (const std::vector< int32 > &phnx, const std::vector< int32 > &words, int32 word_start_sym, int32 word_end_sym, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *prons) |
| void | GetRandomAlignmentForPhone (const ContextDependencyInterface &ctx_dep, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &phone_window, std::vector< int32 > *alignment) |
| void | ChangeReorderingOfAlignment (const TransitionModel &trans_model, std::vector< int32 > *alignment) |
| void | GetPdfToPhonesMap (const TransitionModel &trans_model, std::vector< std::set< int32 > > *pdf2phones) |
| void | ConvertTransitionIdsToPdfs (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &disambig_syms, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| Converts all transition-ids in the FST to pdfs plus one. More... | |
| void | TestVectorToPosteriorEntry () |
| void | TestPosteriorIo () |
| void | WritePosterior (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const Posterior &post) |
| stand-alone function for writing a Posterior. More... | |
| void | ReadPosterior (std::istream &os, bool binary, Posterior *post) |
| stand-alone function for reading a Posterior. More... | |
| void | ScalePosterior (BaseFloat scale, Posterior *post) |
| Scales the BaseFloat (weight) element in the posterior entries. More... | |
| BaseFloat | TotalPosterior (const Posterior &post) |
| Returns the total of all the weights in "post". More... | |
| bool | PosteriorEntriesAreDisjoint (const std::vector< std::pair< int32, BaseFloat > > &post_elem1, const std::vector< std::pair< int32, BaseFloat > > &post_elem2) |
| Returns true if the two lists of pairs have no common .first element. More... | |
| int32 | MergePosteriors (const Posterior &post1, const Posterior &post2, bool merge, bool drop_frames, Posterior *post) |
| Merge two sets of posteriors, which must have the same length. More... | |
| void | AlignmentToPosterior (const std::vector< int32 > &ali, Posterior *post) |
| Convert an alignment to a posterior (with a scale of 1.0 on each entry). More... | |
| void | SortPosteriorByPdfs (const TransitionModel &tmodel, Posterior *post) |
| Sorts posterior entries so that transition-ids with same pdf-id are next to each other. More... | |
| void | ConvertPosteriorToPdfs (const TransitionModel &tmodel, const Posterior &post_in, Posterior *post_out) |
| Converts a posterior over transition-ids to be a posterior over pdf-ids. More... | |
| void | ConvertPosteriorToPhones (const TransitionModel &tmodel, const Posterior &post_in, Posterior *post_out) |
| Converts a posterior over transition-ids to be a posterior over phones. More... | |
| void | WeightSilencePost (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const ConstIntegerSet< int32 > &silence_set, BaseFloat silence_scale, Posterior *post) |
| Weight any silence phones in the posterior (i.e. More... | |
| void | WeightSilencePostDistributed (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const ConstIntegerSet< int32 > &silence_set, BaseFloat silence_scale, Posterior *post) |
| This is similar to WeightSilencePost, except that on each frame it works out the amount by which the overall posterior would be reduced, and scales down everything on that frame by the same amount. More... | |
| static BaseFloat | GetTotalPosterior (const std::vector< std::pair< int32, BaseFloat > > &post_entry) |
| BaseFloat | VectorToPosteriorEntry (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &log_likes, int32 num_gselect, BaseFloat min_post, std::vector< std::pair< int32, BaseFloat > > *post_entry) |
| Given a vector of log-likelihoods (typically of Gaussians in a GMM but could be of pdf-ids), a number gselect >= 1 and a minimum posterior 0 <= min_post < 1, it gets the posterior for each element of log-likes by applying Softmax(), then prunes the posteriors using "gselect" and "min_post" (keeping at least one), and outputs the result into "post_entry", sorted from greatest to least posterior. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | PosteriorToMatrix (const Posterior &post, const int32 post_dim, Matrix< Real > *mat) |
| This converts a Posterior to a Matrix. More... | |
| template void | PosteriorToMatrix< float > (const Posterior &post, const int32 post_dim, Matrix< float > *mat) |
| template void | PosteriorToMatrix< double > (const Posterior &post, const int32 post_dim, Matrix< double > *mat) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | PosteriorToPdfMatrix (const Posterior &post, const TransitionModel &model, Matrix< Real > *mat) |
| This converts a Posterior to a Matrix. More... | |
| template void | PosteriorToPdfMatrix< float > (const Posterior &post, const TransitionModel &model, Matrix< float > *mat) |
| template void | PosteriorToPdfMatrix< double > (const Posterior &post, const TransitionModel &model, Matrix< double > *mat) |
| void | TestTransitionModel () |
| bool | GetPdfsForPhones (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &phones, std::vector< int32 > *pdfs) |
| Works out which pdfs might correspond to the given phones. More... | |
| bool | GetPhonesForPdfs (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const std::vector< int32 > &pdfs, std::vector< int32 > *phones) |
| Works out which phones might correspond to the given pdfs. More... | |
| static int32 | MapPhone (const std::vector< int32 > &phone_map, int32 phone) |
| void | TrimTrailingWhitespace (std::string *str) |
| static fst::StdVectorFst * | CreateGenFst (bool seps, const fst::SymbolTable *pst) |
| ArpaLmCompiler * | Compile (bool seps, const std::string &infile) |
| fst::StdArc::StateId | AddToChainFsa (fst::StdMutableFst *fst, fst::StdArc::StateId last_state, int64 symbol) |
| void | AddSelfLoops (fst::StdMutableFst *fst) |
| bool | CoverageTest (bool seps, const std::string &infile) |
| bool | ScoringTest (bool seps, const std::string &infile, const std::string &sentence, float expected) |
| bool | ThrowsExceptionTest (bool seps, const std::string &infile) |
| bool | BuildConstArpaLm (const ArpaParseOptions &options, const std::string &arpa_rxfilename, const std::string &const_arpa_wxfilename) |
| template<typename FST > | |
| bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental (LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST > &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignments_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| TODO. More... | |
| template<typename FST > | |
| bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster (LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST > &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignments_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| This function DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster is used in several decoders, and we have moved it here. More... | |
| template bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental (LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| template bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental (LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| template bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster (LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| template bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster (LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| bool | DecodeUtteranceLatticeSimple (LatticeSimpleDecoder &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| void | ModifyGraphForCarefulAlignment (fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| This function modifies the decoding graph for what we call "careful
alignment". More... | |
| void | AlignUtteranceWrapper (const AlignConfig &config, const std::string &utt, BaseFloat acoustic_scale, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst, DecodableInterface *decodable, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, BaseFloatWriter *scores_writer, int32 *num_done, int32 *num_error, int32 *num_retried, double *tot_like, int64 *frame_count, BaseFloatVectorWriter *per_frame_acwt_writer=NULL) |
| AlignUtteranceWapper is a wrapper for alignment code used in training, that is called from many different binaries, e.g. More... | |
| static void | AddCompactLatticeArcToLattice (const CompactLatticeArc &clat_arc, LatticeArc::StateId src_state, Lattice *lat) |
| static int32 | TotalNumArcs (const CompactLattice &clat) |
| void | ComposeCompactLatticePruned (const ComposeLatticePrunedOptions &opts, const CompactLattice &clat, fst::DeterministicOnDemandFst< fst::StdArc > *det_fst, CompactLattice *composed_clat) |
| Does pruned composition of a lattice 'clat' with a DeterministicOnDemandFst 'det_fst'; implements LM rescoring. More... | |
| BaseFloat | SentenceLevelConfidence (const CompactLattice &clat, int32 *num_paths, std::vector< int32 > *best_sentence, std::vector< int32 > *second_best_sentence) |
| Caution: this function is not the only way to get confidences in Kaldi. More... | |
| BaseFloat | SentenceLevelConfidence (const Lattice &lat, int32 *num_paths, std::vector< int32 > *best_sentence, std::vector< int32 > *second_best_sentence) |
| This version of SentenceLevelConfidence takes as input a state-level lattice. More... | |
| CompactLattice * | RandCompactLattice () |
| Lattice * | RandLattice () |
| void | TestCompactLatticeTable (bool binary) |
| void | TestCompactLatticeTableCross (bool binary) |
| void | TestLatticeTable (bool binary) |
| void | TestLatticeTableCross (bool binary) |
| template<class OrigWeightType > | |
| CompactLattice * | ConvertToCompactLattice (fst::VectorFst< OrigWeightType > *ifst) |
| Converts lattice types if necessary, deleting its input. More... | |
| template<> | |
| CompactLattice * | ConvertToCompactLattice (CompactLattice *ifst) |
| template<class OrigWeightType > | |
| Lattice * | ConvertToLattice (fst::VectorFst< OrigWeightType > *ifst) |
| Converts lattice types if necessary, deleting its input. More... | |
| template<> | |
| Lattice * | ConvertToLattice (Lattice *ifst) |
| bool | WriteCompactLattice (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const CompactLattice &t) |
| CompactLattice * | ReadCompactLatticeText (std::istream &is) |
| Lattice * | ReadLatticeText (std::istream &is) |
| bool | ReadCompactLattice (std::istream &is, bool binary, CompactLattice **clat) |
| bool | WriteLattice (std::ostream &os, bool binary, const Lattice &t) |
| bool | ReadLattice (std::istream &is, bool binary, Lattice **lat) |
| void | GetPerFrameAcousticCosts (const Lattice &nbest, Vector< BaseFloat > *per_frame_loglikes) |
| This function extracts the per-frame log likelihoods from a linear lattice (which we refer to as an 'nbest' lattice elsewhere in Kaldi code). More... | |
| int32 | LatticeStateTimes (const Lattice &lat, vector< int32 > *times) |
| This function iterates over the states of a topologically sorted lattice and counts the time instance corresponding to each state. More... | |
| int32 | CompactLatticeStateTimes (const CompactLattice &lat, vector< int32 > *times) |
| As LatticeStateTimes, but in the CompactLattice format. More... | |
| bool | ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas (const CompactLattice &clat, vector< double > *alpha) |
| bool | ComputeCompactLatticeBetas (const CompactLattice &clat, vector< double > *beta) |
| template<class LatType > | |
| bool | PruneLattice (BaseFloat beam, LatType *lat) |
| template bool | PruneLattice (BaseFloat beam, Lattice *lat) |
| template bool | PruneLattice (BaseFloat beam, CompactLattice *lat) |
| BaseFloat | LatticeForwardBackward (const Lattice &lat, Posterior *arc_post, double *acoustic_like_sum=NULL) |
| This function does the forward-backward over lattices and computes the posterior probabilities of the arcs. More... | |
| void | LatticeActivePhones (const Lattice &lat, const TransitionModel &trans, const vector< int32 > &silence_phones, vector< std::set< int32 > > *active_phones) |
| Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, outputs for each frame the set of phones active on that frame. More... | |
| void | ConvertLatticeToPhones (const TransitionModel &trans_model, Lattice *lat) |
| Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, replace the output symbols (presumably words), with phones; we use the TransitionModel to work out the phone sequence. More... | |
| static double | LogAddOrMax (bool viterbi, double a, double b) |
| template<typename LatticeType > | |
| double | ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas (const LatticeType &lat, bool viterbi, vector< double > *alpha, vector< double > *beta) |
| template double | ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas (const Lattice &lat, bool viterbi, vector< double > *alpha, vector< double > *beta) |
| template double | ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas (const CompactLattice &lat, bool viterbi, vector< double > *alpha, vector< double > *beta) |
| void | CompactLatticeLimitDepth (int32 max_arcs_per_frame, CompactLattice *clat) |
| This function limits the depth of the lattice, per frame: that means, it does not allow more than a specified number of arcs active on any given frame. More... | |
| void | TopSortCompactLatticeIfNeeded (CompactLattice *clat) |
| Topologically sort the compact lattice if not already topologically sorted. More... | |
| void | TopSortLatticeIfNeeded (Lattice *clat) |
| Topologically sort the lattice if not already topologically sorted. More... | |
| BaseFloat | CompactLatticeDepth (const CompactLattice &clat, int32 *num_frames) |
| Returns the depth of the lattice, defined as the average number of arcs crossing any given frame. More... | |
| void | CompactLatticeDepthPerFrame (const CompactLattice &clat, std::vector< int32 > *depth_per_frame) |
| This function returns, for each frame, the number of arcs crossing that frame. More... | |
| void | ConvertCompactLatticeToPhones (const TransitionModel &trans_model, CompactLattice *clat) |
| Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, replace the sequences of transition-ids with sequences of phones. More... | |
| bool | LatticeBoost (const TransitionModel &trans, const std::vector< int32 > &alignment, const std::vector< int32 > &silence_phones, BaseFloat b, BaseFloat max_silence_error, Lattice *lat) |
| Boosts LM probabilities by b * [number of frame errors]; equivalently, adds -b*[number of frame errors] to the graph-component of the cost of each arc/path. More... | |
| BaseFloat | LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants (const TransitionModel &trans, const std::vector< int32 > &silence_phones, const Lattice &lat, const std::vector< int32 > &num_ali, std::string criterion, bool one_silence_class, Posterior *post) |
| This function implements either the MPFE (minimum phone frame error) or SMBR (state-level minimum bayes risk) forward-backward, depending on whether "criterion" is "mpfe" or "smbr". More... | |
| bool | CompactLatticeToWordAlignment (const CompactLattice &clat, std::vector< int32 > *words, std::vector< int32 > *begin_times, std::vector< int32 > *lengths) |
| This function takes a CompactLattice that should only contain a single linear sequence (e.g. More... | |
| bool | CompactLatticeToWordProns (const TransitionModel &tmodel, const CompactLattice &clat, std::vector< int32 > *words, std::vector< int32 > *begin_times, std::vector< int32 > *lengths, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *prons, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *phone_lengths) |
| This function takes a CompactLattice that should only contain a single linear sequence (e.g. More... | |
| void | CompactLatticeShortestPath (const CompactLattice &clat, CompactLattice *shortest_path) |
| A form of the shortest-path/best-path algorithm that's specially coded for CompactLattice. More... | |
| void | AddWordInsPenToCompactLattice (BaseFloat word_ins_penalty, CompactLattice *clat) |
| This function add the word insertion penalty to graph score of each word in the compact lattice. More... | |
| bool | RescoreCompactLatticeInternal (const TransitionModel *tmodel, BaseFloat speedup_factor, DecodableInterface *decodable, CompactLattice *clat) |
| RescoreCompactLatticeInternal is the internal code for both RescoreCompactLattice and RescoreCompatLatticeSpeedup. More... | |
| bool | RescoreCompactLatticeSpeedup (const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat speedup_factor, DecodableInterface *decodable, CompactLattice *clat) |
| This function is like RescoreCompactLattice, but it is modified to avoid computing probabilities on most frames where all the pdf-ids are the same. More... | |
| bool | RescoreCompactLattice (DecodableInterface *decodable, CompactLattice *clat) |
| This function *adds* the negated scores obtained from the Decodable object, to the acoustic scores on the arcs. More... | |
| bool | RescoreLattice (DecodableInterface *decodable, Lattice *lat) |
| This function *adds* the negated scores obtained from the Decodable object, to the acoustic scores on the arcs. More... | |
| BaseFloat | LatticeForwardBackwardMmi (const TransitionModel &trans, const Lattice &lat, const std::vector< int32 > &num_ali, bool drop_frames, bool convert_to_pdf_ids, bool cancel, Posterior *arc_post) |
| This function can be used to compute posteriors for MMI, with a positive contribution for the numerator and a negative one for the denominator. More... | |
| int32 | LongestSentenceLength (const Lattice &lat) |
| This function returns the number of words in the longest sentence in a CompactLattice (i.e. More... | |
| int32 | LongestSentenceLength (const CompactLattice &lat) |
| This function returns the number of words in the longest sentence in a CompactLattice, i.e. More... | |
| void | ComposeCompactLatticeDeterministic (const CompactLattice &clat, fst::DeterministicOnDemandFst< fst::StdArc > *det_fst, CompactLattice *composed_clat) |
| This function Composes a CompactLattice format lattice with a DeterministicOnDemandFst<fst::StdFst> format fst, and outputs another CompactLattice format lattice. More... | |
| void | ComputeAcousticScoresMap (const Lattice &lat, unordered_map< std::pair< int32, int32 >, std::pair< BaseFloat, int32 >, PairHasher< int32 > > *acoustic_scores) |
| This function computes the mapping from the pair (frame-index, transition-id) to the pair (sum-of-acoustic-scores, num-of-occurences) over all occurences of the transition-id in that frame. More... | |
| void | ReplaceAcousticScoresFromMap (const unordered_map< std::pair< int32, int32 >, std::pair< BaseFloat, int32 >, PairHasher< int32 > > &acoustic_scores, Lattice *lat) |
| This function restores acoustic scores computed using the function ComputeAcousticScoresMap into the lattice. More... | |
| int32 | LatticeStateTimes (const Lattice &lat, std::vector< int32 > *times) |
| This function iterates over the states of a topologically sorted lattice and counts the time instance corresponding to each state. More... | |
| int32 | CompactLatticeStateTimes (const CompactLattice &clat, std::vector< int32 > *times) |
| As LatticeStateTimes, but in the CompactLattice format. More... | |
| bool | ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas (const CompactLattice &lat, std::vector< double > *alpha) |
| bool | ComputeCompactLatticeBetas (const CompactLattice &lat, std::vector< double > *beta) |
| template<typename LatticeType > | |
| double | ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas (const LatticeType &lat, bool viterbi, std::vector< double > *alpha, std::vector< double > *beta) |
| void | LatticeActivePhones (const Lattice &lat, const TransitionModel &trans, const std::vector< int32 > &sil_phones, std::vector< std::set< int32 > > *active_phones) |
| Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, outputs for each frame the set of phones active on that frame. More... | |
| template<class LatticeType > | |
| bool | PruneLattice (BaseFloat beam, LatticeType *lat) |
| Prunes a lattice or compact lattice. More... | |
| CompactLattice * | RandDeterministicCompactLattice () |
| void | TestMinimizeCompactLattice () |
| bool | PhoneAlignLattice (const CompactLattice &lat, const TransitionModel &tmodel, const PhoneAlignLatticeOptions &opts, CompactLattice *lat_out) |
| Outputs a lattice in which the arcs correspond exactly to sequences of phones, so the boundaries between the arcs correspond to the boundaries between phones If remove-epsilon == false and replace-output-symbols == false, but an arc may have >1 phone on it, but the boundaries will still correspond with the boundaries between phones. More... | |
| void | TestPushCompactLatticeStrings () |
| void | TestPushCompactLatticeWeights () |
| void | GenerateLexicon (const std::vector< int32 > &phones, bool allow_zero_words, bool allow_empty_word, bool allow_multiple_prons, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *lexicon) |
| static void | PrintLexicon (const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &lexicon) |
| static void | PrintWordsAndPhones (const std::vector< int32 > &words, const std::vector< int32 > &phones) |
| void | GenerateWordAndPhoneSequence (std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &lexicon, std::vector< int32 > *phone_seq, std::vector< int32 > *word_seq) |
| void | GenerateCompactLatticeRandomly (const std::vector< int32 > &alignment, const std::vector< int32 > &words, CompactLattice *clat) |
| void | TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon () |
| static bool | IsPlausibleWord (const WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo &lexicon_info, const TransitionModel &tmodel, int32 word_id, const std::vector< int32 > &transition_ids) |
| static void | MapSymbols (const WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo &lexicon_info, CompactLattice *lat) |
| Testing code; map word symbols in the lattice "lat" using the equivalence-classes obtained from the lexicon, using the function EquivalenceClassOf in the lexicon_info object. More... | |
| static bool | TestWordAlignedLattice (const WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo &lexicon_info, const TransitionModel &tmodel, CompactLattice clat, CompactLattice aligned_clat, bool allow_duplicate_paths) |
| bool | WordAlignLatticeLexicon (const CompactLattice &lat, const TransitionModel &tmodel, const WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo &lexicon_info, const WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts &opts, CompactLattice *lat_out) |
| Align lattice so that each arc has the transition-ids on it that correspond to the word that is on that arc. More... | |
| bool | ReadLexiconForWordAlign (std::istream &is, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *lexicon) |
| Read the lexicon in the special format required for word alignment. More... | |
| void | TestWordAlignedLatticeLexicon (const CompactLattice &lat, const TransitionModel &tmodel, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &lexicon, const CompactLattice &aligned_lat, bool allow_duplicate_paths) |
| This function is designed to crash if something went wrong with the word-alignment of the lattice. More... | |
| static bool | IsPlausibleWord (const WordBoundaryInfo &info, const TransitionModel &tmodel, const std::vector< int32 > &transition_ids) |
| bool | WordAlignLattice (const CompactLattice &lat, const TransitionModel &tmodel, const WordBoundaryInfo &info, int32 max_states, CompactLattice *lat_out) |
| Align lattice so that each arc has the transition-ids on it that correspond to the word that is on that arc. More... | |
| void | TestWordAlignedLattice (const CompactLattice &lat, const TransitionModel &tmodel, const WordBoundaryInfo &info, const CompactLattice &aligned_lat) |
| You should only test a lattice if WordAlignLattice returned true (i.e. More... | |
| void | RegisterCuAllocatorOptions (OptionsItf *po) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuArray< T > &vec) |
| Print the vector to stream. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | AssertEqual (const std::vector< T > &vec1, const std::vector< T > &vec2) |
| template<class T > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuArray () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static bool | ApproxEqual (const CuBlockMatrix< Real > &A, const CuBlockMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuBlockMatrixIO () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatBlock () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuBlockMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuBlockMatrix< Real > &mat) |
| Print the matrix to stream. More... | |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuBlockMatrix< float > &mat) |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuBlockMatrix< double > &mat) |
| void | CuCompressedMatrixTestSign () |
| void | CuCompressedMatrixTestNonnegative () |
| void | CuCompressedMatrixTestSymmetric () |
| CuCompressedMatrixBase * | NewCuCompressedMatrix (CuCompressedMatrixType t, BaseFloat range, bool truncate=true) |
| This function allocates a new CuCompressedMatrix with type determined by t, and with the 'range' and 'truncate' parameters provided to the constructor of class CuCompressedMatrix. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixResize (int32 size_multiple) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaMatrixResizeTest () |
| void | SynchronizeGpu () |
| The function SynchronizeGpu(), which for convenience is defined whether or not we have compiled for CUDA, is intended to be called in places where threads need to be synchronized. More... | |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMathRandomize () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestEnsureNonzero () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMathCopy () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMathSplice () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMathComputeLstmNonlinearity () |
| void | UnitTestLstmNonlinearity () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestBackpropLstmNonlinearity () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMathNormalizePerRow () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMathNormalizePerRow_v2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuDiffNormalizePerRow () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaMathUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixSum (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixMax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixMin (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixDivRowsVec (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixTransposeNS (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixTransposeS (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixTransposeCross (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddMat (int32 dim, int32 num_row_blocks, int32 num_col_blocks) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks (int32 dim, int32 num_row_blocks, int32 num_col_blocks) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixMatMat (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixMatMatBatched (int32 dim, int32 batchCount) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddDiagVecMat (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestSymInvertPosDef (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | TestCuMatrixCompObjfAndDeriv (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | TestCuFindRowMaxId (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixSigmoid (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixHeaviside (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixMulRowsGroupMat (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixDiffSoftmax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixDiffLogSoftmax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixSoftmax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixLogSoftmax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixGroupPnorm (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixDiffGroupPnorm (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixGroupMax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixGroupMaxAllGroupSizes (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixGroupMaxDeriv (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixTraceMatMat (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCholesky (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyLowerToUpper (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyFromTp (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyFromSp (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyUpperToLower (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixSetZeroAboveDiag (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixLookup (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyRows1 (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyRows2 (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixCopyToRows (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddRows1 (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddRows2 (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddToRows (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuMatrixAddRowRanges (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaMatrixSpeedTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | InitRand (VectorBase< Real > *v) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | InitRand (MatrixBase< Real > *M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | RandZeroToOneMatrix (MatrixBase< Real > *mat) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixTraceMatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuCholesky () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyLog () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExpSpecial () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExpLimited () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSigmoid () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixScale () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAdd () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSoftHinge () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixGroupPnorm () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixGroupMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSet () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyPow () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyPowAbs () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyRowsFromVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyColsFromVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyToRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMulRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddToRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSumColumnRanges () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddRowRanges () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCols () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTextCuMatrixAddMatSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddCols () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyFloor () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyCeiling () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixApplyHeaviside () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixHeaviside () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMulElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixDivElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMin () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMulColsVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsGroupMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixDiffGroupPnorm () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixGroupMaxDeriv () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddDiagVecMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatDiagVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMatElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSetMatMatDivMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixDivRowsVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks1 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks1Trans () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixReduceSum () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixReduceMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixReduceMin () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecToCols () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecToRows () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSymAddMat2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSymInvertPosDef () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMatBatched () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddToDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAdd2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyFromMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyFromTp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatTp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixTranspose () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddTpMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddRowSumMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddRowSumMatLarge () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddColSumMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSubMatrix () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddColSumMatLarge () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorInvertElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixInvertElements () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixIO () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddTpVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuApproxEqual () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorMulTp () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuCopy () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSigmoid () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuDiffSigmoid () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuDiffSoftmax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuDiffLogSoftmax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSoftmax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuLogSoftmax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuFindRowMaxId () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuDiffXent () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestCheck () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSwapCu2Cu () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestSwapCu2M () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestCuTanh () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuDiffTanh () |
| static int32 | DoubleFactorial (int32 i) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSetRandn () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSetRandUniform () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyLowerToUpper () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixSetZeroAboveDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixCopyUpperToLower () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixObjfDeriv () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixAddToElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixLookup () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuMatrixEqualElementMask () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatMat (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &A, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template float | TraceMatMat (const CuMatrixBase< float > &A, const CuMatrixBase< float > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template double | TraceMatMat (const CuMatrixBase< double > &A, const CuMatrixBase< double > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AddMatMatBatched (const Real alpha, std::vector< CuSubMatrix< Real > *> &C, const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< Real > *> &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< Real > *> &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const Real beta) |
| Does multiple matrix multiplications, executing them in parallel using cuBLAS's gemmBatched if we are using a GPU. More... | |
| template void | AddMatMatBatched (const float alpha, std::vector< CuSubMatrix< float > * > &C, const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< float > * > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< float > * > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const float beta) |
| template void | AddMatMatBatched (const double alpha, std::vector< CuSubMatrix< double > * > &C, const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< double > * > &A, MatrixTransposeType transA, const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< double > * > &B, MatrixTransposeType transB, const double beta) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &mat) |
| Print the matrix to stream. More... | |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuMatrixBase< float > &mat) |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuMatrixBase< double > &mat) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ApproxEqual (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &A, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &B, Real tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AssertEqual (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &A, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &B, float tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | SameDim (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &M, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &N) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | SameDimAndStride (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &M, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &N) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &A, const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const PackedMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertDiagEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &B, float value, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertDiagEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const PackedMatrix< Real > &B, float value, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static bool | ApproxEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const PackedMatrix< Real > &B, Real tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixConstructor () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixCopy () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixTrace () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixScale () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixScaleDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixAddToDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuPackedMatrixSetUnit () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaPackedMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &mat) |
| Print the matrix to stream. More... | |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuPackedMatrix< float > &mat) |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuPackedMatrix< double > &mat) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::string | ToString (const T &t) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::string | MeanVariance (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &m) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::string | MeanVariance (const CuVectorBase< Real > &v) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuRandUniformMatrixSpeedTest (const int32 iter) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuRandUniformMatrixBaseSpeedTest (const int32 iter) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuRandGaussianMatrixSpeedTest (const int32 iter) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuRandGaussianMatrixBaseSpeedTest (const int32 iter) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuRandUniformVectorSpeedTest (const int32 iter) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuRandGaussianVectorSpeedTest (const int32 iter) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixInvert (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixCopyFromMat (int32 dim, SpCopyType copy_type) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuSpMatrixSpeedTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixConstructor () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixApproxEqual () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixOperator () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddToDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixCopyFromMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddVec2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddMat2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddSp () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixTraceSpSp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixSetUnit () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixIO () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddSp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaSpMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| void | CudaSpMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| Real | TraceSpSp (const CuSpMatrix< Real > &A, const CuSpMatrix< OtherReal > &B) |
| C++ templatd wrapper of ANSI-C CUBLAS function GEMM (matrix multiply) More... | |
| template float | TraceSpSp (const CuSpMatrix< float > &A, const CuSpMatrix< float > &B) |
| template float | TraceSpSp (const CuSpMatrix< float > &A, const CuSpMatrix< double > &B) |
| template double | TraceSpSp (const CuSpMatrix< double > &A, const CuSpMatrix< float > &B) |
| template double | TraceSpSp (const CuSpMatrix< double > &A, const CuSpMatrix< double > &B) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ApproxEqual (const CuSpMatrix< Real > &A, const CuSpMatrix< Real > &B, Real tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AssertEqual (const CuSpMatrix< Real > &A, const CuSpMatrix< Real > &B, Real tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixConstructFromIndexes () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSelectRowsAndTranspose () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSum () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixCopyToSmat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSwap () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaSparseMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatSmat (const CuMatrixBase< Real > &A, const CuSparseMatrix< Real > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template float | TraceMatSmat (const CuMatrixBase< float > &A, const CuSparseMatrix< float > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template double | TraceMatSmat (const CuMatrixBase< double > &A, const CuSparseMatrix< double > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | InitRand (SpMatrix< Real > *M) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | InitRand (VectorBase< Real > *v) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestSetZeroAboveDiag () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCholesky () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestTrace () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestConstructor () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopySp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCopyFromMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMatrix () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestMulTp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestVector () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | CuMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &A, const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const PackedMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const PackedMatrix< Real > &A, const CuPackedMatrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuTpMatrixInvert () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuTpMatrixCopyFromTp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuTpMatrixCopyFromMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuTpMatrixCholesky () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuTpMatrixIO () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaTpMatrixUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorSoftmax (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorSum (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| void | TestCuVectorCopyFromVec (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorVecVecOne (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorAddDiagMatMat (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType transN, MatrixTransposeType transO) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorAddDiagMat2OnVariousShapes (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorAddDiagMat2 (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorAddRowSumMat (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorAddColSumMat (int32 dim, MatrixTransposeType trans) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorApplyFloor (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorApplyFloorNoCount (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorApplyCeiling (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorApplyCeilingNoCount (int32 dim) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | TestCuVectorAddDiagMatMatShape (int32 num_rows, int32 num_cols, MatrixTransposeType transM, MatrixTransposeType transN) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CudaVectorSpeedTest () |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorIO () |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorCopyFromVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuSubVector () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorMulTp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorAddTp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestVecVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddVecCross () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddVecExtra () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestCopyElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | UnitTestVecMatVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddRowSumMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddColSumMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApproxEqual () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorReplaceValue () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | UnitTestCuVectorSum () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestInvertElements () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestSum () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestScale () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestCopyFromMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromPacked () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestNorm () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestMin () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplySoftMax () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyExp () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyLog () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloor () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloorNoCount () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeiling () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeilingNoCount () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestApplyPow () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddVecVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMat2 () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| static void | CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMatMat () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddMatVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTestAddSpVec () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | CuVectorUnitTest () |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | VecVec (const CuVectorBase< Real > &a, const CuVectorBase< Real > &b) |
| template float | VecVec (const CuVectorBase< float > &a, const CuVectorBase< float > &b) |
| template double | VecVec (const CuVectorBase< double > &a, const CuVectorBase< double > &b) |
| template<typename Real , typename OtherReal > | |
| Real | VecVec (const CuVectorBase< Real > &A, const CuVectorBase< OtherReal > &B) |
| template float | VecVec (const CuVectorBase< float > &A, const CuVectorBase< double > &B) |
| template double | VecVec (const CuVectorBase< double > &A, const CuVectorBase< float > &B) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | VecMatVec (const CuVectorBase< Real > &v1, const CuMatrixBase< Real > &M, const CuVectorBase< Real > &v2) |
Returns 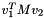 . More... . More... | |
| template float | VecMatVec (const CuVectorBase< float > &v1, const CuMatrixBase< float > &M, const CuVectorBase< float > &v2) |
| template double | VecMatVec (const CuVectorBase< double > &v1, const CuMatrixBase< double > &M, const CuVectorBase< double > &v2) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuVectorBase< Real > &vec) |
| Print the vector to stream. More... | |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuVectorBase< float > &vec) |
| template std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const CuVectorBase< double > &vec) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| bool | ApproxEqual (const CuVectorBase< Real > &a, const CuVectorBase< Real > &b, Real tol=0.01) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| void | AssertEqual (const CuVectorBase< Real > &a, const CuVectorBase< Real > &b, Real tol=0.01) |
| void | GetSeenPhones (BuildTreeStatsType &stats, int P, std::vector< int32 > *phones_out) |
| void | AddToCount (int32 location_to_add, double value_to_add, std::vector< double > *counts) |
| void | AddToConfusionMatrix (int32 phone1, int32 phone2, Matrix< double > *counts) |
| void | WriteAsKaldiVector (const std::vector< double > &counts, std::string &wxfilename, bool binary) |
| int32 | ProcessTopo (const HmmTopology &topo, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &questions) |
| void | FrameLevelLpp (const SubVector< BaseFloat > &prob_row, const std::vector< std::set< int32 > > &pdf2phones, const std::vector< int32 > *phone_map, Vector< BaseFloat > *out_frame_level_lpp) |
| FrameLevelLpp compute a log posterior for pure-phones by sum the posterior of the states belonging to those triphones whose current phone is the canonical phone: More... | |
| void | GetEditsSingleHyp (const std::string &hyp_rspecifier, const std::string &ref_rspecifier, const std::string &mode, std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > &edit_word_per_hyp) |
| void | GetEditsDualHyp (const std::string &hyp_rspecifier, const std::string &hyp_rspecifier2, const std::string &ref_rspecifier, const std::string &mode, std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > &edit_word_per_hyp, std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > &edit_word_per_hyp2) |
| void | GetBootstrapWERInterval (const std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > &edit_word_per_hyp, int32 replications, BaseFloat *mean, BaseFloat *interval) |
| void | GetBootstrapWERTwoSystemComparison (const std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > &edit_word_per_hyp, const std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > &edit_word_per_hyp2, int32 replications, BaseFloat *p_improv) |
| void | ApplySoftMaxPerRow (MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| int32 | TypeOneUsage (const ParseOptions &po, BaseFloat scale1, BaseFloat scale2) |
| int32 | TypeOneUsageAverage (const ParseOptions &po) |
| int32 | TypeTwoUsage (const ParseOptions &po, bool binary) |
| int32 | TypeThreeUsage (const ParseOptions &po, bool binary, bool average) |
| int32 | TypeOneUsage (const ParseOptions &po) |
| int32 | TypeTwoUsage (const ParseOptions &po, bool binary, bool average=false) |
| int32 | TypeThreeUsage (const ParseOptions &po, bool binary) |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const GaussPost &gpost, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmDiagGmm &am_gmm, FmllrDiagGmmAccs *spk_stats) |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const Posterior &post, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmDiagGmm &am_gmm, FmllrDiagGmmAccs *spk_stats) |
| fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > * | ReadNetwork (std::string filename) |
| void | AccStatsForUtterance (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmDiagGmm &am_gmm, const GaussPost &gpost, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, FmllrRawAccs *accs) |
| void | AccStatsForUtterance (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmDiagGmm &am_gmm, const Posterior &post, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, FmllrRawAccs *accs) |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const GaussPost &gpost, const AmDiagGmm &am_gmm, FmllrDiagGmmAccs *spk_stats) |
| bool | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const DiagGmm &gmm, const std::string &key, RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReader *weights_reader, RandomAccessInt32VectorVectorReader *gselect_reader, AccumFullGmm *fullcov_stats) |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const Posterior &post, const DiagGmm &gmm, FmllrDiagGmmAccs *spk_stats) |
| void | InitGmmFromRandomFrames (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, DiagGmm *gmm) |
| void | TrainOneIter (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const MleDiagGmmOptions &gmm_opts, int32 iter, int32 num_threads, DiagGmm *gmm) |
| void | ReadSharedPhonesList (std::string rxfilename, std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > *list_out) |
| EventMap * | GetFullBiphoneStubMap (const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > &phone2num_pdf_classes, const std::vector< int32 > &ci_phones_list, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &bi_counts, int32 biphone_min_count, const std::vector< int32 > &mono_counts, int32 mono_min_count) |
| ContextDependency * | BiphoneContextDependencyFull (std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > phone_sets, const std::vector< int32 > phone2num_pdf_classes, const std::vector< int32 > &ci_phones_list, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &bi_counts, int32 biphone_min_count, const std::vector< int32 > &mono_counts, int32 mono_min_count) |
| void | GetFeatureMeanAndVariance (const std::string &feat_rspecifier, Vector< BaseFloat > *inv_var_out, Vector< BaseFloat > *mean_out) |
| void | InitAmGmm (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, const EventMap &to_pdf_map, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm, const TransitionModel &trans_model, BaseFloat var_floor) |
| InitAmGmm initializes the GMM with one Gaussian per state. More... | |
| void | GetOccs (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, const EventMap &to_pdf_map, Vector< BaseFloat > *occs) |
| Get state occupation counts. More... | |
| void | InitAmGmmFromOld (const BuildTreeStatsType &stats, const EventMap &to_pdf_map, int32 N, int32 P, const std::string &old_tree_rxfilename, const std::string &old_model_rxfilename, BaseFloat var_floor, AmDiagGmm *am_gmm) |
| InitAmGmmFromOld initializes the GMM based on a previously trained model and tree, which must require no more phonetic context than the current tree. More... | |
| bool | DecodeUtterance (LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder &decoder, DecodableInterface &decodable, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, std::string utt, double acoustic_scale, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignment_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| void | MergeFullGmm (const FullGmm &src, FullGmm *dst) |
| merges GMMs by appending Gaussians in "src" to "dst". More... | |
| void | AppendPostToFeats (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &in, const Posterior &post, const int32 post_dim, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out) |
| void | AppendVectorToFeats (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &in, const Vector< BaseFloat > &vec, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out) |
| void | GetUtterancePairs (const std::string &reco2file_and_channel_rxfilename, std::vector< std::vector< std::string > > *utt_pairs) |
| void | AccCmvnStatsForPair (const std::string &utt1, const std::string &utt2, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &feats1, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &feats2, BaseFloat quieter_channel_weight, MatrixBase< double > *cmvn_stats1, MatrixBase< double > *cmvn_stats2) |
| bool | AccCmvnStatsWrapper (const std::string &utt, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &feats, RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReader *weights_reader, Matrix< double > *cmvn_stats) |
| void | ConcatFeats (const std::vector< Matrix< BaseFloat > > &in, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out) |
| void | IncreaseTransformDimension (int32 new_dimension, Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| void | LinearlyInterpolatePitch (Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| bool | AppendFeats (const std::vector< Matrix< BaseFloat > > &in, const std::string &utt, int32 tolerance, Matrix< BaseFloat > *out) |
| void | ProcessPovFeatures (Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| void | TakeLogOfPitch (Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| void | SubtractMovingAverage (int32 normalization_window_size, Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| void | SetToMovingAverage (int32 average_window_size, Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| void | ShiftFeatureMatrix (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &src, int32 shift, Matrix< BaseFloat > *rearranged) |
| void | AddVectorsOfUnequalLength (const VectorBase< BaseFloat > &signal1, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal2) |
| void | AddVectorsWithOffset (const Vector< BaseFloat > &signal1, int32 offset, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal2) |
| BaseFloat | MaxAbsolute (const Vector< BaseFloat > &vector) |
| BaseFloat | ComputeEarlyReverbEnergy (const Vector< BaseFloat > &rir, const Vector< BaseFloat > &signal, BaseFloat samp_freq) |
| float | DoReverberation (const Vector< BaseFloat > &rir, BaseFloat samp_freq, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal) |
| void | AddNoise (Vector< BaseFloat > *noise, BaseFloat snr_db, BaseFloat time, BaseFloat samp_freq, BaseFloat signal_power, Vector< BaseFloat > *signal) |
| void | ReadCommaSeparatedCommand (const std::string &s, std::vector< BaseFloat > *v) |
| bool | ReadData (SequentialBaseFloatMatrixReader &feature_reader, RandomAccessPosteriorReader &target_reader, RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReader &weights_reader, int32 length_tolerance, Matrix< BaseFloat > *feats, Posterior *targets, Vector< BaseFloat > *weights, int32 *num_no_tgt_mat, int32 *num_other_error) |
| bool | CompactLatticeNormalize (CompactLattice *clat, BaseFloat weight) |
| void | SplitStringToWeights (const string &full, const char *delim, vector< BaseFloat > *out) |
| int32 | CopySubsetLattices (std::string filename, SequentialLatticeReader *lattice_reader, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, bool include=true, bool ignore_missing=false, bool sorted=false) |
| int32 | CopySubsetLattices (std::string filename, SequentialCompactLatticeReader *lattice_reader, CompactLatticeWriter *lattice_writer, bool include=true, bool ignore_missing=false, bool sorted=false) |
| bool | DeterminizeLatticeWrapper (const Lattice &lat, const std::string &key, bool prune, BaseFloat beam, BaseFloat beam_ratio, int32 max_mem, int32 max_loop, BaseFloat delta, int32 num_loops, CompactLattice *clat) |
| void | ReadSymbolList (const std::string &rxfilename, fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, LabelPairVector *lpairs) |
| void | ConvertLatticeToUnweightedAcceptor (const kaldi::Lattice &ilat, const LabelPairVector &wildcards, fst::StdVectorFst *ofst) |
| void | CreateEditDistance (const fst::StdVectorFst &fst1, const fst::StdVectorFst &fst2, fst::StdVectorFst *pfst) |
| void | CountErrors (const fst::StdVectorFst &fst, int32 *correct, int32 *substitutions, int32 *insertions, int32 *deletions, int32 *num_words) |
| bool | CheckFst (const fst::StdVectorFst &fst, string name, string key) |
| void | LatticeAcousticRescore (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &log_likes, const std::vector< int32 > &state_times, Lattice *lat) |
| void | MakeLatticeFromLinear (const std::vector< int32 > &ali, const std::vector< int32 > &words, BaseFloat lm_cost, BaseFloat ac_cost, Lattice *lat_out) |
| static float | _RandGauss () |
| void | ComputeFeatureNormalizingTransform (const FullGmm &gmm, Matrix< BaseFloat > *xform) |
| Computes the inverse of an LDA transform (without dimensionality reduction) The computed transform is used in initializing the phonetic and speaker subspaces, as well as while increasing the dimensions of those spaces. More... | |
| static void | ApplyPreXformToGradient (const Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams &globals, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &gradient_in, Matrix< BaseFloat > *gradient_out) |
| static void | ApplyInvPreXformToChange (const Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams &globals, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &delta_in, Matrix< BaseFloat > *delta_out) |
| static void | ApplyHessianXformToGradient (const Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams &globals, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &gradient_in, Matrix< BaseFloat > *gradient_out) |
| static void | ApplyInvHessianXformToChange (const Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams &globals, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &delta_in, Matrix< BaseFloat > *delta_out) |
| static BaseFloat | CalcFmllrStepSize (const AffineXformStats &stats, const AmSgmm2 &sgmm, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &Delta, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &A, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &G, int32 max_iters) |
| void | EstimateSgmm2FmllrSubspace (const SpMatrix< double > &fmllr_grad_scatter, int32 num_fmllr_bases, int32 feat_dim, Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams *fmllr_globals, double min_eig=0.0) |
| Computes the fMLLR basis matrices given the scatter of the vectorized gradients (eq: B.10). More... | |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &transformed_feats, const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > &gselect, const Posterior &post, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmSgmm2 &am_sgmm, BaseFloat logdet, Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars *spk_vars, FmllrSgmm2Accs *spk_stats) |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const Sgmm2GauPost &gpost, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmSgmm2 &am_sgmm, Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars *spk_vars, MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs *spk_stats) |
| void | AccumulateForUtterance (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const Posterior &post, const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AmSgmm2 &am_sgmm, const vector< vector< int32 > > &gselect, Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars *spk_vars, MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs *spk_stats) |
| void | ProcessUtterance (const AmSgmm2 &am_sgmm, const TransitionModel &trans_model, double log_prune, double acoustic_scale, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &features, RandomAccessInt32VectorVectorReader &gselect_reader, RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReaderMapped &spkvecs_reader, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, const std::string &utt, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignments_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, LatticeFasterDecoder *decoder, double *like_sum, int64 *frame_sum, int32 *num_done, int32 *num_err, TaskSequencer< DecodeUtteranceLatticeFasterClass > *sequencer) |
| bool | ProcessUtterance (LatticeFasterDecoder &decoder, const AmSgmm2 &am_sgmm, const TransitionModel &trans_model, double log_prune, double acoustic_scale, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &features, RandomAccessInt32VectorVectorReader &gselect_reader, RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReaderMapped &spkvecs_reader, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, const std::string &utt, bool determinize, bool allow_partial, Int32VectorWriter *alignments_writer, Int32VectorWriter *words_writer, CompactLatticeWriter *compact_lattice_writer, LatticeWriter *lattice_writer, double *like_ptr) |
| void | GetWeights (const std::string &weights_str, int32 num_inputs, std::vector< BaseFloat > *weights) |
| std::vector< bool > | GetSkipLayers (const std::string &skip_layers_str, const int32 first_layer_idx, const int32 last_layer_idx) |
| bool | SplitEgsKey (const std::string &key, std::string *utt_id, int32 *frame_id) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertAffineTransformComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component, const bool use_preconditioned_affine_component) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertSoftmaxComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertSigmoidComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertSpliceComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertAddShiftComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertRescaleComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component) |
| nnet2::Component * | ConvertComponent (const nnet1::Component &nnet1_component, const bool use_preconditioned_affine_component) |
| nnet2::Nnet * | ConvertNnet1ToNnet2 (const nnet1::Nnet &nnet1, const bool use_preconditioned_affine_component) |
| void | ReadModels (std::vector< std::pair< std::string, BaseFloat > > models_and_weights, nnet3::Nnet *output_nnet, int32 *success) |
| int32 | GetCount (double expected_count) |
| void | SplitArgOnEquals (const std::string &arg, std::string *name, std::string *rspecifier) |
| void | HandleOutput (bool determinize, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, nnet3::NnetBatchDecoder *decoder, CompactLatticeWriter *clat_writer, LatticeWriter *lat_writer) |
| bool | CompareInterval (const Interval &i1, const Interval &i2) |
| bool | ClusterLattice (CompactLattice *clat, const std::vector< int32 > &state_times) |
| bool | CreateFactorTransducer (const CompactLattice &clat, const std::vector< int32 > &state_times, int32 utterance_id, KwsProductFst *factor_transducer) |
| void | RemoveLongSilences (int32 max_silence_frames, const std::vector< int32 > &state_times, KwsProductFst *factor_transducer) |
| template<class Arc > | |
| static void | DifferenceWrapper (const fst::VectorFst< Arc > &fst1, const fst::VectorFst< Arc > &fst2, fst::VectorFst< Arc > *difference) |
| void | MaybeDoSanityCheck (const KwsLexicographicFst &index_transducer) |
| void | MaybeDoSanityCheck (const KwsProductFst &product_transducer) |
| void | DoFactorMerging (KwsProductFst *factor_transducer, KwsLexicographicFst *index_transducer) |
| void | DoFactorDisambiguation (KwsLexicographicFst *index_transducer) |
| void | OptimizeFactorTransducer (KwsLexicographicFst *index_transducer, int32 max_states, bool allow_partial) |
| template<class Arc > | |
| static void | ReplaceSymbolWithEpsilon (typename Arc::Label symbol, fst::VectorFst< Arc > *fst) |
| uint64 | EncodeLabel (StateId ilabel, StateId olabel) |
| StateId | DecodeLabelUid (uint64 osymbol) |
| bool | GenerateActivePaths (const KwsLexicographicFst &proxy, std::vector< ActivePath > *paths, KwsLexicographicFst::StateId cur_state, std::vector< KwsLexicographicArc::Label > cur_path, KwsLexicographicArc::Weight cur_weight) |
| void | SetLinearAcceptorWeight (double cost, fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > *fst) |
| void | AgglomerativeCluster (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &costs, BaseFloat threshold, int32 min_clusters, int32 first_pass_max_points, BaseFloat max_cluster_fraction, std::vector< int32 > *assignments_out) |
| This is the function that is called to perform the agglomerative clustering. More... | |
| void | TestIvectorExtractorIO (const IvectorExtractor &extractor) |
| void | TestIvectorExtractorStatsIO (IvectorExtractorStats &stats) |
| void | TestIvectorExtraction (const IvectorExtractor &extractor, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &feats, const FullGmm &fgmm) |
| void | UnitTestIvectorExtractor () |
| static double | GetLogDetNoFailure (const SpMatrix< double > &var) |
| static void | ConvertPostToGaussInfo (const std::vector< std::vector< std::pair< int32, BaseFloat > > > &gauss_post, std::unordered_map< int32, GaussInfo > *gauss_info) |
| double | EstimateIvectorsOnline (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &feats, const Posterior &post, const IvectorExtractor &extractor, int32 ivector_period, int32 num_cg_iters, BaseFloat max_count, Matrix< BaseFloat > *ivectors) |
| void | UnitTestPosteriors () |
| void | UnitTestTrain () |
| void | UnitTestPldaEstimation (int32 dim) |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | ComputeNormalizingTransform (const SpMatrix< Real > &covar, MatrixBase< Real > *proj) |
| This function computes a projection matrix that when applied makes the covariance unit (i.e. More... | |
| void | ComputeVadEnergy (const VadEnergyOptions &opts, const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > &input_features, Vector< BaseFloat > *output_voiced) |
| Compute voice-activity vector for a file: 1 if we judge the frame as voiced, 0 otherwise. More... | |
| BaseFloat | ComputeEer (std::vector< BaseFloat > *target_scores, std::vector< BaseFloat > *nontarget_scores, BaseFloat *threshold) |
| ComputeEer computes the Equal Error Rate (EER) for the given scores and returns it as a proportion beween 0 and 1. More... | |
| void | PrepareMap (const std::string &map_rxfilename, int32 num_classes, unordered_map< int32, int32 > *map) |
| PrepareMap creates a map that specifies the mapping between the input and output class labels. More... | |
| void | PreparePriors (const std::string &priors_str, int32 num_classes, std::vector< BaseFloat > *priors) |
| PreparePriors creates a table specifying the priors for each class. More... | |
| template<class Real > | |
| void | ComputeNormalizingTransform (const SpMatrix< Real > &covar, Real floor, MatrixBase< Real > *proj) |
| void | ComputeLdaTransform (const std::map< std::string, Vector< BaseFloat > *> &utt2ivector, const std::map< std::string, std::vector< std::string > > &spk2utt, BaseFloat total_covariance_factor, BaseFloat covariance_floor, MatrixBase< BaseFloat > *lda_out) |
| void | ComputeAndSubtractMean (std::map< std::string, Vector< BaseFloat > *> utt2ivector, Vector< BaseFloat > *mean_out) |
| int32 | RunPerSpeaker (const std::string &ivector_extractor_rxfilename, const IvectorEstimationOptions &opts, bool compute_objf_change, const std::string &spk2utt_rspecifier, const std::string &feature_rspecifier, const std::string &posterior_rspecifier, const std::string &ivector_wspecifier) |
| bool | EstPca (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &ivector_mat, BaseFloat target_energy, const std::string &reco, Matrix< BaseFloat > *mat) |
| void | TransformIvectors (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &ivectors_in, const PldaConfig &plda_config, const Plda &plda, Matrix< BaseFloat > *ivectors_out) |
| void | ApplyPca (const Matrix< BaseFloat > &ivectors_in, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &pca_mat, Matrix< BaseFloat > *ivectors_out) |
| void | PrepareMap (const std::string map_rxfilename, unordered_map< std::pair< int32, int32 >, int32, PairHasher< int32 > > *map) |
| PrepareMap creates a mapping between the pairs of VAD decisions and the output label. More... | |
| int | PaCallback (const void *input, void *output, long unsigned frame_count, const PaStreamCallbackTimeInfo *time_info, PaStreamCallbackFlags status_flags, void *user_data) |
| template<class Real > | |
| static void | AssertEqual (const Matrix< Real > &A, const Matrix< Real > &B, float tol=0.001) |
| void | GetOutput (OnlineFeatInputItf *a, Matrix< BaseFloat > *output) |
| void | TestOnlineMatrixInput () |
| void | TestOnlineFeatureMatrix () |
| void | TestOnlineLdaInput () |
| void | TestOnlineDeltaInput () |
| void | TestOnlineCmnInput () |
| fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > * | ReadDecodeGraph (const std::string &filename) |
| void | PrintPartialResult (const std::vector< int32 > &words, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, bool line_break) |
| bool | WriteFull (int32 desc, char *data, int32 size) |
| bool | ReadLine (int32 desc, std::string *str) |
| std::string | TimeToTimecode (float time) |
| bool | WriteLine (int32 socket, std::string line) |
| void | SendPartialResult (const std::vector< int32 > &words, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, const bool line_break, const int32 serv_sock, const sockaddr_in &client_addr) |
| static bool | RuleActivated (const OnlineEndpointRule &rule, const std::string &rule_name, BaseFloat trailing_silence, BaseFloat relative_cost, BaseFloat utterance_length) |
| bool | EndpointDetected (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, int32 num_frames_decoded, int32 trailing_silence_frames, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, BaseFloat final_relative_cost) |
| This function returns true if this set of endpointing rules thinks we should terminate decoding. More... | |
| template<typename FST , typename DEC > | |
| int32 | TrailingSilenceLength (const TransitionModel &tmodel, const std::string &silence_phones, const DEC &decoder) |
| returns the number of frames of trailing silence in the best-path traceback (not using final-probs). More... | |
| template<typename FST > | |
| bool | EndpointDetected (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< FST > &decoder) |
| This is a higher-level convenience function that works out the arguments to the EndpointDetected function above, from the decoder. More... | |
| template<typename FST > | |
| bool | EndpointDetected (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< FST > &decoder) |
| This is a higher-level convenience function that works out the arguments to the EndpointDetected function above, from the decoder. More... | |
| template bool | EndpointDetected< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > &decoder) |
| template bool | EndpointDetected< fst::GrammarFst > (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > &decoder) |
| template bool | EndpointDetected< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > &decoder) |
| template bool | EndpointDetected< fst::GrammarFst > (const OnlineEndpointConfig &config, const TransitionModel &tmodel, BaseFloat frame_shift_in_seconds, const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > &decoder) |
| template void | OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > (const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > &decoder) |
| template void | OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::GrammarFst > (const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > &decoder) |
| template void | OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > (const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > &decoder) |
| template void | OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::GrammarFst > (const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > &decoder) |
| void | FindQuietestSegment (const Vector< BaseFloat > &wav_in, BaseFloat samp_rate, Vector< BaseFloat > *wav_sil, BaseFloat search_dur=0.5, BaseFloat seg_dur=0.1, BaseFloat seg_shift_dur=0.05) |
| void | ExtendWaveWithSilence (const Vector< BaseFloat > &wav_in, BaseFloat samp_rate, Vector< BaseFloat > *wav_out, BaseFloat sil_search_len, BaseFloat sil_extract_len, BaseFloat sil_extract_shift) |
| std::string | LatticeToString (const Lattice &lat, const fst::SymbolTable &word_syms) |
| std::string | GetTimeString (int32 t_beg, int32 t_end, BaseFloat time_unit) |
| int32 | GetLatticeTimeSpan (const Lattice &lat) |
| std::string | LatticeToString (const CompactLattice &clat, const fst::SymbolTable &word_syms) |
| void | GetDiagnosticsAndPrintOutput (const std::string &utt, const fst::SymbolTable *word_syms, const CompactLattice &clat, int64 *tot_num_frames, double *tot_like) |
| template<typename Real > | |
| Real | TraceMatMat (const MatrixBase< Real > &A, const MatrixBase< Real > &B, MatrixTransposeType trans=kNoTrans) |
| We need to declare this here as it will be a friend function. More... | |
| void | AccumulateTreeStats (const TransitionModel &trans_model, const AccumulateTreeStatsInfo &info, const std::vector< int32 > &alignment, const Matrix< BaseFloat > &features, std::map< EventType, GaussClusterable * > *stats) |
| Accumulates the stats needed for training context-dependency trees (in the "normal" way). More... | |
| void | ReadPhoneMap (std::string phone_map_rxfilename, std::vector< int32 > *phone_map) |
Variables | |
| int32 | g_kaldi_verbose_level = 0 |
| This is set by util/parse-options. More... | |
| static std::string | program_name |
| static LogHandler | log_handler = NULL |
| static std::mutex | _RandMutex |
| static const double | kMinLogDiffDouble = Log(DBL_EPSILON) |
| static const float | kMinLogDiffFloat = Log(FLT_EPSILON) |
| const float | kLogZeroFloat = -std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity() |
| const double | kLogZeroDouble = -std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity() |
| const BaseFloat | kLogZeroBaseFloat = -std::numeric_limits<BaseFloat>::infinity() |
| ProfileStats | g_profile_stats |
| int32 | g_num_threads = 8 |
| static ShellType | kShellType = kBash |
| const char * | ws_delim = " \t\n\r" |
| bool | pitch_use_naive_search = false |
| const BaseFloat | kWaveSampleMax = 32768.0 |
| For historical reasons, we scale waveforms to the range (2^15-1)*[-1, 1], not the usual default DSP range [-1, 1]. More... | |
| static const EventKeyType | kPdfClass = -1 |
| const int32 | kMaxVal = 20 |
| static const int32 | kNoPdf = -1 |
| A constant used in the HmmTopology class as the pdf-class kNoPdf, which is used when a HMM-state is nonemitting (has no associated PDF). More... | |
| static const int | kRandomSentences = 50 |
| const int | kTemporaryEpsilon = -2 |
| const int | kNumStatesOffset = 1000 |
| CuAllocatorOptions | g_allocator_options |
| int32 | buffer_offset = 0 |
| int32 | buffer_fill = 0 |
| char | read_buffer [1025] |
| const float | kFramesPerSecond = 100.0f |
This code computes Goodness of Pronunciation (GOP) and extracts phone-level pronunciation feature for mispronunciations detection tasks, the reference:
Relabels neural network egs with the read pdf-id alignments.
"Improved mispronunciation detection with deep neural network trained acoustic models and transfer learning based logistic regression classifiers" by Hu et al., Speech Comunication, 2015.
GOP is widely used to detect mispronunciations. The DNN-based GOP was defined as the log phone posterior ratio between the canonical phone and the one with the highest score.
To compute GOP, we need to compute Log Phone Posterior (LPP): LPP(p) = p(p| o; t_s,t_e) where { o} is the input observations, p is the canonical phone, {t_s, t_e} are the start and end frame indexes.
LPP could be calculated as the average of the frame-level LPP, i.e. p(p|o_t): LPP(p) = {1}{t_e-t_s+1} {t=t_s}^{t_e} p(p|o_t) p(p|o_t) = {s p} p(s|o_t) where s is the senone label, {s|s p} is the states belonging to those triphones whose current phone is p.
GOP is extracted from LPP: GOP(p) = {LPP(p)}{{q Q} LPP(q)}
An array of a phone-level feature for each phone is extracted as well, which could be used to train a classifier to detect mispronunciations. Normally the classifier-based approach archives better performance than the GOP-based approach.
The phone-level feature is defined as: {[LPP(p_1),,LPP(p_M), LPR(p_1|p_i), , LPR(p_j|p_i),]}^T
where the Log Posterior Ratio (LPR) between phone p_j and p_i is defined as: LPR(p_j|p_i) = p(p_j| o; t_s, t_e) - p(p_i| o; t_s, t_e)
| typedef KwsLexicographicArc Arc |
Definition at line 35 of file lattice-determinize-non-compact.cc.
Definition at line 29 of file kaldi-types.h.
| typedef fst::VectorFst<CompactLatticeArc> CompactLattice |
Definition at line 46 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
| typedef fst::ArcTpl<CompactLatticeWeight> CompactLatticeArc |
Definition at line 42 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 35 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
| typedef fst::CompactLatticeWeightCommonDivisorTpl<LatticeWeight, int32> CompactLatticeWeightCommonDivisor |
Definition at line 38 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 149 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
| typedef double double64 |
Definition at line 54 of file kaldi-types.h.
| typedef int32 EventAnswerType |
As far as the event-map code itself is concerned, things of type EventAnswerType may take any value except kNoAnswer (== -1).
However, some specific uses of EventMap (e.g. in build-tree-utils.h) assume these quantities are nonnegative.
Definition at line 56 of file event-map.h.
| typedef int32 EventKeyType |
Things of type EventKeyType can take any value.
The code does not assume they are contiguous. So values like -1, 1000000 and the like are acceptable.
Definition at line 45 of file event-map.h.
| typedef std::vector<std::pair<EventKeyType, EventValueType> > EventType |
Definition at line 58 of file event-map.h.
| typedef int32 EventValueType |
Given current code, things of type EventValueType should generally be nonnegative and in a reasonably small range (e.g.
not one million), as we sometimes construct vectors of the size: [largest value we saw for this key]. This deficiency may be fixed in future [would require modifying TableEventMap]
Definition at line 51 of file event-map.h.
Definition at line 53 of file kaldi-types.h.
| typedef uint16 GmmFlagsType |
Bitwise OR of the above flags.
Definition at line 35 of file model-common.h.
| typedef kaldi::int32 int32 |
Definition at line 27 of file online-tcp-source.cc.
| typedef int16 int_smaller |
Definition at line 33 of file cluster-utils.cc.
| typedef StdLStdLStdArc KwsLexicographicArc |
Definition at line 45 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::VectorFst<KwsLexicographicArc> KwsLexicographicFst |
Definition at line 46 of file kaldi-kws.h.
Definition at line 44 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef LogXStdXStdprimeArc KwsProductArc |
Definition at line 48 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::VectorFst<KwsProductArc> KwsProductFst |
Definition at line 49 of file kaldi-kws.h.
Definition at line 47 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::StdArc::Label Label |
Definition at line 32 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
| typedef std::vector<std::pair<Label, Label> > LabelPairVector |
Definition at line 33 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
| typedef fst::VectorFst<LatticeArc> Lattice |
Definition at line 44 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
| typedef fst::ArcTpl<LatticeWeight> LatticeArc |
Definition at line 40 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 37 of file lattice-biglm-faster-decoder.h.
| typedef LatticeFasterDecoderTpl<fst::StdFst, decoder::StdToken> LatticeFasterDecoder |
Definition at line 522 of file lattice-faster-decoder.h.
| typedef LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl<fst::StdFst> LatticeFasterOnlineDecoder |
Definition at line 142 of file lattice-faster-online-decoder.h.
| typedef LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl<fst::StdFst, decoder::StdToken> LatticeIncrementalDecoder |
Definition at line 724 of file lattice-incremental-decoder.h.
| typedef LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl<fst::StdFst> LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoder |
Definition at line 127 of file lattice-incremental-online-decoder.h.
| typedef fst::LatticeWeightTpl<BaseFloat> LatticeWeight |
Definition at line 32 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
| typedef TableWriter<LatticeHolder> LatticeWriter |
Definition at line 145 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
| typedef fst::ArcTpl<LogXStdXStdprimeWeight> LogXStdXStdprimeArc |
Definition at line 41 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::ProductWeight<LogWeight, StdXStdprimeWeight> LogXStdXStdprimeWeight |
Definition at line 40 of file kaldi-kws.h.
Definition at line 133 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef TableWriter< KaldiObjectHolder<AmDiagGmm> > MapAmDiagGmmWriter |
Definition at line 130 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef int32 MatrixIndexT |
Definition at line 98 of file matrix-common.h.
| typedef basic_pipebuf<char> PipebufType |
Definition at line 55 of file kaldi-io.cc.
Definition at line 151 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 147 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 131 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< KaldiObjectHolder<AmDiagGmm> > RandomAccessMapAmDiagGmmReaderMapped |
Definition at line 132 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef RandomAccessTableReader< KaldiObjectHolder<RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm> > RandomAccessRegtreeFmllrDiagGmmReader |
Definition at line 138 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< KaldiObjectHolder<RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm> > RandomAccessRegtreeFmllrDiagGmmReaderMapped |
Definition at line 140 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef RandomAccessTableReader< KaldiObjectHolder<RegtreeMllrDiagGmm> > RandomAccessRegtreeMllrDiagGmmReader |
Definition at line 156 of file regtree-mllr-diag-gmm.h.
| typedef RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< KaldiObjectHolder<RegtreeMllrDiagGmm> > RandomAccessRegtreeMllrDiagGmmReaderMapped |
Definition at line 158 of file regtree-mllr-diag-gmm.h.
Definition at line 579 of file am-sgmm2.h.
| typedef SequentialTableReader< KaldiObjectHolder<RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm> > RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmSeqReader |
Definition at line 141 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm.h.
Definition at line 136 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm.h.
Definition at line 160 of file regtree-mllr-diag-gmm.h.
Definition at line 154 of file regtree-mllr-diag-gmm.h.
Definition at line 150 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 146 of file kaldi-lattice.h.
Definition at line 580 of file am-sgmm2.h.
Definition at line 578 of file am-sgmm2.h.
Definition at line 581 of file am-sgmm2.h.
| typedef uint16 SgmmUpdateFlagsType |
Bitwise OR of the above flags.
Definition at line 59 of file model-common.h.
| typedef uint16 SgmmWriteFlagsType |
Bitwise OR of the above flags.
Definition at line 70 of file model-common.h.
| typedef int32 SignedMatrixIndexT |
Definition at line 99 of file matrix-common.h.
| typedef Arc::StateId StateId |
Definition at line 34 of file lattice-determinize-non-compact.cc.
| typedef fst::ArcTpl<StdLStdLStdWeight> StdLStdLStdArc |
Definition at line 36 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::LexicographicWeight<TropicalWeight, StdLStdWeight> StdLStdLStdWeight |
Definition at line 35 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::LexicographicWeight<TropicalWeight, TropicalWeight> StdLStdWeight |
Definition at line 34 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef fst::ProductWeight<TropicalWeight, ArcticWeight> StdXStdprimeWeight |
Definition at line 39 of file kaldi-kws.h.
| typedef uint16 uint_smaller |
Definition at line 32 of file cluster-utils.cc.
| typedef uint32 UnsignedMatrixIndexT |
Definition at line 100 of file matrix-common.h.
| typedef Arc::Weight Weight |
Definition at line 31 of file kws-search.cc.
| anonymous enum |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kEps | |
| kDisambig | |
| kBos | |
| kEos | |
Definition at line 33 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
| enum cova_type |
Generate features for a certain covariance type covariance_type == 0: full covariance covariance_type == 1: diagonal covariance.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| full | |
| diag | |
Definition at line 58 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kCompressedMatrixInt8 | |
| kCompressedMatrixUint8 | |
| kCompressedMatrixInt16 | |
| kCompressedMatrixUint16 | |
Definition at line 140 of file cu-compressed-matrix.h.
| enum DetectionDecision |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kKwsFalseAlarm | |
| kKwsMiss | |
| kKwsCorr | |
| kKwsCorrUndetected | |
| kKwsUnseen | |
Definition at line 81 of file kws-scoring.h.
| enum GmmUpdateFlags |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kGmmMeans | |
| kGmmVariances | |
| kGmmWeights | |
| kGmmTransitions | |
| kGmmAll | |
Definition at line 28 of file model-common.h.
| enum MatrixResizeType |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kSetZero | |
| kUndefined | |
| kCopyData | |
Definition at line 37 of file matrix-common.h.
| enum MatrixStrideType |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kDefaultStride | |
| kStrideEqualNumCols | |
Definition at line 44 of file matrix-common.h.
| enum MatrixTransposeType |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kTrans | |
| kNoTrans | |
Definition at line 32 of file matrix-common.h.
| enum SgmmUpdateFlags |
Definition at line 47 of file model-common.h.
| enum SgmmWriteFlags |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kSgmmGlobalParams | |
| kSgmmStateParams | g |
| kSgmmNormalizers | s |
| kSgmmBackgroundGmms | n |
| kSgmmWriteAll | u |
Definition at line 62 of file model-common.h.
| enum ShellType |
| enum SpCopyType |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kTakeLower | |
| kTakeUpper | |
| kTakeMean | |
| kTakeMeanAndCheck | |
Definition at line 49 of file matrix-common.h.
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 34 of file am-sgmm2.cc.
References RandGauss().
Referenced by AmSgmm2::SplitSubstatesInGroup().
| void AccCmvnStats | ( | const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| BaseFloat | weight, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | stats | ||
| ) |
Accumulation from a single frame (weighted).
Definition at line 30 of file cmvn.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Data(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::RowData().
Referenced by AccCmvnStats(), AccCmvnStatsForPair(), AccCmvnStatsWrapper(), and main().
| void AccCmvnStats | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const VectorBase< BaseFloat > * | weights, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | stats | ||
| ) |
Accumulation from a feature file (possibly weighted– useful in excluding silence).
Definition at line 49 of file cmvn.cc.
References AccCmvnStats(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
| void kaldi::AccCmvnStatsForPair | ( | const std::string & | utt1, |
| const std::string & | utt2, | ||
| const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | feats1, | ||
| const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | feats2, | ||
| BaseFloat | quieter_channel_weight, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | cmvn_stats1, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | cmvn_stats2 | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 69 of file compute-cmvn-stats-two-channel.cc.
References AccCmvnStats(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::AccCmvnStatsWrapper | ( | const std::string & | utt, |
| const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | feats, | ||
| RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReader * | weights_reader, | ||
| Matrix< double > * | cmvn_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 28 of file compute-cmvn-stats.cc.
References AccCmvnStats(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::AccStatsForUtterance | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans_model, |
| const AmDiagGmm & | am_gmm, | ||
| const GaussPost & | gpost, | ||
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, | ||
| FmllrRawAccs * | accs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 31 of file gmm-est-fmllr-raw-gpost.cc.
References FmllrRawAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by UtteranceSplitter::ExitStatus(), IvectorExtractorStats::IvectorExtractorStats(), and main().
| void kaldi::AccStatsForUtterance | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans_model, |
| const AmDiagGmm & | am_gmm, | ||
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, | ||
| FmllrRawAccs * | accs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 31 of file gmm-est-fmllr-raw.cc.
References FmllrRawAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), ConvertPosteriorToPdfs(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
| bool kaldi::AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const DiagGmm & | gmm, | ||
| const std::string & | key, | ||
| RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReader * | weights_reader, | ||
| RandomAccessInt32VectorVectorReader * | gselect_reader, | ||
| AccumFullGmm * | fullcov_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 32 of file gmm-global-est-fmllr.cc.
References AccumFullGmm::AccumulateForComponent(), AccumFullGmm::AccumulateFromDiag(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), rnnlm::i, RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_WARN, DiagGmm::LogLikelihoodsPreselect(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value().
| void kaldi::AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const Sgmm2GauPost & | gpost, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const AmSgmm2 & | am_sgmm, | ||
| Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars * | spk_vars, | ||
| MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 33 of file sgmm2-est-spkvecs-gpost.cc.
References MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), AmSgmm2::ComputePerFrameVars(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPdf().
| void kaldi::AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const DiagGmm & | gmm, | ||
| FmllrDiagGmmAccs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 34 of file gmm-global-est-lvtln-trans.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriorsPreselect(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
| void kaldi::AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const GaussPost & | gpost, | ||
| const AmDiagGmm & | am_gmm, | ||
| FmllrDiagGmmAccs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 34 of file gmm-est-lvtln-trans.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
| void AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const GaussPost & | gpost, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const AmDiagGmm & | am_gmm, | ||
| FmllrDiagGmmAccs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file gmm-basis-fmllr-accs-gpost.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by main().
| void AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const AmDiagGmm & | am_gmm, | ||
| FmllrDiagGmmAccs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file gmm-basis-fmllr-accs.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), ConvertPosteriorToPdfs(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
| void kaldi::AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | transformed_feats, | ||
| const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | gselect, | ||
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const AmSgmm2 & | am_sgmm, | ||
| BaseFloat | logdet, | ||
| Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars * | spk_vars, | ||
| FmllrSgmm2Accs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file sgmm2-est-fmllr.cc.
References FmllrSgmm2Accs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), AmSgmm2::ComponentPosteriors(), AmSgmm2::ComputePerFrameVars(), ConvertPosteriorToPdfs(), rnnlm::j, MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Scale().
| void kaldi::AccumulateForUtterance | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const AmSgmm2 & | am_sgmm, | ||
| const vector< vector< int32 > > & | gselect, | ||
| Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars * | spk_vars, | ||
| MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs * | spk_stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 36 of file sgmm2-est-spkvecs.cc.
References MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs::Accumulate(), AmSgmm2::ComputePerFrameVars(), ConvertPosteriorToPdfs(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
| void AccumulateTreeStats | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans_model, |
| const AccumulateTreeStatsInfo & | info, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | alignment, | ||
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | features, | ||
| std::map< EventType, GaussClusterable * > * | stats | ||
| ) |
Accumulates the stats needed for training context-dependency trees (in the "normal" way).
It adds to 'stats' the stats obtained from this file. Any new GaussClusterable* pointers in "stats" will be allocated with "new".
Definition at line 36 of file tree-accu.cc.
References AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::central_position, AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::ci_phones, AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::context_width, rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kPdfClass, MapPhone(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::phone_map, MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), SplitToPhones(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPdfClass(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone(), and AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::var_floor.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 1106 of file lattice-incremental-decoder.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by LatticeIncrementalDeterminizer::InitializeRawLatticeChunk().
| void AddMatMatBatched | ( | const Real | alpha, |
| std::vector< CuSubMatrix< Real > *> & | C, | ||
| const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< Real > *> & | A, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< Real > *> & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const Real | beta | ||
| ) |
Does multiple matrix multiplications, executing them in parallel using cuBLAS's gemmBatched if we are using a GPU.
Vectors A, B and C must have the same length; for each i, this function executes the matrix operation C[i] = alpha * A[i](^T)*B[i](^T) + beta * C[i].
Definition at line 2207 of file cu-matrix.cc.
References AddMatMatBatched(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::data_, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, rnnlm::n, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by TestCuMatrixMatMatBatched(), and UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMatBatched().
| template void kaldi::AddMatMatBatched | ( | const float | alpha, |
| std::vector< CuSubMatrix< float > * > & | C, | ||
| const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< float > * > & | A, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< float > * > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const float | beta | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::AddMatMatBatched | ( | const double | alpha, |
| std::vector< CuSubMatrix< double > * > & | C, | ||
| const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< double > * > & | A, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const std::vector< CuSubMatrix< double > * > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const double | beta | ||
| ) |
Referenced by AddMatMatBatched().
| void kaldi::AddNoise | ( | Vector< BaseFloat > * | noise, |
| BaseFloat | snr_db, | ||
| BaseFloat | time, | ||
| BaseFloat | samp_freq, | ||
| BaseFloat | signal_power, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | signal | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 104 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References AddVectorsWithOffset(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_VLOG, VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and VecVec().
Referenced by main().
| template void kaldi::AddOuterProductPlusMinus< double > | ( | double | alpha, |
| const VectorBase< double > & | a, | ||
| const VectorBase< double > & | b, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | plus, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | minus | ||
| ) |
Referenced by AddOuterProductPlusMinus().
| template void kaldi::AddOuterProductPlusMinus< float > | ( | float | alpha, |
| const VectorBase< float > & | a, | ||
| const VectorBase< float > & | b, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | plus, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | minus | ||
| ) |
Referenced by AddOuterProductPlusMinus().
| void kaldi::AddSelfLoops | ( | fst::StdMutableFst * | fst | ) |
Definition at line 109 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
References kDisambig, and kEps.
|
static |
Definition at line 555 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References TransitionModel::GetNonSelfLoopLogProb(), TransitionModel::GetTransitionLogProb(), KALDI_ASSERT, fst::MakeFollowingInputSymbolsSameClass(), TransitionModel::SelfLoopOf(), and fst::Times().
Referenced by AddSelfLoops().
|
static |
Definition at line 472 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References TransitionModel::GetNonSelfLoopLogProb(), TransitionModel::GetTransitionLogProb(), KALDI_ASSERT, fst::MakePrecedingInputSymbolsSameClass(), TransitionModel::SelfLoopOf(), and fst::Times().
Referenced by AddSelfLoops().
| fst::StdArc::StateId kaldi::AddToChainFsa | ( | fst::StdMutableFst * | fst, |
| fst::StdArc::StateId | last_state, | ||
| int64 | symbol | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 100 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
Referenced by ScoringTest().
Definition at line 40 of file compare-int-vector.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, kCopyData, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::AddToCount | ( | int32 | location_to_add, |
| double | value_to_add, | ||
| std::vector< double > * | counts | ||
| ) |
| void kaldi::AddVectorsOfUnequalLength | ( | const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | signal1, |
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | signal2 | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 31 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), and VectorBase< Real >::Range().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::AddVectorsWithOffset | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | signal1, |
| int32 | offset, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | signal2 | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 44 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), and VectorBase< Real >::Range().
Referenced by AddNoise().
| void AddWordInsPenToCompactLattice | ( | BaseFloat | word_ins_penalty, |
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
This function add the word insertion penalty to graph score of each word in the compact lattice.
Definition at line 1181 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::SetValue1(), and LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1().
Referenced by main().
| void AgglomerativeCluster | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | costs, |
| BaseFloat | threshold, | ||
| int32 | min_clusters, | ||
| int32 | first_pass_max_points, | ||
| BaseFloat | max_cluster_fraction, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | assignments_out | ||
| ) |
This is the function that is called to perform the agglomerative clustering.
It takes the following arguments:
The basic algorithm is as follows:
The cost between two clusters is the average cost of all pairwise costs between points across the two clusters.
The algorithm takes advantage of the fact that the sum of the pairwise costs between the points of clusters I and J is equiavlent to the sum of the pairwise costs between cluster I and the parents of cluster J. In other words, the total cost between I and J is the sum of the costs between clusters I and M and clusters I and N, where cluster J was formed by merging clusters M and N.
If the number of points to cluster is larger than first-pass-max-points, then clustering is done in two passes. In the first pass, input points are divided into contiguous subsets of size at most first-pass-max-points and each subset is clustered separately. In the second pass, the first pass clusters are merged into the final set of clusters.
Definition at line 223 of file agglomerative-clustering.cc.
References AgglomerativeClusterer::Cluster(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| void AlignUtteranceWrapper | ( | const AlignConfig & | config, |
| const std::string & | utt, | ||
| BaseFloat | acoustic_scale, | ||
| fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | fst, | ||
| DecodableInterface * | decodable, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| BaseFloatWriter * | scores_writer, | ||
| int32 * | num_done, | ||
| int32 * | num_error, | ||
| int32 * | num_retried, | ||
| double * | tot_like, | ||
| int64 * | frame_count, | ||
| BaseFloatVectorWriter * | per_frame_acwt_writer = NULL |
||
| ) |
AlignUtteranceWapper is a wrapper for alignment code used in training, that is called from many different binaries, e.g.
gmm-align, gmm-align-compiled, sgmm-align, etc. The writers for alignments and words will only be written to if they are open. The num_done, num_error, num_retried, tot_like and frame_count pointers will (if non-NULL) be incremented or added to, not set, by this function.
Definition at line 576 of file decoder-wrappers.cc.
References FasterDecoderOptions::beam, AlignConfig::beam, AlignConfig::careful, FasterDecoder::Decode(), FasterDecoder::GetBestPath(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), GetPerFrameAcousticCosts(), TableWriter< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, ModifyGraphForCarefulAlignment(), DecodableInterface::NumFramesReady(), FasterDecoder::ReachedFinal(), AlignConfig::retry_beam, VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), FasterDecoder::SetOptions(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), words, and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main(), and AlignConfig::Register().
| bool kaldi::AppendFeats | ( | const std::vector< Matrix< BaseFloat > > & | in, |
| const std::string & | utt, | ||
| int32 | tolerance, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 30 of file paste-feats.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::Range(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::AppendPostToFeats | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | in, |
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const int32 | post_dim, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 28 of file append-post-to-feats.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ColRange(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), PosteriorToMatrix(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
Definition at line 1377 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), kCopyData, VectorBase< Real >::Range(), and Vector< Real >::Resize().
| void kaldi::AppendVectorToFeats | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | in, |
| const Vector< BaseFloat > & | vec, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 29 of file append-vector-to-feats.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ColRange(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
| void ApplyAffineTransform | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | xform, |
| VectorBase< BaseFloat > * | vec | ||
| ) |
Applies the affine transform 'xform' to the vector 'vec' and overwrites the contents of 'vec'.
Definition at line 168 of file transform-common.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by AffineXformStats::AffineXformStats(), main(), TestOnlineTransform(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmm(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmDiagonal(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmOffset(), and UnitTestFmllrRaw().
| void ApplyCmvn | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | stats, |
| bool | norm_vars, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | feats | ||
| ) |
Apply cepstral mean and variance normalization to a matrix of features.
If norm_vars == true, expects stats to be of dimension 2 by (dim+1), but if norm_vars == false, will accept stats of dimension 1 by (dim+1); these are produced by the balanced-cmvn code when it computes an offset and represents it as "fake stats".
Definition at line 64 of file cmvn.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), count, rnnlm::d, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::RowData().
Referenced by OnlineCmvn::GetFrame(), and main().
| void ApplyCmvnReverse | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | stats, |
| bool | norm_vars, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | feats | ||
| ) |
This is as ApplyCmvn, but does so in the reverse sense, i.e.
applies a transform that would take zero-mean, unit-variance input and turn it into output with the stats of "stats". This can be useful if you trained without CMVN but later want to correct a mismatch, so you would first apply CMVN and then do the "reverse" CMVN with the summed stats of your training data.
Definition at line 117 of file cmvn.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), count, rnnlm::d, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by main().
| void ApplyFeatureTransformToStats | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | xform, |
| AffineXformStats * | stats | ||
| ) |
This function applies a feature-level transform to stats (useful for certain techniques based on fMLLR).
Assumes the stats are of the standard diagonal sort. The transform "xform" may be either dim x dim (linear), dim x dim+1 (affine), or dim+1 x dim+1 (affine with the last row equal to 0 0 0 .. 0 1).
Definition at line 381 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), AffineXformStats::Dim(), AffineXformStats::G_, rnnlm::i, AffineXformStats::K_, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), LinearVtln::ComputeTransform(), and UnitTestFmllrDiagGmm().
|
static |
Definition at line 59 of file fmllr-sgmm2.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::mean_scatter_, VectorBase< Real >::Min(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by FmllrSgmm2Accs::AccumulateForFmllrSubspace(), and FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update().
|
static |
Definition at line 81 of file fmllr-sgmm2.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::mean_scatter_, VectorBase< Real >::Min(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update().
|
static |
Definition at line 45 of file fmllr-sgmm2.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::inv_xform_, kNoTrans, kSetZero, kUndefined, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::pre_xform_, and MatrixBase< Real >::Range().
Referenced by FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update().
| void ApplyModelTransformToStats | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | xform, |
| AffineXformStats * | stats | ||
| ) |
ApplyModelTransformToStats takes a transform "xform", which must be diagonal (i.e.
of the form T = [ D; b ] where D is diagonal), and applies it to the stats as if we had made it a model-space transform (note that the transform applied to the model means is the inverse transform of T). Thus, if we are estimating a transform T U, and we get stats valid for estimating T U and we estimate T, we can then call this function (treating T as a model-space transform) and will get stats valid for estimating U. This only works if T is diagonal, because otherwise the standard stats format is not valid. xform must be of dimension d x d+1
Definition at line 421 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References AffineXformStats::Dim(), AffineXformStats::G_, rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::IsDiagonal(), rnnlm::j, AffineXformStats::K_, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmDiagonal(), and UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmOffset().
| void kaldi::ApplyPca | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | ivectors_in, |
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | pca_mat, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | ivectors_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 101 of file ivector-plda-scoring-dense.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 31 of file fmllr-sgmm2.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::inv_xform_, kNoTrans, kSetZero, kTrans, kUndefined, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::pre_xform_, and MatrixBase< Real >::Range().
Referenced by FmllrSgmm2Accs::AccumulateForFmllrSubspace(), and FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update().
| void kaldi::ApplySoftMaxPerRow | ( | MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | mat | ) |
Definition at line 27 of file copy-matrix.cc.
References rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 3323 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
Referenced by UnitTestTrace().
|
static |
Definition at line 35 of file cu-block-matrix-test.cc.
|
static |
Definition at line 100 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::d, KALDI_ASSERT, PackedMatrix< Real >::Max(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Min(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
inline |
Definition at line 141 of file cu-sp-matrix.h.
return abs(a - b) <= relative_tolerance * (abs(a)+abs(b)).
Definition at line 265 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by AssertEqual(), MleAmSgmm2Accs::Check(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), CreateEigenvalueMatrix(), CuVectorUnitTestNorm(), CuVectorUnitTestScale(), DecisionTreeSplitter::DoSplitInternal(), EstPca(), kaldi::nnet3::ExampleApproxEqual(), FindBestSplitForKey(), LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), AmSgmm2::LogLikelihood(), main(), FullGmm::Merge(), DiagGmm::Merge(), FullGmm::MergePreselect(), NnetIo::operator==(), OnlinePreconditioner::PreconditionDirectionsInternal(), KlHmm::PropagateFnc(), MultiBasisComponent::PropagateFnc(), LatticeSimpleDecoder::PruneForwardLinksFinal(), LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< fst::StdFst, decoder::BackpointerToken >::PruneForwardLinksFinal(), LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder::PruneForwardLinksFinal(), LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST, decoder::BackpointerToken >::PruneForwardLinksFinal(), OnlinePitchFeatureImpl::RecomputeBacktraces(), ScoringTest(), TestCuMatrixCompObjfAndDeriv(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::TestDataBackprop(), kaldi::nnet3::TestNnetComponentVectorizeUnVectorize(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::TestParamsBackprop(), TestPushCompactLatticeWeights(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentDataDerivative(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentModelDerivative(), UnitTestApproxEqual(), UnitTestComplexFft2(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix2(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatMat(), UnitTestCuDiffLogSoftmax(), UnitTestCuDiffSigmoid(), UnitTestCuDiffSoftmax(), UnitTestCuDiffTanh(), UnitTestCuDiffXent(), UnitTestCuLogSoftmax(), UnitTestCuMatrixAdd(), UnitTestCuMatrixAdd2(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddCols(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddDiagVecMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks1(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks1Trans(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks2(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatDiagVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMatBatched(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMatElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddRowRanges(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToDiag(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecToCols(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecToRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyCeiling(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExp(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExpLimited(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExpSpecial(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyFloor(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyHeaviside(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyLog(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyPow(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyPowAbs(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCols(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyColsFromVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross2(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyRowsFromVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyToRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixDiffGroupPnorm(), UnitTestCuMatrixDivElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixDivRowsVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixGroupMax(), UnitTestCuMatrixGroupMaxDeriv(), UnitTestCuMatrixGroupPnorm(), UnitTestCuMatrixHeaviside(), UnitTestCuMatrixInvertElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuMatrixMax(), UnitTestCuMatrixMin(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulColsVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsGroupMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixObjfDeriv(), UnitTestCuMatrixReduceMax(), UnitTestCuMatrixReduceMin(), UnitTestCuMatrixReduceSum(), UnitTestCuMatrixScale(), UnitTestCuMatrixSet(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetMatMatDivMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetRandn(), UnitTestCuMatrixSigmoid(), UnitTestCuMatrixSoftHinge(), UnitTestCuMatrixSumColumnRanges(), UnitTestCuMatrixSymAddMat2(), UnitTestCuMatrixSymInvertPosDef(), UnitTestCuMatrixTraceMatMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixTranspose(), UnitTestCuSigmoid(), UnitTestCuSoftmax(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixCopyFromMat(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixTraceSpSp(), UnitTestCuTanh(), UnitTestCuVectorAddColSumMat(), UnitTestCuVectorAddColSumMatLarge(), UnitTestCuVectorAddRowSumMat(), UnitTestCuVectorAddRowSumMatLarge(), UnitTestCuVectorAddTpVec(), UnitTestCuVectorAddVec(), UnitTestCuVectorInvertElements(), UnitTestCuVectorMulTp(), UnitTestCuVectorSum(), UnitTestDelay(), UnitTestEstimateDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateFullGmm(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmm(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmDiagonal(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmOffset(), UnitTestLinearResample(), UnitTestLstmNonlinearity(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetCompute(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestNnetDecodable(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetInputDerivatives(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetModelDerivatives(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetOptimizeWithOptions(), UnitTestNorm(), UnitTestPieces(), UnitTestPosteriors(), UnitTestRange(), UnitTestReadConfig(), UnitTestSnipEdges(), UnitTestSplitRadixComplexFft2(), UnitTestSwapCu2Cu(), UnitTestSwapCu2M(), UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble(), UnitTestTableSequentialBaseFloatVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialDouble(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleMatrixBoth(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddMatSmat(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmat(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmatMat(), IvectorExtractorStats::UpdatePrior(), and MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs::UpdateWithU().
| bool kaldi::ApproxEqual | ( | const CuVectorBase< Real > & | a, |
| const CuVectorBase< Real > & | b, | ||
| Real | tol = 0.01 |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 364 of file cu-vector.h.
| bool kaldi::ApproxEqual | ( | const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | A, |
| const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | B, | ||
| Real | tol = 0.01 |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 937 of file cu-matrix.h.
|
static |
Definition at line 68 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by UnitTestCuPackedMatrixAddToDiag().
|
static |
Definition at line 78 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
| void kaldi::AssertEqual | ( | const std::vector< T > & | vec1, |
| const std::vector< T > & | vec2 | ||
| ) |
|
static |
Definition at line 41 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
static |
Definition at line 46 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
static |
Definition at line 52 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
static |
Definition at line 57 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
static |
Definition at line 63 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
static |
Definition at line 69 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
|
static |
Definition at line 89 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
|
inline |
Definition at line 147 of file cu-sp-matrix.h.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::ApproxEqual(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
assert abs(a - b) <= relative_tolerance * (abs(a)+abs(b))
Definition at line 276 of file kaldi-math.h.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, and RoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo().
Referenced by AddToClustersOptimized(), CholeskyUnitTestTr(), CuCompressedMatrixTestSign(), CuVectorUnitTestAddColSumMat(), CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMat2(), CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMatMat(), CuVectorUnitTestAddMatVec(), CuVectorUnitTestAddRowSumMat(), CuVectorUnitTestAddSpVec(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVec(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVecCross(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVecExtra(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVecVec(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeiling(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeilingNoCount(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloor(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloorNoCount(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyPow(), CuVectorUnitTestApplySoftMax(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross2(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromMat(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyElements(), CuVectorUnitTestInvertElements(), CuVectorUnitTestVecVec(), RegressionTree::GatherStats(), PldaEstimator::GetOutput(), fst::LatticeWeightTest(), OnlinePreconditionerSimple::PreconditionDirectionsCpu(), OnlineNaturalGradientSimple::PreconditionDirectionsCpu(), test_flags_driven_update(), test_io(), TestAddToClusters(), TestAddToClustersOptimized(), TestAmDiagGmmAccsIO(), TestAmDiagGmmIO(), TestComponentAcc(), fst::TestContextFst(), TestCuMatrixCopyFromSp(), TestCuMatrixCopyFromTp(), TestCuMatrixCopyLowerToUpper(), TestCuMatrixCopyUpperToLower(), TestCuMatrixTransposeCross(), TestDistance(), TestMllrAccsIO(), TestObjfMinus(), TestObjfPlus(), TestOnlineMatrixCacheFeature(), TestOnlineMatrixInput(), TestOnlineMfcc(), TestOnlinePlp(), TestOnlineTransform(), TestRefineClusters(), TestSgmm2AccsIO(), TestSgmm2FmllrAccsIO(), TestSgmm2IncreaseDim(), TestSgmm2Init(), TestSgmm2IO(), TestSgmm2Substates(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentPropagateProperties(), TestSplitStates(), TestSum(), TestSumObjfAndSumNormalizer(), TestXformMean(), UnitTestAddDiagMat2(), UnitTestAddDiagMatMat(), UnitTestAddDiagVecMat(), UnitTestAddMat2(), UnitTestAddMat2Sp(), UnitTestAddMatDiagVec(), UnitTestAddMatMatElements(), UnitTestAddMatSelf(), UnitTestAddMatSmat(), UnitTestAddOuterProductPlusMinus(), UnitTestAddRows(), UnitTestAddSp(), UnitTestAddToDiag(), UnitTestAddToDiagMatrix(), UnitTestAddToRows(), UnitTestAddVec2Sp(), UnitTestAddVecCross(), UnitTestAddVecToCols(), UnitTestAddVecToRows(), UnitTestAddVecVec(), UnitTestApplyExpSpecial(), UnitTestAssertFunc(), kaldi::nnet3::attention::UnitTestAttentionDotProductAndAddScales(), UnitTestAxpy(), UnitTestBackpropLstmNonlinearity(), UnitTestCholesky(), UnitTestComplexFft(), UnitTestComplexFt(), UnitTestComplexPower(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix(), kaldi::nnet1::UnitTestConvolutionalComponent3x3(), kaldi::nnet1::UnitTestConvolutionalComponentUnity(), UnitTestCopyCols(), UnitTestCopyRows(), UnitTestCopySp(), UnitTestCopyToRows(), UnitTestCuArray(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatBlock(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuDiffNormalizePerRow(), UnitTestCuMathComputeLstmNonlinearity(), UnitTestCuMathCopy(), UnitTestCuMathNormalizePerRow(), UnitTestCuMathNormalizePerRow_v2(), UnitTestCuMathRandomize(), UnitTestCuMathSplice(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixConstructor(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixCopy(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixScale(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixScaleDiag(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixTrace(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixConstructFromIndexes(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixCopyToSmat(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSelectRowsAndTranspose(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSwap(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddMat2(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddSp(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddToDiag(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddVec2(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixConstructor(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixInvert(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixSetUnit(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixCopyFromMat(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuVectorAddTp(), UnitTestCuVectorCopyFromVec(), UnitTestCuVectorIO(), UnitTestCuVectorMulTp(), UnitTestCuVectorReplaceValue(), UnitTestDeterminantSign(), UnitTestDiagGmm(), UnitTestDiagGmmGenerate(), kaldi::nnet1::UnitTestDropoutComponent(), UnitTestEig(), UnitTestEigSymmetric(), UnitTestEndless1(), UnitTestEndless2(), UnitTestEstimateDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateFullGmm(), UnitTestFFTbasedBlockConvolution(), UnitTestFFTbasedConvolution(), UnitTestFloorCeiling(), UnitTestFullGmm(), UnitTestGeneralMatrix(), UnitTestHtkIo(), UnitTestInnerProd(), UnitTestInvert(), UnitTestIo(), UnitTestIoCross(), UnitTestIoNew(), UnitTestIoPipe(), kaldi::nnet1::UnitTestLengthNorm(), UnitTestLinearResample2(), UnitTestMat2Vec(), UnitTestMatrixAddMatSmat(), UnitTestMatrixAddSmatMat(), UnitTestMatrixRandomizer(), UnitTestMax2(), UnitTestMaxAbsEig(), UnitTestMaxMin(), kaldi::nnet1::UnitTestMaxPoolingComponent(), UnitTestMmulSym(), UnitTestMono22K(), UnitTestMul(), UnitTestMulTp(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestNnetCompute(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestNnetComputeChunked(), UnitTestNonsymmetricPower(), UnitTestPca(), UnitTestPca2(), UnitTestPieces(), UnitTestPower(), UnitTestPowerAbs(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), UnitTestRankNUpdate(), UnitTestRealFft(), UnitTestReplaceValue(), UnitTestResize(), UnitTestResizeCopyDataDifferentStrideType(), UnitTestRow(), UnitTestScaleDiag(), UnitTestSearch(), UnitTestSetDiag(), UnitTestSigmoid(), UnitTestSimple(), UnitTestSimpleForMat(), UnitTestSimpleForVec(), kaldi::nnet1::UnitTestSimpleSentenceAveragingComponent(), UnitTestSnipEdges(), UnitTestSoftHinge(), UnitTestSolve(), UnitTestSpAddDiagVec(), UnitTestSpAddVecVec(), UnitTestSparseMatrixAddToMat(), UnitTestSparseMatrixConstructor(), UnitTestSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm(), UnitTestSparseMatrixSum(), UnitTestSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), UnitTestSparseVectorAddToVec(), UnitTestSparseVectorMax(), UnitTestSparseVectorSum(), UnitTestSpliceRows(), UnitTestSplitRadixComplexFft(), UnitTestSplitRadixRealFft(), UnitTestSpVec(), UnitTestStdVectorRandomizer(), UnitTestStereo8K(), UnitTestSubvector(), UnitTestSvd(), UnitTestSvdJustvec(), UnitTestSymAddMat2(), UnitTestTanh(), UnitTestTopEigs(), UnitTestTp2(), UnitTestTp2Sp(), UnitTestTrace(), UnitTestTraceSpSpLower(), UnitTestTranspose(), UnitTestTridiagonalize(), UnitTestTridiagonalizeAndQr(), UnitTestTriVecSolver(), UnitTestVecMatVec(), UnitTestVecmul(), UnitTestVector(), UnitTestVectorRandomizer(), UnitTestVtln(), FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update(), and AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator().
|
inline |
|
inline |
| template bool kaldi::AttemptComplexPower | ( | double * | x_re, |
| double * | x_im, | ||
| double | power | ||
| ) |
Referenced by AttemptComplexPower(), and MatrixBase< float >::Power().
| GmmFlagsType AugmentGmmFlags | ( | GmmFlagsType | f | ) |
Returns "augmented" version of flags: e.g.
if just updating means, need weights too.
Definition at line 52 of file model-common.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kGmmAll, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, and kGmmWeights.
Referenced by DiagGmmToStats(), AccumFullGmm::Resize(), and AccumDiagGmm::Resize().
| ContextDependency* kaldi::BiphoneContextDependencyFull | ( | std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > | phone_sets, |
| const std::vector< int32 > | phone2num_pdf_classes, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | ci_phones_list, | ||
| const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | bi_counts, | ||
| int32 | biphone_min_count, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | mono_counts, | ||
| int32 | mono_min_count | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 180 of file gmm-init-biphone.cc.
References GetFullBiphoneStubMap(), rnnlm::i, and rnnlm::j.
Referenced by main().
| bool BuildConstArpaLm | ( | const ArpaParseOptions & | options, |
| const std::string & | arpa_rxfilename, | ||
| const std::string & | const_arpa_wxfilename | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 1074 of file const-arpa-lm.cc.
References KALDI_LOG, ArpaFileParser::Read(), Input::Stream(), and WriteKaldiObject().
|
static |
This function takes the step direction (delta) of fMLLR matrix as argument, and optimize step size using Newton's method.
This is an iterative method, where each iteration should not decrease the auxiliary function. Note that the resulting step size should be close to 1. If <<1 or >>1, there maybe problems with preconditioning or the speaker stats.
Definition at line 374 of file basis-fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), AffineXformStats::beta_, MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::d, AffineXformStats::dim_, MatrixBase< Real >::InvertDouble(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), TraceMat(), TraceMatMat(), and VecVec().
Referenced by BasisFmllrEstimate::ComputeTransform().
|
static |
Definition at line 286 of file fmllr-sgmm2.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AffineXformStats::beta_, MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::d, AmSgmm2::FeatureDim(), AffineXformStats::G_, AmSgmm2::GetInvCovars(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::InvertDouble(), AffineXformStats::K_, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), rnnlm::n, AmSgmm2::NumGauss(), TraceMat(), TraceMatMat(), and TraceMatSpMatSp().
Referenced by FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update().
Definition at line 48 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 52 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 74 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::AddDiagVecMat(), MatrixBase< float >::AddMat(), MatrixBase< float >::AddMatSmat(), PackedMatrix< float >::AddPacked(), MatrixBase< float >::AddRows(), VectorBase< float >::AddRowSumMat(), MatrixBase< float >::AddSmatMat(), MatrixBase< float >::AddToRows(), VectorBase< float >::AddVec(), SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize(), and Xgemv_sparsevec().
|
inline |
Definition at line 78 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 37 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::CopyDiagFromMat(), MatrixBase< float >::CopyRows(), and MatrixBase< float >::CopyToRows().
|
inline |
Definition at line 42 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 64 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::AddDiagMat2(), VectorBase< float >::AddDiagMatMat(), TpMatrix< float >::Cholesky(), VectorBase< float >::Sum(), TraceMatMat(), TraceSpSp(), TraceSpSpLower(), SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize(), and VecVec().
|
inline |
Definition at line 69 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 178 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::AddVecVec().
|
inline |
Definition at line 187 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 224 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
References kNoTrans.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::AddMatMat().
|
inline |
Definition at line 239 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
References kNoTrans.
|
inline |
Definition at line 162 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::AddMat2Sp(), VectorBase< float >::AddMatVec(), and SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize().
|
inline |
Definition at line 169 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 275 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::AddVecVec(), and SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize().
|
inline |
Definition at line 281 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 56 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by QrStep().
|
inline |
Definition at line 60 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
matrix-vector multiply using a banded matrix; we always call this with b = 1 meaning we're multiplying by a diagonal matrix.
This is used for elementwise multiplication. We miss some of the arguments out of this wrapper.
Definition at line 317 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 328 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Definition at line 82 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::AddRowSumMat(), HouseBackward(), MatrixBase< float >::MulRowsGroupMat(), PackedMatrix< float >::Scale(), MatrixBase< float >::Scale(), VectorBase< float >::Scale(), and Xgemv_sparsevec().
|
inline |
Definition at line 86 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 90 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::AddMat2Sp(), VectorBase< float >::AddSpVec(), SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize(), UnitTestTridiagonalize(), UnitTestTridiagonalizeAndQr(), and VecSpVec().
|
inline |
Definition at line 95 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 124 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 130 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 152 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::AddMat2Vec(), and SpMatrix< float >::AddVec2().
|
inline |
Definition at line 156 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 138 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::AddVecVec(), and SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize().
|
inline |
Definition at line 144 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 256 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::AddSpSp().
|
inline |
Definition at line 265 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 295 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::AddMat2(), and MatrixBase< float >::SymAddMat2().
|
inline |
Definition at line 304 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 100 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::MulTp().
|
inline |
Definition at line 105 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 112 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::Solve().
|
inline |
Definition at line 117 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
| std::string CharToString | ( | const char & | c | ) |
Definition at line 36 of file kaldi-utils.cc.
Referenced by SequentialTableReaderArchiveImpl< Holder >::Next(), BasicHolder< BasicType >::Read(), EventMap::Read(), TokenHolder::Read(), ReadBasicType< bool >(), RandomAccessTableReaderArchiveImplBase< Holder >::ReadNextObject(), ReadToken(), TreeRenderer::RenderSubTree(), StringToGmmFlags(), StringToSgmmUpdateFlags(), StringToSgmmWriteFlags(), UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble(), UnitTestTableRandomBothDoubleMatrix(), UnitTestTableSequentialBaseFloatVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialBool(), UnitTestTableSequentialDouble(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleMatrixBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32PairVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorBoth(), and UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorVectorBoth().
| bool kaldi::CheckFst | ( | const fst::StdVectorFst & | fst, |
| string | name, | ||
| string | key | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 151 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::CheckToken | ( | const char * | token | ) |
Definition at line 122 of file io-funcs.cc.
References KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by ExpectToken(), and WriteToken().
|
static |
Definition at line 140 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), TpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), TpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), MatrixBase< Real >::Invert(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, and Rand().
|
inline |
Definition at line 415 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::LapackGesvd().
|
inline |
Definition at line 425 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 392 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::Invert().
|
inline |
Definition at line 397 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 404 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::Invert().
|
inline |
Definition at line 409 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 445 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::Invert().
|
inline |
Definition at line 449 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 436 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::Invert().
|
inline |
Definition at line 440 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 385 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
Referenced by TpMatrix< float >::Invert().
|
inline |
Definition at line 388 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
|
static |
Definition at line 803 of file build-tree-utils.cc.
References ClusterEventMapGetMapping(), rnnlm::i, and SplitStatsByKey().
Referenced by ClusterEventMapRestrictedByKeys().
| BaseFloat kaldi::ClusterKMeansOnce | ( | const std::vector< Clusterable *> & | points, |
| int32 | num_clust, | ||
| std::vector< Clusterable *> * | clusters_out, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | assignments_out, | ||
| ClusterKMeansOptions & | cfg | ||
| ) |
ClusterKMeansOnce is called internally by ClusterKMeans; it is equivalent to calling ClusterKMeans with cfg.num_tries == 1.
It returns the objective function improvement versus everything being in one cluster.
Definition at line 918 of file cluster-utils.cc.
References count, Gcd(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, ClusterKMeansOptions::num_iters, Clusterable::Objf(), Rand(), ClusterKMeansOptions::refine_cfg, RefineClusters(), SumClusterable(), SumClusterableNormalizer(), SumClusterableObjf(), and ClusterKMeansOptions::verbose.
Referenced by ClusterKMeans().
| bool ClusterLattice | ( | CompactLattice * | clat, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | state_times | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 40 of file kws-functions.cc.
References CompareInterval(), rnnlm::i, and Interval::Overlap().
Referenced by main().
| BaseFloat CompactLatticeDepth | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| int32 * | num_frames | ||
| ) |
Returns the depth of the lattice, defined as the average number of arcs crossing any given frame.
Returns the depth of the lattice, defined as the average number of arcs (or final-prob strings) crossing any given frame.
Returns 1 for empty lattices. Requires that input is topologically sorted.
Returns 1 for empty lattices. Requires that clat is topologically sorted!
Definition at line 628 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References CompactLatticeStateTimes(), and KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by main().
| void CompactLatticeDepthPerFrame | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | depth_per_frame | ||
| ) |
This function returns, for each frame, the number of arcs crossing that frame.
Definition at line 659 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References CompactLatticeStateTimes(), KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by main().
| void CompactLatticeLimitDepth | ( | int32 | max_arcs_per_frame, |
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
This function limits the depth of the lattice, per frame: that means, it does not allow more than a specified number of arcs active on any given frame.
This can be used to reduce the size of the "very deep" portions of the lattice.
Definition at line 532 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References LatticeArcRecord::arc, CompactLatticeStateTimes(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), fst::ConvertToCost(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, LatticeArcRecord::logprob, LatticeArcRecord::state, and TopSortCompactLatticeIfNeeded().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::CompactLatticeNormalize | ( | CompactLattice * | clat, |
| BaseFloat | weight | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 54 of file lattice-combine.cc.
References ComputeCompactLatticeBetas(), KALDI_WARN, Log(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::SetValue1(), CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::SetWeight(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), and CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Weight().
Referenced by main().
| void CompactLatticeShortestPath | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| CompactLattice * | shortest_path | ||
| ) |
A form of the shortest-path/best-path algorithm that's specially coded for CompactLattice.
Requires that clat be acyclic.
Definition at line 1097 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References fst::ConvertToCost(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, and KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental(), GetDiagnosticsAndPrintOutput(), LatticeToString(), and main().
| int32 kaldi::CompactLatticeStateTimes | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | times | ||
| ) |
As LatticeStateTimes, but in the CompactLattice format.
Note: must be topologically sorted. Returns length of the utterance in frames, which might not be the same as the maximum time in the lattice, due to frames in the final-prob.
Definition at line 111 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, and CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Zero().
Referenced by DiscriminativeNnetExample::Check(), CompactLatticeDepth(), CompactLatticeDepthPerFrame(), CompactLatticeLimitDepth(), kaldi::nnet2::LatticeToDiscriminativeExample(), main(), ArcPosteriorComputer::OutputPosteriors(), MinimumBayesRisk::PrepareLatticeAndInitStats(), and RescoreCompactLatticeInternal().
| int32 kaldi::CompactLatticeStateTimes | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | times | ||
| ) |
As LatticeStateTimes, but in the CompactLattice format.
Note: must be topologically sorted. Returns length of the utterance in frames, which might not be the same as the maximum time in the lattice, due to frames in the final-prob.
Definition at line 111 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, and CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Zero().
Referenced by DiscriminativeNnetExample::Check(), CompactLatticeDepth(), CompactLatticeDepthPerFrame(), CompactLatticeLimitDepth(), kaldi::nnet2::LatticeToDiscriminativeExample(), main(), ArcPosteriorComputer::OutputPosteriors(), MinimumBayesRisk::PrepareLatticeAndInitStats(), and RescoreCompactLatticeInternal().
| bool CompactLatticeToWordAlignment | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | words, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | begin_times, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | lengths | ||
| ) |
This function takes a CompactLattice that should only contain a single linear sequence (e.g.
derived from lattice-1best), and that should have been processed so that the arcs in the CompactLattice align correctly with the word boundaries (e.g. by lattice-align-words). It outputs 3 vectors of the same size, which give, for each word in the lattice (in sequence), the word label and the begin time and length in frames. This is done even for zero (epsilon) words, generally corresponding to optional silence– if you don't want them, just ignore them in the output. This function will print a warning and return false, if the lattice did not have the correct format (e.g. if it is empty or it is not linear).
Definition at line 975 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by main().
| bool CompactLatticeToWordProns | ( | const TransitionModel & | tmodel, |
| const CompactLattice & | clat, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | words, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | begin_times, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | lengths, | ||
| std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > * | prons, | ||
| std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > * | phone_lengths | ||
| ) |
This function takes a CompactLattice that should only contain a single linear sequence (e.g.
derived from lattice-1best), and that should have been processed so that the arcs in the CompactLattice align correctly with the word boundaries (e.g. by lattice-align-words). It outputs 4 vectors of the same size, which give, for each word in the lattice (in sequence), the word label, the begin time and length in frames, and the pronunciation (sequence of phones). This is done even for zero words, corresponding to optional silences – if you don't want them, just ignore them in the output. This function will print a warning and return false, if the lattice did not have the correct format (e.g. if it is empty or it is not linear).
Definition at line 1026 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, SplitToPhones(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 33 of file kws-functions.cc.
References Interval::End(), and Interval::Start().
Referenced by ClusterLattice().
| ArpaLmCompiler* kaldi::Compile | ( | bool | seps, |
| const std::string & | infile | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 75 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
References ArpaParseOptions::bos_symbol, ArpaParseOptions::eos_symbol, ArpaParseOptions::kAddToSymbols, kBos, kDisambig, kEos, kEps, ArpaParseOptions::oov_handling, ArpaFileParser::Read(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by CoverageTest(), ScoringTest(), and ThrowsExceptionTest().
| template void kaldi::ComplexFft | ( | VectorBase< float > * | v, |
| bool | forward, | ||
| Vector< float > * | tmp_in | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::ComplexFft | ( | VectorBase< double > * | v, |
| bool | forward, | ||
| Vector< double > * | tmp_in | ||
| ) |
| void kaldi::ComplexFftRecursive | ( | Real * | data, |
| int | nffts, | ||
| int | N, | ||
| const int * | factor_begin, | ||
| const int * | factor_end, | ||
| bool | forward, | ||
| Vector< Real > * | tmp_vec | ||
| ) |
ComplexFftRecursive is a recursive function that computes the complex FFT of size N.
The "nffts" arguments specifies how many separate FFTs to compute in parallel (we assume the data for each one is consecutive in memory). The "forward argument" specifies whether to do the FFT (true) or IFFT (false), although note that we do not include the factor of 1/N (the user should do this if required. The iterators factor_begin and factor_end point to the beginning and end (i.e. one past the last element) of an array of small factors of N (typically prime factors). See the comments below this code for the detailed equations of the recursion.
Definition at line 97 of file matrix-functions.cc.
References ComplexAddProduct(), ComplexImExp(), ComplexMul(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_COMPLEXFFT_BLOCKSIZE, M_2PI, rnnlm::n, and Vector< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by ComplexFft().
| template void kaldi::ComplexFt | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | in, |
| VectorBase< float > * | out, | ||
| bool | forward | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::ComplexFt | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | in, |
| VectorBase< double > * | out, | ||
| bool | forward | ||
| ) |
| void ComposeCompactLatticeDeterministic | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| fst::DeterministicOnDemandFst< fst::StdArc > * | det_fst, | ||
| CompactLattice * | composed_clat | ||
| ) |
This function Composes a CompactLattice format lattice with a DeterministicOnDemandFst<fst::StdFst> format fst, and outputs another CompactLattice format lattice.
The first element (the one that corresponds to LM weight) in CompactLatticeWeight is used for composition.
Note that the DeterministicOnDemandFst interface is not "const", therefore we cannot use "const" for <det_fst>.
Definition at line 1528 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References DeterministicOnDemandFst< Arc >::Final(), DeterministicOnDemandFst< Arc >::GetArc(), KALDI_ASSERT, and DeterministicOnDemandFst< Arc >::Start().
Referenced by main().
| void ComposeCompactLatticePruned | ( | const ComposeLatticePrunedOptions & | opts, |
| const CompactLattice & | clat, | ||
| fst::DeterministicOnDemandFst< fst::StdArc > * | det_fst, | ||
| CompactLattice * | composed_clat | ||
| ) |
Does pruned composition of a lattice 'clat' with a DeterministicOnDemandFst 'det_fst'; implements LM rescoring.
| [in] | opts | Class containing options |
| [in] | clat | The input lattice, which is expected to already have a reasonable acoustic scale applied (e.g. 0.1 if it's a normal cross-entropy system, but 1.0 for a chain system); this scale affects the pruning. |
| [in] | det_fst | The on-demand FST that we are composing with; its ilabels will correspond to words and it should be an acceptor in practice (ilabel == olabel). Will often contain a weighted difference of language model scores, with scores of the form alpha * new - alpha * old, where alpha is the interpolation weight for the 'new' language model (e.g. 0.5 or 0.8). It's non-const because 'det_fst' is on-demand. |
| [out] | composed_clat | The output, which is a result of composing 'clat' with '*det_fst'. Notionally, '*det_fst' is on the right, although both are acceptors so it doesn't really matter in practice. Although the two FSTs are of different types, the code manually does the conversion. The weights in '*det_fst' will be interpreted as graph weights (Value1()) in the lattice semiring. |
Definition at line 946 of file compose-lattice-pruned.cc.
References PrunedCompactLatticeComposer::Compose().
Referenced by main(), and ComposeLatticePrunedOptions::Register().
| bool ComposeTransforms | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | a, |
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | b, | ||
| bool | b_is_affine, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | c | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 132 of file transform-common.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by AffineXformStats::AffineXformStats(), LinearVtln::ComputeTransform(), and main().
| void ComputeAcousticScoresMap | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| unordered_map< std::pair< int32, int32 >, std::pair< BaseFloat, int32 >, PairHasher< int32 > > * | acoustic_scores | ||
| ) |
This function computes the mapping from the pair (frame-index, transition-id) to the pair (sum-of-acoustic-scores, num-of-occurences) over all occurences of the transition-id in that frame.
frame-index in the lattice. This function is useful for retaining the acoustic scores in a non-compact lattice after a process like determinization where the frame-level acoustic scores are typically lost. The function ReplaceAcousticScoresFromMap is used to restore the acoustic scores computed by this function.
| [in] | lat | Input lattice. Expected to be top-sorted. Otherwise the function will crash. |
| [out] | acoustic_scores | Pointer to a map from the pair (frame-index, transition-id) to a pair (sum-of-acoustic-scores, num-of-occurences). Usually the acoustic scores for a pdf-id (and hence transition-id) on a frame will be the same for all the occurences of the pdf-id in that frame. But if not, we will take the average of the acoustic scores. Hence, we store both the sum-of-acoustic-scores and the num-of-occurences of the transition-id in that frame. |
Definition at line 1652 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_VLOG, LatticeStateTimes(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), and LatticeWeightTpl< BaseFloat >::Zero().
Referenced by main().
| BaseFloat ComputeAmGmmFeatureDeriv | ( | const AmDiagGmm & | am_gmm, |
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const Posterior & | posterior, | ||
| const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | features, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | direct_deriv, | ||
| const AccumAmDiagGmm * | model_diff = NULL, |
||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | indirect_deriv = NULL |
||
| ) |
Computes derivatives of the likelihood of these states (weighted), w.r.t.
the feature values. Used in fMPE training. Note, the weights "posterior" may be positive or negative– for MMI, MPE, etc., they will typically be of both signs. Will resize "deriv". Returns the sum of (GMM likelihood * weight), which may be used as an approximation to the objective function. Last two parameters are optional. See GetStatsDerivative() for or fMPE paper (ICASSP, 2005) more info on indirect derivative. Caution: if you supply the last two parameters, this function only works in the MMI case as it assumes the stats with positive weight are numerator == ml stats– this is only the same thing in the MMI case, not fMPE.
Definition at line 522 of file fmpe.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), DiagGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, DiagGmm::inv_vars(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), DiagGmm::means_invvars(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPdf(), and AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::ComputeAndSubtractMean | ( | std::map< std::string, Vector< BaseFloat > *> | utt2ivector, |
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | mean_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 186 of file ivector-compute-lda.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), and Vector< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| std::vector< double > * | alpha | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 150 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, and LogAdd().
Referenced by CreateFactorTransducer(), and ArcPosteriorComputer::OutputPosteriors().
| bool kaldi::ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| vector< double > * | alpha | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 150 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, and LogAdd().
Referenced by CreateFactorTransducer(), and ArcPosteriorComputer::OutputPosteriors().
| bool kaldi::ComputeCompactLatticeBetas | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| std::vector< double > * | beta | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 188 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, and LogAdd().
Referenced by CompactLatticeNormalize(), CreateFactorTransducer(), and ArcPosteriorComputer::OutputPosteriors().
| bool kaldi::ComputeCompactLatticeBetas | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| vector< double > * | beta | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 188 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, and LogAdd().
Referenced by CompactLatticeNormalize(), CreateFactorTransducer(), and ArcPosteriorComputer::OutputPosteriors().
| void kaldi::ComputeCorrelation | ( | const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | wave, |
| int32 | first_lag, | ||
| int32 | last_lag, | ||
| int32 | nccf_window_size, | ||
| VectorBase< BaseFloat > * | inner_prod, | ||
| VectorBase< BaseFloat > * | norm_prod | ||
| ) |
This function computes some dot products that are required while computing the NCCF.
For each integer lag from start to end-1, this function outputs to (*inner_prod)(lag - start), the dot-product of a window starting at 0 with a window starting at lag. All windows are of length nccf_window_size. It outputs to (*norm_prod)(lag - start), e1 * e2, where e1 is the dot-product of the un-shifted window with itself, and d2 is the dot-product of the window shifted by "lag" with itself.
Definition at line 102 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Add(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), and VecVec().
Referenced by OnlinePitchFeatureImpl::AcceptWaveform().
| template void kaldi::ComputeDctMatrix | ( | Matrix< double > * | M | ) |
| BaseFloat kaldi::ComputeEarlyReverbEnergy | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | rir, |
| const Vector< BaseFloat > & | signal, | ||
| BaseFloat | samp_freq | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 64 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals(), KALDI_VLOG, VectorBase< Real >::Max(), VectorBase< Real >::Range(), and VecVec().
Referenced by DoReverberation().
| BaseFloat kaldi::ComputeEer | ( | std::vector< BaseFloat > * | target_scores, |
| std::vector< BaseFloat > * | nontarget_scores, | ||
| BaseFloat * | threshold | ||
| ) |
ComputeEer computes the Equal Error Rate (EER) for the given scores and returns it as a proportion beween 0 and 1.
If we set the threshold at x, then the target error-rate is the proportion of target_scores below x; and the non-target error-rate is the proportion of non-target scores above x. We seek a threshold x for which these error rates are the same; this error rate is the EER.
We compute this by iterating over the positions in target_scores: 0, 1, 2, and so on, and for each position consider whether the cutoff could be here. For each of these position we compute the corresponding position in nontarget_scores where the cutoff would be if the EER were the same. For instance, if the vectors had the same length, this would be position length() - 1, length() - 2, and so on. As soon as the value at that position in nontarget_scores at that position is less than the value from target_scores, we have our EER.
In coding this we weren't particularly careful about edge cases or making sure whether it's actually n + 1 instead of n.
Definition at line 48 of file compute-eer.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
Computes the inverse of an LDA transform (without dimensionality reduction) The computed transform is used in initializing the phonetic and speaker subspaces, as well as while increasing the dimensions of those spaces.
Definition at line 1297 of file am-sgmm2.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2(), TpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromTp(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), FullGmm::Dim(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), FullGmm::GetCovarsAndMeans(), rnnlm::i, TpMatrix< Real >::InvertDouble(), MatrixBase< Real >::InvertDouble(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, kTrans, FullGmm::NumGauss(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), SortSvd(), and FullGmm::weights().
Referenced by AmSgmm2::GetVarScaledSubstateSpeakerMean(), AmSgmm2::InitializeFromFullGmm(), main(), and TestSgmm2IncreaseDim().
| BaseFloat kaldi::ComputeFmllrDiagGmm | ( | const FmllrDiagGmmAccs & | accs, |
| const FmllrOptions & | opts, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | out_fmllr, | ||
| BaseFloat * | logdet | ||
| ) |
Referenced by InitFmllr().
Definition at line 176 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.h.
References ApplyFeatureTransformToStats(), ApplyModelTransformToStats(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal2(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmOffset(), FmllrAuxfGradient(), FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm(), FmllrInnerUpdate(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), FmllrOptions::num_iters, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
| BaseFloat ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | in_xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats, | ||
| std::string | fmllr_type, | ||
| int32 | num_iters, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | out_xform | ||
| ) |
This function internally calls ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm{Full, Diagonal, Offset}, depending on "fmllr_type".
Definition at line 169 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmOffset(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), and LinearVtln::ComputeTransform().
| BaseFloat ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | in_xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | out_xform | ||
| ) |
This does diagonal fMLLR (i.e.
only estimate an offset and scale per dimension). The format of the output is the same as for the full case. Of course, these statistics are unnecessarily large for this case. Returns the objective function improvement, not normalized by number of frames.
Definition at line 275 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References AffineXformStats::beta_, MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm(), AffineXformStats::G_, rnnlm::i, AffineXformStats::K_, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, and MatrixBase< Real >::Range().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), and RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update().
| BaseFloat kaldi::ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal2 | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | in_xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | out_xform | ||
| ) |
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet().
| BaseFloat ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | in_xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats, | ||
| int32 | num_iters, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | out_xform | ||
| ) |
Updates the FMLLR matrix using Mark Gales' row-by-row update.
Uses full fMLLR matrix (no structure). Returns the objective function improvement, not normalized by number of frames.
Definition at line 236 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), AffineXformStats::beta_, MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::d, FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm(), FmllrInnerUpdate(), AffineXformStats::G_, AffineXformStats::K_, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, and kNoTrans.
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), and RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update().
| BaseFloat ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmOffset | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | in_xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | out_xform | ||
| ) |
This does offset-only fMLLR, i.e. it only estimates an offset.
Definition at line 350 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), AffineXformStats::G_, rnnlm::i, AffineXformStats::K_, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmm(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), and RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update().
|
static |
Definition at line 112 of file decodable-am-diag-gmm-regtree.cc.
References rnnlm::d, VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_ISINF, KALDI_ISNAN, KALDI_WARN, Log(), M_LOG_2PI, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by DecodableAmDiagGmmRegtreeMllr::GetXformedMeanInvVars().
| BaseFloat kaldi::ComputeInitialSplit | ( | const std::vector< Clusterable *> & | summed_stats, |
| const Questions & | q_opts, | ||
| EventKeyType | key, | ||
| std::vector< EventValueType > * | yes_set | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 297 of file build-tree-utils.cc.
References AddToClustersOptimized(), DeletePointers(), Questions::GetQuestionsOf(), rnnlm::i, QuestionsForKey::initial_questions, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, Clusterable::Objf(), SumClusterable(), and SumClusterableObjf().
Referenced by FindBestSplitForKey().
| void kaldi::ComputeKaldiPitchFirstPass | ( | const PitchExtractionOptions & | opts, |
| const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | wave, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | output | ||
| ) |
This function is called from ComputeKaldiPitch when the user specifies opts.simulate_first_pass_online == true.
It gives the "first-pass" version of the features, which you would get on the first decoding pass in an online setting. These may differ slightly from the final features due to both the way the Viterbi traceback works (this is affected by opts.max_frames_latency), and the online way we compute the average signal energy.
Definition at line 1248 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References OnlinePitchFeature::AcceptWaveform(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), PitchExtractionOptions::frame_shift_ms, PitchExtractionOptions::frames_per_chunk, OnlinePitchFeature::GetFrame(), OnlinePitchFeature::InputFinished(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kCopyData, OnlinePitchFeature::NumFramesReady(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::RowRange(), and PitchExtractionOptions::samp_freq.
Referenced by ComputeKaldiPitch().
| double kaldi::ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas | ( | const LatticeType & | lat, |
| bool | viterbi, | ||
| std::vector< double > * | alpha, | ||
| std::vector< double > * | beta | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 452 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), fst::ConvertToCost(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, and LogAddOrMax().
Referenced by CompactLatticeLimitDepth(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), and DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::ComputeLatticeScores().
| double kaldi::ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas | ( | const LatticeType & | lat, |
| bool | viterbi, | ||
| vector< double > * | alpha, | ||
| vector< double > * | beta | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 452 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), fst::ConvertToCost(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, and LogAddOrMax().
Referenced by CompactLatticeLimitDepth(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), and DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::ComputeLatticeScores().
| template double kaldi::ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| bool | viterbi, | ||
| vector< double > * | alpha, | ||
| vector< double > * | beta | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| bool | viterbi, | ||
| vector< double > * | alpha, | ||
| vector< double > * | beta | ||
| ) |
| void kaldi::ComputeLdaTransform | ( | const std::map< std::string, Vector< BaseFloat > *> & | utt2ivector, |
| const std::map< std::string, std::vector< std::string > > & | spk2utt, | ||
| BaseFloat | total_covariance_factor, | ||
| BaseFloat | covariance_floor, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | lda_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 107 of file ivector-compute-lda.cc.
References CovarianceStats::AccStats(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), ComputeNormalizingTransform(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), CovarianceStats::Empty(), CovarianceStats::GetTotalCovar(), CovarianceStats::GetWithinCovar(), CovarianceStats::Info(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), CovarianceStats::SingularTotCovar(), and SortSvd().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::ComputeLocalCost | ( | const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | nccf_pitch, |
| const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | lags, | ||
| const PitchExtractionOptions & | opts, | ||
| VectorBase< BaseFloat > * | local_cost | ||
| ) |
This function computes the local-cost for the Viterbi computation, see eq.
(5) in the paper.
| opts | The options as provided by the user |
| nccf_pitch | The nccf as computed for the pitch computation (with ballast). |
| lags | The log-spaced lags at which nccf_pitch is sampled. |
| local_cost | We output the local-cost to here. |
Definition at line 178 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Set(), and PitchExtractionOptions::soft_min_f0.
Referenced by PitchFrameInfo::ComputeBacktraces().
|
static |
Definition at line 283 of file regtree-mllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::d, SpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit().
Referenced by RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs::Update().
| void kaldi::ComputeNccf | ( | const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | inner_prod, |
| const VectorBase< BaseFloat > & | norm_prod, | ||
| BaseFloat | nccf_ballast, | ||
| VectorBase< BaseFloat > * | nccf_vec | ||
| ) |
Computes the NCCF as a fraction of the numerator term (a dot product between two vectors) and a denominator term which equals sqrt(e1*e2 + nccf_ballast) where e1 and e2 are both dot-products of bits of the wave with themselves, and e1*e2 is supplied as "norm_prod".
These quantities are computed by "ComputeCorrelation".
Definition at line 131 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by OnlinePitchFeatureImpl::AcceptWaveform().
|
static |
This function, called from ConvertAlignmentInternal(), works out suitable new lengths of phones in the case where subsample_factor != 1.
The input vectors 'mapped_phones' and 'old_lengths' must be the same size– the length of the phone sequence. The 'topology' object and 'mapped_phones' are needed to work out the minimum length of each phone in the sequence. Returns false only if it could not assign lengths (because the topology was too long relative to the number of frames).
| topology | [in] The new phone lengths are computed with regard to this topology |
| mapped_phones | [in] The phones for which this function computes new lengths |
| old_lengths | [in] The old lengths |
| conversion_shift | [in] This will normally equal subsample_factor - 1 but may be less than that if the 'repeat_frames' option is true; it's used for generating 'frame-shifted' versions of alignments that we will later interpolate. This helps us keep the phone boundaries of the subsampled and interpolated alignments the same as the original alignment. |
| subsample_factor | [in] The frame subsampling factor... normally 1, but might be > 1 if we're converting to a reduced-frame-rate system. |
| new_lengths | [out] The vector for storing new lengths. |
Definition at line 849 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and HmmTopology::MinLength().
Referenced by ConvertAlignmentInternal().
|
static |
This function computes a projection matrix that when applied makes the covariance unit (i.e.
all 1).
Definition at line 46 of file plda.cc.
References TpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromTp(), TpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), kNoTrans, and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by Plda::ApplyTransform(), ComputeLdaTransform(), and PldaEstimator::GetOutput().
| void kaldi::ComputeNormalizingTransform | ( | const SpMatrix< Real > & | covar, |
| Real | floor, | ||
| MatrixBase< Real > * | proj | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 84 of file ivector-compute-lda.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddDiagVecMat(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), KALDI_WARN, kTrans, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and SortSvd().
| template void kaldi::ComputePca | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | X, |
| MatrixBase< float > * | U, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | A, | ||
| bool | print_eigs, | ||
| bool | exact | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::ComputePca | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | X, |
| MatrixBase< double > * | U, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | A, | ||
| bool | print_eigs, | ||
| bool | exact | ||
| ) |
|
static |
Definition at line 320 of file build-tree.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, EventMap::Map(), EventMap::MaxResult(), and SplitStatsByMap().
Referenced by BuildTreeTwoLevel().
| void ComputeVadEnergy | ( | const VadEnergyOptions & | opts, |
| const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | input_features, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | output_voiced | ||
| ) |
Compute voice-activity vector for a file: 1 if we judge the frame as voiced, 0 otherwise.
There are no continuity constraints. This method is a very simple energy-based method which only looks at the first coefficient of "input_features", which is assumed to be a log-energy or something similar. A cutoff is set– we use a formula of the general type: cutoff = 5.0 + 0.5 * (average log-energy in this file), and for each frame the decision is based on the proportion of frames in a context window around the current frame, which are above this cutoff.
Definition at line 27 of file voice-activity-detection.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), VadEnergyOptions::vad_energy_mean_scale, VadEnergyOptions::vad_energy_threshold, VadEnergyOptions::vad_frames_context, and VadEnergyOptions::vad_proportion_threshold.
Referenced by main(), and VadEnergyOptions::Register().
| void kaldi::ConcatFeats | ( | const std::vector< Matrix< BaseFloat > > & | in, |
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file concat-feats.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::Range(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::ContainsNullPointers | ( | const std::vector< A *> & | v | ) |
Returns true if the vector of pointers contains NULL pointers.
Definition at line 197 of file stl-utils.h.
Referenced by ClusterBottomUp(), ClusterBottomUpCompartmentalized(), ClusterKMeans(), RefineClusters(), TestContainsNullPointers(), and TreeCluster().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertAddShiftComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component | ) |
Definition at line 99 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References AddShift::GetParams(), FixedBiasComponent::Init(), KALDI_ASSERT, and AddShift::NumParams().
Referenced by ConvertComponent().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertAffineTransformComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component, |
| const bool | use_preconditioned_affine_component | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 32 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References AffineTransform::GetBias(), AffineTransform::GetLinearity(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ConvertComponent().
|
inlinestatic |
This function is used internally inside ConvertAlignment; it converts the alignment for a single phone.
'new_phone_window' is the window of phones as required by the tree. The size of 'new_phone_alignment' is the length requested, which may not always equal 'old_phone_alignment' (in case the 'subsample' value is not 1).
Definition at line 742 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References ContextDependencyInterface::CentralPosition(), ChangeReorderingOfAlignment(), ContextDependencyInterface::Compute(), GetRandomAlignmentForPhone(), TransitionModel::GetTopo(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, TransitionModel::PairToTransitionId(), HmmTopology::TopologyForPhone(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToHmmState(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToTransitionIndex(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToTransitionState(), TransitionModel::TransitionStateToForwardPdfClass(), TransitionModel::TransitionStateToSelfLoopPdfClass(), TransitionModel::TupleToTransitionState(), and WriteIntegerVector().
Referenced by ConvertAlignmentInternal().
|
static |
This function is the same as 'ConvertAligment', but instead of the 'repeat_frames' option it supports the 'conversion_shift' option; see the documentation of ComputeNewPhoneLengths() for what 'conversion_shift' is for.
Definition at line 926 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References ContextDependencyInterface::CentralPosition(), ComputeNewPhoneLengths(), ContextDependencyInterface::ContextWidth(), ConvertAlignmentForPhone(), TransitionModel::GetTopo(), rnnlm::i, IsReordered(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, SplitToPhones(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by ConvertAlignment().
| void ConvertCompactLatticeToPhones | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans_model, |
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, replace the sequences of transition-ids with sequences of phones.
Note that this is different from ConvertLatticeToPhones, in that we replace the transition-ids not the words.
Definition at line 700 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References TransitionModel::IsFinal(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by main().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component, |
| const bool | use_preconditioned_affine_component | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 130 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References ConvertAddShiftComponent(), ConvertAffineTransformComponent(), ConvertRescaleComponent(), ConvertSigmoidComponent(), ConvertSoftmaxComponent(), ConvertSpliceComponent(), Component::GetType(), Component::kAddShift, Component::kAffineTransform, KALDI_ERR, Component::kRescale, Component::kSigmoid, Component::kSoftmax, Component::kSplice, and Component::TypeToMarker().
Referenced by ConvertNnet1ToNnet2().
| std::string kaldi::ConvertIntToString | ( | const int & | number | ) |
Definition at line 38 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
Referenced by UnitTestComputeGPE(), UnitTestDiffSampleRate(), UnitTestKeele(), UnitTestKeeleNccfBallast(), UnitTestPenaltyFactor(), UnitTestPitchExtractionSpeed(), UnitTestPitchExtractorCompareKeele(), and UnitTestProcess().
| void ConvertLatticeToPhones | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans_model, |
| Lattice * | lat | ||
| ) |
Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, replace the output symbols (presumably words), with phones; we use the TransitionModel to work out the phone sequence.
Note that the phone labels are not exactly aligned with the phone boundaries. We put a phone label to coincide with any transition to the final, nonemitting state of a phone (this state always exists, we ensure this in HmmTopology::Check()). This would be the last transition-id in the phone if reordering is not done (but typically we do reorder). Also see PhoneAlignLattice, in phone-align-lattice.h.
Definition at line 423 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References TransitionModel::IsSelfLoop(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToHmmState(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::ConvertLatticeToUnweightedAcceptor | ( | const kaldi::Lattice & | ilat, |
| const LabelPairVector & | wildcards, | ||
| fst::StdVectorFst * | ofst | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 63 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
References fst::ConvertLattice().
Referenced by main().
| nnet2::Nnet* kaldi::ConvertNnet1ToNnet2 | ( | const nnet1::Nnet & | nnet1, |
| const bool | use_preconditioned_affine_component | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 156 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References ConvertComponent(), Nnet::GetComponent(), rnnlm::i, and Nnet::NumComponents().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 594 of file ivector-extractor.cc.
References GaussInfo::frame_weights, and GaussInfo::tot_weight.
Referenced by OnlineIvectorEstimationStats::AccStats().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertRescaleComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component | ) |
Definition at line 114 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References Rescale::GetParams(), FixedScaleComponent::Init(), KALDI_ASSERT, and Rescale::NumParams().
Referenced by ConvertComponent().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertSigmoidComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component | ) |
Definition at line 71 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References Component::InputDim(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ConvertComponent().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertSoftmaxComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component | ) |
Definition at line 63 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References Component::InputDim(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ConvertComponent().
| nnet2::Component* kaldi::ConvertSpliceComponent | ( | const nnet1::Component & | nnet1_component | ) |
Definition at line 79 of file nnet1-to-raw-nnet.cc.
References SpliceComponent::Init(), Component::InputDim(), KALDI_ASSERT, ReadIntegerVector(), and Splice::WriteData().
Referenced by ConvertComponent().
| bool kaldi::ConvertStringToInteger | ( | const std::string & | str, |
| Int * | out | ||
| ) |
Converts a string into an integer via strtoll and returns false if there was any kind of problem (i.e.
the string was not an integer or contained extra non-whitespace junk, or the integer was too large to fit into the type it is being converted into). Only sets *out if everything was OK and it returns true.
Definition at line 118 of file text-utils.h.
References ConvertStringToReal(), rnnlm::i, IsLine(), IsToken(), KALDI_ASSERT_IS_INTEGER_TYPE, KALDI_STRTOLL, SplitStringOnFirstSpace(), StringsApproxEqual(), and Trim().
Referenced by ExampleMergingConfig::ComputeDerived(), ConfigLine::GetValue(), WordBoundaryInfo::Init(), MultiTaskLoss::InitFromString(), main(), GeneralDescriptor::ParseConst(), kaldi::nnet2::ParseFromString(), kaldi::nnet3::ProcessRangeFile(), ArpaFileParser::Read(), HmmTopology::Read(), fst::ReadFstKaldi(), kaldi::nnet3::ReadIntegerToken(), ReadPosterior(), LatticeReader::ReadText(), kaldi::nnet3::SelectFromExample(), Fmpe::SetContexts(), OffsetFileInputImpl::SplitFilename(), TestConvertStringToInteger(), ParseOptions::ToInt(), and ParseOptions::ToUint().
| bool ConvertStringToReal | ( | const std::string & | str, |
| T * | out | ||
| ) |
ConvertStringToReal converts a string into either float or double and returns false if there was any kind of problem (i.e.
the string was not a floating point number or contained extra non-whitespace junk). Be careful- this function will successfully read inf's or nan's.
Definition at line 238 of file text-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by ConvertStringToInteger(), kaldi::nnet3::DescriptorTokenize(), ConfigLine::GetValue(), MultiTaskLoss::InitFromString(), main(), GeneralDescriptor::ParseConst(), kaldi::nnet2::ParseFromString(), GeneralDescriptor::ParseScale(), ArpaFileParser::Read(), ReadCommaSeparatedCommand(), Fmpe::SetContexts(), SplitStringToFloats(), TestConvertStringToReal(), TestInf(), TestNan(), ParseOptions::ToDouble(), and ParseOptions::ToFloat().
| template bool kaldi::ConvertStringToReal | ( | const std::string & | str, |
| double * | out | ||
| ) |
| CompactLattice* kaldi::ConvertToCompactLattice | ( | fst::VectorFst< OrigWeightType > * | ifst | ) |
Converts lattice types if necessary, deleting its input.
Definition at line 29 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References fst::ConvertLattice().
Referenced by ReadCompactLattice(), and ReadCompactLatticeText().
| CompactLattice* kaldi::ConvertToCompactLattice | ( | CompactLattice * | ifst | ) |
Definition at line 40 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
| Lattice* kaldi::ConvertToLattice | ( | fst::VectorFst< OrigWeightType > * | ifst | ) |
Converts lattice types if necessary, deleting its input.
Definition at line 46 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References fst::ConvertLattice().
Referenced by ReadLattice(), and ReadLatticeText().
Definition at line 57 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
Definition at line 34 of file signal.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Vector< Real >::Resize(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
Referenced by UnitTestFFTbasedConvolution().
| void kaldi::CopyMapKeysToSet | ( | const std::map< A, B > & | m, |
| std::set< A > * | s | ||
| ) |
Copies the keys in a map to a set.
Definition at line 150 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by TestCopyMapKeysToSet(), and TestFindAllKeys().
| void kaldi::CopyMapKeysToVector | ( | const std::map< A, B > & | m, |
| std::vector< A > * | v | ||
| ) |
Copies the keys in a map to a vector.
Definition at line 126 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by Questions::GetKeysWithQuestions(), TestCopyMapKeysToSet(), and TestCopyMapKeysToVector().
| void kaldi::CopyMapToVector | ( | const std::map< A, B > & | m, |
| std::vector< std::pair< A, B > > * | v | ||
| ) |
Copies the (key, value) pairs in a map to a vector of pairs.
Definition at line 112 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by GenRandStats(), TestCopyMapToVector(), TestFindAllKeys(), and TestPossibleValues().
| void kaldi::CopyMapValuesToSet | ( | const std::map< A, B > & | m, |
| std::set< B > * | s | ||
| ) |
Copies the values in a map to a set.
Definition at line 161 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by TestCopyMapValuesToSet().
| void kaldi::CopyMapValuesToVector | ( | const std::map< A, B > & | m, |
| std::vector< B > * | v | ||
| ) |
Copies the values in a map to a vector.
Definition at line 138 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by TestCopyMapValuesToSet(), and TestCopyMapValuesToVector().
| void kaldi::CopySetToVector | ( | const std::set< T > & | s, |
| std::vector< T > * | v | ||
| ) |
Copies the elements of a set to a vector.
Definition at line 86 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ConstIntegerSet< EventValueType >::ConstIntegerSet(), fst::GetInputSymbols(), kaldi::nnet3::GetIoNames(), fst::GetOutputSymbols(), GetSeenPhones(), ConstIntegerSet< EventValueType >::Init(), PossibleValues(), RandomEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapRestricted(), fst::TestContextFst(), TestCopySetToVector(), TestEventMapIo(), TestFindAllKeys(), TestGenRandContextDependency(), TestMonophoneContextDependency(), TestPossibleValues(), TestQuestionsInitRand(), TestShareEventMapLeaves(), and TestSplitDecisionTree().
| void kaldi::CopySetToVector | ( | const unordered_set< T > & | s, |
| std::vector< T > * | v | ||
| ) |
| int32 kaldi::CopySubsetLattices | ( | std::string | filename, |
| SequentialLatticeReader * | lattice_reader, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| bool | include = true, |
||
| bool | ignore_missing = false, |
||
| bool | sorted = false |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 28 of file lattice-copy.cc.
References SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), SplitStringToVector(), Input::Stream(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| int32 kaldi::CopySubsetLattices | ( | std::string | filename, |
| SequentialCompactLatticeReader * | lattice_reader, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| bool | include = true, |
||
| bool | ignore_missing = false, |
||
| bool | sorted = false |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 79 of file lattice-copy.cc.
References SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), SplitStringToVector(), Input::Stream(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
| void kaldi::CopyVectorToSet | ( | const std::vector< A > & | v, |
| std::set< A > * | s | ||
| ) |
Copies the contents of a vector to a set.
Definition at line 172 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by kaldi::nnet3::ComputeCommandPairs(), TestCopyMapKeysToSet(), and TestCopyMapValuesToSet().
| void kaldi::CopyVectorToVector | ( | const std::vector< A > & | vec_in, |
| std::vector< B > * | vec_out | ||
| ) |
Copies the contents a vector of one type to a vector of another type.
Definition at line 207 of file stl-utils.h.
References rnnlm::i, and KALDI_ASSERT.
| void kaldi::CountErrors | ( | const fst::StdVectorFst & | fst, |
| int32 * | correct, | ||
| int32 * | substitutions, | ||
| int32 * | insertions, | ||
| int32 * | deletions, | ||
| int32 * | num_words | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 114 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 119 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
References AddSelfLoops(), Compile(), CreateGenFst(), ArpaLmCompiler::Fst(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_WARN, kRandomSentences, and ArpaLmCompiler::MutableFst().
Referenced by RunAllTests().
| void kaldi::CreateEditDistance | ( | const fst::StdVectorFst & | fst1, |
| const fst::StdVectorFst & | fst2, | ||
| fst::StdVectorFst * | pfst | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 77 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
References fst::GetInputSymbols(), fst::GetOutputSymbols(), rnnlm::i, and rnnlm::j.
Referenced by main().
| template void kaldi::CreateEigenvalueMatrix | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | re, |
| const VectorBase< float > & | im, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | D | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::CreateEigenvalueMatrix | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | re, |
| const VectorBase< double > & | im, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | D | ||
| ) |
Referenced by CreateEigenvalueMatrix(), and MatrixBase< float >::Power().
| bool CreateFactorTransducer | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | state_times, | ||
| int32 | utterance_id, | ||
| KwsProductFst * | factor_transducer | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 160 of file kws-functions.cc.
References ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas(), ComputeCompactLatticeBetas(), fst::ComputeStateInfo(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_WARN, fst::kStateHasEpsilonArcsEntering, fst::kStateHasEpsilonArcsLeaving, fst::kStateHasNonEpsilonArcsEntering, fst::kStateHasNonEpsilonArcsLeaving, and ArcticWeightTpl< T >::One().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 44 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
References kBos, kDisambig, kEos, and kEps.
Referenced by CoverageTest().
|
static |
Definition at line 34 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CuBlockMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 173 of file cu-block-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CuCompressedMatrixTestNonnegative | ( | ) |
Definition at line 54 of file cu-compressed-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), CuCompressedMatrixBase::CopyFromMat(), CuCompressedMatrixBase::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kCompressedMatrixUint16, kCompressedMatrixUint8, kUndefined, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Max(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Min(), NewCuCompressedMatrix(), RandInt(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::CuCompressedMatrixTestSign | ( | ) |
Definition at line 34 of file cu-compressed-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuCompressedMatrixBase::CopyFromMat(), CuCompressedMatrixBase::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Heaviside(), kCompressedMatrixUint8, kUndefined, NewCuCompressedMatrix(), RandInt(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::CuCompressedMatrixTestSymmetric | ( | ) |
Definition at line 107 of file cu-compressed-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), CuCompressedMatrixBase::CopyFromMat(), CuCompressedMatrixBase::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kCompressedMatrixInt16, kCompressedMatrixInt8, kUndefined, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Max(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Min(), NewCuCompressedMatrix(), RandInt(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::CudaMathUnitTest | ( | ) |
| void kaldi::CudaMatrixResizeTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 81 of file cu-device-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaMatrixSpeedTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1012 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References kNoTrans, and kTrans.
| void kaldi::CudaMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 2941 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaPackedMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 231 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaSparseMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 271 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaSpMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 342 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaSpMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 356 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaTpMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 176 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CudaVectorSpeedTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 402 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, kNoTrans, and kTrans.
|
static |
Definition at line 561 of file cu-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CuRandGaussianMatrixBaseSpeedTest | ( | const int32 | iter | ) |
Definition at line 129 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, MeanVariance(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and CuRand< Real >::RandGaussian().
| void kaldi::CuRandGaussianMatrixSpeedTest | ( | const int32 | iter | ) |
Definition at line 110 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, MeanVariance(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and CuRand< Real >::RandGaussian().
| void kaldi::CuRandGaussianVectorSpeedTest | ( | const int32 | iter | ) |
Definition at line 167 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::Dim(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, MeanVariance(), and CuRand< Real >::RandGaussian().
| void kaldi::CuRandUniformMatrixBaseSpeedTest | ( | const int32 | iter | ) |
Definition at line 91 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, MeanVariance(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and CuRand< Real >::RandUniform().
| void kaldi::CuRandUniformMatrixSpeedTest | ( | const int32 | iter | ) |
Definition at line 72 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, MeanVariance(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and CuRand< Real >::RandUniform().
| void kaldi::CuRandUniformVectorSpeedTest | ( | const int32 | iter | ) |
Definition at line 148 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::Dim(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, MeanVariance(), and CuRand< Real >::RandUniform().
| void kaldi::CuSpMatrixSpeedTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 107 of file cu-sp-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References kTakeLower, kTakeMean, and kTakeUpper.
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 780 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddColSumMat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 264 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), AssertEqual(), Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMat2 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 668 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), AssertEqual(), kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 692 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMatMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), rnnlm::d, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Scale(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddMatVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 725 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddRowSumMat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 249 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), AssertEqual(), Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddSpVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 754 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 155 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddVecCross | ( | ) |
Definition at line 169 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddVecExtra | ( | ) |
Definition at line 194 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestAddVecVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 647 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeiling | ( | ) |
Definition at line 591 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeilingNoCount | ( | ) |
Definition at line 613 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), AssertEqual(), Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyExp | ( | ) |
Definition at line 522 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), Exp(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloor | ( | ) |
Definition at line 554 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloorNoCount | ( | ) |
Definition at line 576 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), AssertEqual(), Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyLog | ( | ) |
Definition at line 536 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyLog(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Log(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplyPow | ( | ) |
Definition at line 628 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), AssertEqual(), Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApplySoftMax | ( | ) |
Definition at line 506 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplySoftMax(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplySoftMax(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestApproxEqual | ( | ) |
Definition at line 280 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross | ( | ) |
Definition at line 424 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross2 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 438 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromMat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 452 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), rnnlm::i, kUndefined, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Sum(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), MatrixBase< Real >::Trace(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Trace(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromPacked | ( | ) |
Definition at line 409 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromPacked(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromPacked(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kUndefined, Rand(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestCopyElements | ( | ) |
Definition at line 207 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyElements(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, kNoTrans, kTrans, kUndefined, rnnlm::n, Rand(), CuMatrix< Real >::Resize(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestCopyFromMat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 375 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromVec(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestInvertElements | ( | ) |
Definition at line 327 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::InvertElements(), CuVectorBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecVec().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestMax | ( | ) |
Definition at line 494 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, CuVectorBase< Real >::Max(), VectorBase< Real >::Max(), Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestMin | ( | ) |
Definition at line 482 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, CuVectorBase< Real >::Min(), VectorBase< Real >::Min(), Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestNorm | ( | ) |
Definition at line 472 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, and CuVectorBase< Real >::Norm().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestScale | ( | ) |
Definition at line 361 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestSum | ( | ) |
Definition at line 341 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApplyAbs(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Set(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), and VecVec().
| void kaldi::CuVectorUnitTestVecVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 144 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecVec().
|
static |
Referenced by prefixp().
|
static |
Definition at line 110 of file kaldi-cygwin-io-inl.h.
| StateId kaldi::DecodeLabelUid | ( | uint64 | osymbol | ) |
| bool kaldi::DecodeUtterance | ( | LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 36 of file gmm-latgen-biglm-faster.cc.
References fst::AcousticLatticeScale(), LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder::Decode(), LatticeFasterDecoderConfig::det_opts, fst::DeterminizeLatticePhonePrunedWrapper(), LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder::GetBestPath(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder::GetOptions(), LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder::GetRawLattice(), rnnlm::i, TableWriter< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, LatticeFasterDecoderConfig::lattice_beam, LatticeBiglmFasterDecoder::ReachedFinal(), fst::ScaleLattice(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), words, and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| bool DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster | ( | LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST > & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignments_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
This function DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster is used in several decoders, and we have moved it here.
Note: this is really "binary-level" code as it involves table readers and writers; we've just put it here as there is no other obvious place to put it. If determinize == false, it writes to lattice_writer, else to compact_lattice_writer. The writers for alignments and words will only be written to if they are open.
Caution: this will only link correctly if FST is either fst::Fst<fst::StdArc>, or fst::GrammarFst, as the template function is defined in the .cc file and only instantiated for those two types.
Definition at line 287 of file decoder-wrappers.cc.
References fst::AcousticLatticeScale(), LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::Decode(), DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental(), fst::DeterminizeLatticePhonePrunedWrapper(), LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::GetBestPath(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::GetOptions(), LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::GetRawLattice(), rnnlm::i, TableWriter< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::ReachedFinal(), fst::ScaleLattice(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), words, and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main(), ProcessUtterance(), and AlignConfig::Register().
| template bool kaldi::DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster | ( | LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster | ( | LatticeFasterDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
| bool DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental | ( | LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST > & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
TODO.
Definition at line 199 of file decoder-wrappers.cc.
References fst::AcousticLatticeScale(), CompactLatticeShortestPath(), fst::ConvertLattice(), LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::Decode(), LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::GetLattice(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), rnnlm::i, TableWriter< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::NumFramesDecoded(), LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< FST, Token >::ReachedFinal(), fst::ScaleLattice(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), words, and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster(), main(), and AlignConfig::Register().
| template bool kaldi::DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental | ( | LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::DecodeUtteranceLatticeIncremental | ( | LatticeIncrementalDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
| bool DecodeUtteranceLatticeSimple | ( | LatticeSimpleDecoder & | decoder, |
| DecodableInterface & | decodable, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| std::string | utt, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignment_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 448 of file decoder-wrappers.cc.
References fst::AcousticLatticeScale(), LatticeSimpleDecoder::Decode(), LatticeSimpleDecoderConfig::det_opts, fst::DeterminizeLatticePhonePrunedWrapper(), LatticeSimpleDecoder::GetBestPath(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), LatticeSimpleDecoder::GetOptions(), LatticeSimpleDecoder::GetRawLattice(), rnnlm::i, TableWriter< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, LatticeSimpleDecoderConfig::lattice_beam, LatticeSimpleDecoder::ReachedFinal(), fst::ScaleLattice(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), words, TableWriter< Holder >::Write(), and LatticeWeightTpl< BaseFloat >::Zero().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::DeletePointers | ( | std::vector< A *> * | v | ) |
Deletes any non-NULL pointers in the vector v, and sets the corresponding entries of v to NULL.
Definition at line 184 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by AutomaticallyObtainQuestions(), BlockAffineComponent::Backprop(), RegressionTree::BuildTree(), ClusterEventMap(), ClusterEventMapGetMapping(), ClusterEventMapRestrictedByKeys(), ClusterEventMapRestrictedByMap(), ClusterEventMapToNClustersRestrictedByMap(), ClusterGaussiansToUbm(), ClusterKMeans(), ComputeInitialSplit(), AmDiagGmm::CopyFromAmDiagGmm(), DoTableSplit(), FindBestSplitForKey(), RegressionTree::GatherStats(), GetHTransducer(), AmDiagGmm::Init(), AccumAmDiagGmm::Init(), RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs::Init(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Init(), CompositeComponent::Init(), InitAmGmm(), DecodableAmDiagGmmRegtreeMllr::InitCache(), CompositeComponent::InitFromConfig(), KMeansClusterPhones(), main(), MapEventMapLeaves(), DiagGmm::MergeKmeans(), ObjfGivenMap(), BlockAffineComponent::Propagate(), Questions::Read(), RenumberEventMap(), ShareEventMapLeaves(), TestAddToClusters(), TestAddToClustersOptimized(), TestClusterBottomUp(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap2(), TestClusterKMeans(), TestClusterKMeansVector(), TestClusterTopDown(), TestEnsureClusterableVectorNotNull(), TestRefineClusters(), TestTreeCluster(), TypeOneUsage(), TypeOneUsageAverage(), UnitTestRegtreeFmllrDiagGmm(), RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), AccumAmDiagGmm::~AccumAmDiagGmm(), AmDiagGmm::~AmDiagGmm(), BottomUpClusterer::~BottomUpClusterer(), CompartmentalizedBottomUpClusterer::~CompartmentalizedBottomUpClusterer(), CompositeComponent::~CompositeComponent(), DecodableAmDiagGmmRegtreeMllr::~DecodableAmDiagGmmRegtreeMllr(), DecodableAmNnetSimpleParallel::~DecodableAmNnetSimpleParallel(), GeneralDescriptor::~GeneralDescriptor(), Questions::~Questions(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::~RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs(), RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs::~RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs(), SwitchingForwardingDescriptor::~SwitchingForwardingDescriptor(), TableEventMap::~TableEventMap(), and TreeClusterer::~TreeClusterer().
| bool DeterminizeLatticeWrapper | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| const std::string & | key, | ||
| bool | prune, | ||
| BaseFloat | beam, | ||
| BaseFloat | beam_ratio, | ||
| int32 | max_mem, | ||
| int32 | max_loop, | ||
| BaseFloat | delta, | ||
| int32 | num_loops, | ||
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 38 of file lattice-determinize-non-compact.cc.
References DeterminizeLatticeOptions::delta, fst::DeterminizeLattice(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_WARN, DeterminizeLatticeOptions::max_loop, DeterminizeLatticeOptions::max_mem, fst::NumArcs(), and PruneLattice().
Referenced by main().
| void DiagGmmToStats | ( | const DiagGmm & | gmm, |
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| double | state_occ, | ||
| AccumDiagGmm * | dst_stats | ||
| ) |
Creates stats from the GMM. Resizes them as needed.
Definition at line 339 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::AddStatsForComponent(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), AugmentGmmFlags(), DiagGmm::Dim(), DiagGmmNormal::means_, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), VectorBase< Real >::SetZero(), DiagGmmNormal::vars_, and DiagGmmNormal::weights_.
Referenced by IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmmFromModel(), and EbwWeightOptions::Register().
|
static |
Definition at line 303 of file kws-functions.cc.
References fst::RemoveWeights().
Referenced by MaybeDoSanityCheck().
| bool kaldi::DirExist | ( | const std::string & | dirname | ) |
Returns a / b, rounding towards negative infinity in all cases.
Definition at line 287 of file kaldi-math.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by BackpropTruncationComponent::PrecomputeIndexes(), GeneralDropoutComponent::PrecomputeIndexes(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::RoundDownToMultipleOf(), and UnitTestDivideRoundingDown().
| void DoFactorDisambiguation | ( | KwsLexicographicFst * | index_transducer | ) |
Definition at line 98 of file kws-functions2.cc.
Referenced by main().
| void DoFactorMerging | ( | KwsProductFst * | factor_transducer, |
| KwsLexicographicFst * | index_transducer | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 53 of file kws-functions2.cc.
References fst::DeterminizeStar(), KALDI_VLOG, MaybeDoSanityCheck(), and ReplaceSymbolWithEpsilon().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::DoRescalingUpdate | ( | const AccumDiagGmm & | old_ml_acc, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | new_ml_acc, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_variance, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_gaussian_occupancy, | ||
| DiagGmm * | gmm, | ||
| double * | tot_count, | ||
| double * | tot_divergence | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 177 of file indirect-diff-diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmmNormal::CopyToDiagGmm(), rnnlm::d, DiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, Log(), AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), DiagGmmNormal::means_, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator(), and DiagGmmNormal::vars_.
Referenced by DoRescalingUpdate(), and main().
| void DoRescalingUpdate | ( | const AccumAmDiagGmm & | old_ml_accs, |
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | new_ml_accs, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_variance, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_gaussian_occupancy, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 232 of file indirect-diff-diag-gmm.cc.
References AmDiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), DoRescalingUpdate(), AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), and AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs().
| float kaldi::DoReverberation | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | rir, |
| BaseFloat | samp_freq, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | signal | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 93 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References ComputeEarlyReverbEnergy(), and FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 444 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
Referenced by DoubleFactorial(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetRandn(), and UnitTestSetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 31 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, Log(), VectorBase< Real >::Min(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
Referenced by UpdateEbwDiagGmm().
Definition at line 26 of file signal.cc.
References ComplexMul(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), and rnnlm::i.
Referenced by FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals(), and FFTbasedConvolveSignals().
Definition at line 35 of file kws-search.cc.
Referenced by main().
| template bool kaldi::EndpointDetected< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > | ( | const OnlineEndpointConfig & | config, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| BaseFloat | frame_shift_in_seconds, | ||
| const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > & | decoder | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::EndpointDetected< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > | ( | const OnlineEndpointConfig & | config, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| BaseFloat | frame_shift_in_seconds, | ||
| const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > & | decoder | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::EndpointDetected< fst::GrammarFst > | ( | const OnlineEndpointConfig & | config, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| BaseFloat | frame_shift_in_seconds, | ||
| const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > & | decoder | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::EndpointDetected< fst::GrammarFst > | ( | const OnlineEndpointConfig & | config, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| BaseFloat | frame_shift_in_seconds, | ||
| const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > & | decoder | ||
| ) |
| double EstimateIvectorsOnline | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const Posterior & | post, | ||
| const IvectorExtractor & | extractor, | ||
| int32 | ivector_period, | ||
| int32 | num_cg_iters, | ||
| BaseFloat | max_count, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | ivectors | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 1778 of file ivector-extractor.cc.
References IvectorExtractor::IvectorDim(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), IvectorExtractor::PriorOffset(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by main().
| void EstimateSgmm2FmllrSubspace | ( | const SpMatrix< double > & | fmllr_grad_scatter, |
| int32 | num_fmllr_bases, | ||
| int32 | feat_dim, | ||
| Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams * | fmllr_globals, | ||
| double | min_eig = 0.0 |
||
| ) |
Computes the fMLLR basis matrices given the scatter of the vectorized gradients (eq: B.10).
The result is stored in 'fmllr_globals'. The actual number of bases may be less than 'num_fmllr_bases' depending on the feature dimension and number of eigenvalues greater than 'min_eig'.
Definition at line 506 of file fmllr-sgmm2.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), Sgmm2FmllrGlobalParams::fmllr_bases_, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, kSetZero, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and SortSvd().
Referenced by TestSgmm2FmllrSubspace().
| bool kaldi::EstPca | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | ivector_mat, |
| BaseFloat | target_energy, | ||
| const std::string & | reco, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | mat | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 29 of file ivector-plda-scoring-dense.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), VectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2(), ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), KALDI_WARN, kCopyData, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), SpMatrix< Real >::Resize(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), SortSvd(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
Referenced by main().
| std::string EventTypeToString | ( | const EventType & | evec | ) |
Definition at line 253 of file event-map.cc.
Referenced by FilterStatsByKey(), MakeEventPair(), SplitStatsByKey(), and SplitStatsByMap().
|
inline |
Definition at line 83 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by MinimumBayesRisk::AccStats(), VectorBase< float >::ApplyExp(), VectorBase< float >::ApplyLogSoftMax(), VectorBase< float >::ApplySoftMax(), MatrixBase< float >::ApplySoftMax(), TransitionModel::ComputeDerivedOfProbs(), AmSgmm2::ComputeNormalizers(), AmSgmm2::ComputeNormalizersInternal(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyExp(), MinimumBayesRisk::EditDistance(), Exp(), MatrixBase< float >::Exp(), MatrixBase< float >::ExpLimited(), MatrixBase< float >::ExpSpecial(), generate_features(), AmSgmm2::GetDjms(), TransitionModel::GetTransitionProb(), init_rand_diag_gmm(), kaldi::unittest::InitRandDiagGmm(), InitRandomGmm(), LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), LogAdd(), LogSub(), VectorBase< float >::LogSumExp(), MatrixBase< float >::LogSumExp(), main(), NccfToPov(), PushSpecialClass::PushSpecialClass(), rand_diag_gmm(), kaldi::cu::ScalarSigmoid(), kaldi::cu::ScalarTanh(), VectorBase< float >::Sigmoid(), MatrixBase< float >::SoftHinge(), VectorBase< float >::Tanh(), PushSpecialClass::TestAccuracy(), TestSgmm2Fmllr(), UnitTestDefines(), UnitTestDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateSgmm2(), UnitTestExpSpeed(), UnitTestLbfgs(), UnitTestLogAddSub(), UnitTestMleAmDiagGmm(), UnitTestSigmoid(), UnitTestSimple(), UnitTestSimpleForVec(), UnitTestSoftHinge(), UnitTestTanh(), and VectorToPosteriorEntry().
| void ExpectOneOrTwoTokens | ( | std::istream & | is, |
| bool | binary, | ||
| const std::string & | token1, | ||
| const std::string & | token2 | ||
| ) |
This function is like ExpectToken but for two tokens, and it will either accept token1 and then token2, or just token2.
This is useful in Read functions where the first token may already have been consumed.
Definition at line 536 of file text-utils.cc.
References ExpectToken(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, and ReadToken().
Referenced by PnormComponent::Read(), DistributeComponent::Read(), DistributeComponentPrecomputedIndexes::Read(), RestrictedAttentionComponent::Read(), ElementwiseProductComponent::Read(), RestrictedAttentionComponent::PrecomputedIndexes::Read(), BatchNormComponent::Read(), StatisticsExtractionComponent::Read(), ConvolutionModel::Read(), TimeHeightConvolutionComponent::PrecomputedIndexes::Read(), StatisticsExtractionComponentPrecomputedIndexes::Read(), ConvolutionComputation::Read(), StatisticsPoolingComponent::Read(), StatisticsPoolingComponentPrecomputedIndexes::Read(), BackpropTruncationComponent::Read(), MaxpoolingComponent::Read(), TdnnComponent::PrecomputedIndexes::Read(), BackpropTruncationComponentPrecomputedIndexes::Read(), NonlinearComponent::Read(), DropoutMaskComponent::Read(), GeneralDropoutComponent::Read(), GeneralDropoutComponentPrecomputedIndexes::Read(), FixedAffineComponent::Read(), SpecAugmentTimeMaskComponent::Read(), SumGroupComponent::Read(), SpecAugmentTimeMaskComponentPrecomputedIndexes::Read(), FixedScaleComponent::Read(), FixedBiasComponent::Read(), NoOpComponent::Read(), SumBlockComponent::Read(), ClipGradientComponent::Read(), and PermuteComponent::Read().
| void ExtendWaveWithSilence | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | wav_in, |
| BaseFloat | samp_rate, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | wav_out, | ||
| BaseFloat | sil_search_len, | ||
| BaseFloat | sil_extract_len, | ||
| BaseFloat | sil_extract_shift | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 152 of file extend-wav-with-silence.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), FindQuietestSegment(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, M_2PI, and VectorBase< Real >::Range().
Referenced by main().
| template bool kaldi::ExtractObjectRange | ( | const CompressedMatrix & | , |
| const std::string & | , | ||
| Matrix< float > * | |||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::ExtractObjectRange | ( | const CompressedMatrix & | , |
| const std::string & | , | ||
| Matrix< double > * | |||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::ExtractObjectRange | ( | const Matrix< double > & | , |
| const std::string & | , | ||
| Matrix< double > * | |||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::ExtractObjectRange | ( | const Matrix< float > & | , |
| const std::string & | , | ||
| Matrix< float > * | |||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::ExtractObjectRange | ( | const Vector< double > & | , |
| const std::string & | , | ||
| Vector< double > * | |||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::ExtractObjectRange | ( | const Vector< float > & | , |
| const std::string & | , | ||
| Vector< float > * | |||
| ) |
| void kaldi::Factorize | ( | I | m, |
| std::vector< I > * | factors | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 325 of file kaldi-math.h.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ComplexFft(), and UnitTestFactorizeTpl().
| void FakeStatsForSomeDims | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | dims, |
| MatrixBase< double > * | stats | ||
| ) |
Modify the stats so that for some dimensions (specified in "dims"), we replace them with "fake" stats that have zero mean and unit variance; this is done to disable CMVN for those dimensions.
Definition at line 168 of file cmvn.cc.
References count, rnnlm::d, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by OnlineCmvn::GetFrame(), and main().
| void FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | filter, |
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | signal | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 77 of file signal.cc.
References SplitRadixRealFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), ElementwiseProductOfFft(), KALDI_VLOG, kCopyData, VectorBase< Real >::Range(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), RoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
Referenced by ComputeEarlyReverbEnergy(), DoReverberation(), and UnitTestFFTbasedBlockConvolution().
Definition at line 50 of file signal.cc.
References SplitRadixRealFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), ElementwiseProductOfFft(), KALDI_VLOG, VectorBase< Real >::Range(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), RoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
Referenced by UnitTestFFTbasedBlockConvolution(), and UnitTestFFTbasedConvolution().
| template void kaldi::FilterMatrixRows | ( | const Matrix< float > & | in, |
| const std::vector< bool > & | keep_rows, | ||
| Matrix< float > * | out | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::FilterMatrixRows | ( | const Matrix< double > & | in, |
| const std::vector< bool > & | keep_rows, | ||
| Matrix< double > * | out | ||
| ) |
Referenced by FilterCompressedMatrixRows(), FilterGeneralMatrixRows(), and FilterMatrixRows().
| template void kaldi::FilterSparseMatrixRows | ( | const SparseMatrix< float > & | in, |
| const std::vector< bool > & | keep_rows, | ||
| SparseMatrix< float > * | out | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::FilterSparseMatrixRows | ( | const SparseMatrix< double > & | in, |
| const std::vector< bool > & | keep_rows, | ||
| SparseMatrix< double > * | out | ||
| ) |
Referenced by FilterGeneralMatrixRows(), and FilterSparseMatrixRows().
| void FindQuietestSegment | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | wav_in, |
| BaseFloat | samp_rate, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | wav_sil, | ||
| BaseFloat | search_dur = 0.5, |
||
| BaseFloat | seg_dur = 0.1, |
||
| BaseFloat | seg_shift_dur = 0.05 |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 195 of file extend-wav-with-silence.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, VectorBase< Real >::Range(), and VecVec().
Referenced by ExtendWaveWithSilence().
| BaseFloat FmllrAuxfGradient | ( | const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats, | ||
| MatrixBase< BaseFloat > * | grad_out | ||
| ) |
Returns the (diagonal-GMM) FMLLR auxiliary function value given the transform and the stats.
Definition at line 510 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), AffineXformStats::beta_, MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), rnnlm::d, AffineXformStats::G_, AffineXformStats::K_, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::Range(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), TraceMatMat(), and VecVec().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet().
| float FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats | ||
| ) |
Returns the (diagonal-GMM) FMLLR auxiliary function value given the transform and the stats.
Definition at line 481 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), AffineXformStats::beta_, rnnlm::d, AffineXformStats::G_, AffineXformStats::K_, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), TraceMatMat(), and VecVec().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmDiagonal(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull(), LinearVtln::ComputeTransform(), and BasisFmllrEstimate::ComputeTransform().
| double FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | xform, |
| const AffineXformStats & | stats | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 496 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), AffineXformStats::beta_, rnnlm::d, AffineXformStats::G_, AffineXformStats::K_, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), TraceMatMat(), and VecVec().
| void FmllrInnerUpdate | ( | SpMatrix< double > & | inv_G, |
| VectorBase< double > & | k, | ||
| double | beta, | ||
| int32 | row, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | transform | ||
| ) |
This function does one row of the inner-loop fMLLR transform update.
We export it because it's needed in the RawFmllr code. Here, if inv_G is the inverse of the G matrix indexed by this row, and k is the corresponding row of the K matrix.
Definition at line 193 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Log(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), VectorBase< Real >::Range(), MatrixBase< Real >::Range(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and VecVec().
Referenced by ComputeFmllrLogDet(), ComputeFmllrMatrixDiagGmmFull(), and FmllrRawAccs::Update().
| void kaldi::FrameLevelLpp | ( | const SubVector< BaseFloat > & | prob_row, |
| const std::vector< std::set< int32 > > & | pdf2phones, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > * | phone_map, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | out_frame_level_lpp | ||
| ) |
FrameLevelLpp compute a log posterior for pure-phones by sum the posterior of the states belonging to those triphones whose current phone is the canonical phone:
p(p|o_t) = {s p} p(s|o_t),
where s is the senone label, {s|s p} is the states belonging to those riphones whose current phone is the canonical phone p.
Definition at line 76 of file compute-gop.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApplyLog(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| I kaldi::Gcd | ( | I | m, |
| I | n | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 297 of file kaldi-math.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, and rnnlm::n.
Referenced by ClusterKMeansOnce(), ConvolutionModel::ComputeDerived(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::FindGcdOfDifferences(), RestrictedAttentionComponent::GetComputationStructure(), Lcm(), LinearResample::LinearResample(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::PadComputationInputTime(), and UnitTestGcdLcmTpl().
|
static |
Definition at line 64 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::d, diag, Exp(), full, rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::Invert(), rnnlm::j, kNoTrans, RandFullCova(), RandGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero().
Referenced by UnitTestRegtreeFmllrDiagGmm().
| bool kaldi::GenerateActivePaths | ( | const KwsLexicographicFst & | proxy, |
| std::vector< ActivePath > * | paths, | ||
| KwsLexicographicFst::StateId | cur_state, | ||
| std::vector< KwsLexicographicArc::Label > | cur_path, | ||
| KwsLexicographicArc::Weight | cur_weight | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 90 of file kws-search.cc.
References ActivePath::last, ActivePath::path, fst::Times(), and ActivePath::weight.
Referenced by OutputDetailedStatistics().
| void kaldi::GenerateCompactLatticeRandomly | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | alignment, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | words, | ||
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 132 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, LatticeWeightTpl< BaseFloat >::One(), CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::One(), and RandInt().
Referenced by TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void kaldi::GenerateLexicon | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | phones, |
| bool | allow_zero_words, | ||
| bool | allow_empty_word, | ||
| bool | allow_multiple_prons, | ||
| std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > * | lexicon | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 32 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), and SortAndUniq().
Referenced by TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void GeneratePathThroughHmm | ( | const HmmTopology & | topology, |
| bool | reorder, | ||
| int32 | phone, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > * | path | ||
| ) |
This function generates a random path through the HMM for the given phone.
The 'path' output is a list of pairs (HMM-state, transition-index) in which any nonemitting states will have been removed. This is used in other test code. the 'reorder' option is as described in the documentation; if true, the self-loops from a state are reordered to come after the forward-transition.
Definition at line 190 of file hmm-test-utils.cc.
References HmmTopology::HmmState::forward_pdf_class, KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), HmmTopology::TopologyForPhone(), and HmmTopology::HmmState::transitions.
Referenced by GenerateRandomAlignment().
| void GenerateRandomAlignment | ( | const ContextDependencyInterface & | ctx_dep, |
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| bool | reorder, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | phone_sequence, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | alignment | ||
| ) |
For use in test code, this function generates an alignment (a sequence of transition-ids) corresponding to a given phone sequence.
Definition at line 232 of file hmm-test-utils.cc.
References ContextDependencyInterface::CentralPosition(), ContextDependencyInterface::Compute(), ContextDependencyInterface::ContextWidth(), GeneratePathThroughHmm(), TransitionModel::GetTopo(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, TransitionModel::PairToTransitionId(), HmmTopology::TopologyForPhone(), and TransitionModel::TupleToTransitionState().
Referenced by TestConvertAlignment(), TestSplitToPhones(), and TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void kaldi::GenerateWordAndPhoneSequence | ( | std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | lexicon, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | phone_seq, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | word_seq | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 109 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, and RandInt().
Referenced by TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| ContextDependency * GenRandContextDependency | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | phones, |
| bool | ensure_all_covered, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | num_pdf_classes | ||
| ) |
GenRandContextDependency is mainly of use for debugging.
Phones must be sorted and uniq on input.
| phones | [in] A vector of phone id's [must be sorted and uniq]. |
| ensure_all_covered | [in] boolean argument; if true, GenRandContextDependency generates a context-dependency object that "works" for all phones [no gaps]. |
| num_pdf_classes | [out] outputs a vector indexed by phone, of the number of pdf classes (e.g. states) for that phone. |
Definition at line 46 of file context-dep.cc.
References BuildTree(), ContextDependency::ContextDependency(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), GenRandStats(), rnnlm::i, Questions::InitRand(), IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_VLOG, kAllKeysUnion, Rand(), and RandUniform().
Referenced by TestGenRandContextDependency().
| ContextDependency * GenRandContextDependencyLarge | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | phones, |
| int | N, | ||
| int | P, | ||
| bool | ensure_all_covered, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | num_pdf_classes | ||
| ) |
GenRandContextDependencyLarge is like GenRandContextDependency but generates a larger tree with specified N and P for use in "one-time" larger-scale tests.
Definition at line 97 of file context-dep.cc.
References BuildTree(), ContextDependency::ContextDependency(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), GenRandStats(), rnnlm::i, Questions::InitRand(), IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_VLOG, kAllKeysUnion, Rand(), and RandUniform().
Referenced by GenRandTransitionModel(), TestConvertAlignment(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAmNnet(), and kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestNnetDecodable().
| HmmTopology GenRandTopology | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | phones, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | num_pdf_classes | ||
| ) |
This method of generating an arbitrary HmmTopology object allows you to specify the number of pdf-classes for each phone separately.
'num_pdf_classes' is indexed by the phone-index (so the length will be longer than the length of the 'phones' vector, which for example lacks the zero index and may have gaps).
Definition at line 87 of file hmm-test-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSortedAndUniq(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, RandInt(), and HmmTopology::Read().
Referenced by GenRandTopology(), GenRandTransitionModel(), TestConvertAlignment(), and TestHmmTopology().
| HmmTopology GenRandTopology | ( | ) |
This version of GenRandTopology() generates the phone list and number of pdf classes randomly.
Definition at line 174 of file hmm-test-utils.cc.
References GenRandTopology(), GetDefaultTopology(), rnnlm::i, and RandInt().
| TransitionModel * GenRandTransitionModel | ( | ContextDependency ** | ctx_dep_out | ) |
Definition at line 26 of file hmm-test-utils.cc.
References GenRandContextDependencyLarge(), GenRandTopology(), and rnnlm::i.
Referenced by TestSplitToPhones(), TestTransitionModel(), and TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
|
static |
Definition at line 129 of file regression-tree.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by RegressionTree::GatherStats().
| void kaldi::GetBootstrapWERInterval | ( | const std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > & | edit_word_per_hyp, |
| int32 | replications, | ||
| BaseFloat * | mean, | ||
| BaseFloat * | interval | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 113 of file compute-wer-bootci.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and RandInt().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::GetBootstrapWERTwoSystemComparison | ( | const std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > & | edit_word_per_hyp, |
| const std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > & | edit_word_per_hyp2, | ||
| int32 | replications, | ||
| BaseFloat * | p_improv | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 137 of file compute-wer-bootci.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and RandInt().
Referenced by main().
| int32 kaldi::GetCount | ( | double | expected_count | ) |
Definition at line 29 of file nnet3-discriminative-copy-egs.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and WithProb().
| HmmTopology GetDefaultTopology | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | phones | ) |
This function returns a HmmTopology object giving a normal 3-state topology, covering all phones in the list "phones".
This is mainly of use in testing code.
Definition at line 50 of file hmm-test-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, and HmmTopology::Read().
Referenced by GenRandTopology(), TestHmmTopology(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAmNnet(), and kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestNnetDecodable().
| void GetDiagnosticsAndPrintOutput | ( | const std::string & | utt, |
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| const CompactLattice & | clat, | ||
| int64 * | tot_num_frames, | ||
| double * | tot_like | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 31 of file online2-wav-gmm-latgen-faster.cc.
References CompactLatticeShortestPath(), fst::ConvertLattice(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value1(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::Value2(), and words.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::GetEditsDualHyp | ( | const std::string & | hyp_rspecifier, |
| const std::string & | hyp_rspecifier2, | ||
| const std::string & | ref_rspecifier, | ||
| const std::string & | mode, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > & | edit_word_per_hyp, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > & | edit_word_per_hyp2 | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 63 of file compute-wer-bootci.cc.
References SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), KALDI_ERR, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), LevenshteinEditDistance(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::GetEditsSingleHyp | ( | const std::string & | hyp_rspecifier, |
| const std::string & | ref_rspecifier, | ||
| const std::string & | mode, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< int32, int32 > > & | edit_word_per_hyp | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 32 of file compute-wer-bootci.cc.
References SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), KALDI_ERR, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), LevenshteinEditDistance(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 81 of file build-tree-utils.cc.
Referenced by FindAllKeys().
| void kaldi::GetFeatDeriv | ( | const DiagGmm & | gmm, |
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | deriv | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 32 of file fmpe-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), DiagGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), rnnlm::i, DiagGmm::inv_vars(), kTrans, DiagGmm::means_invvars(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
Referenced by TestFmpe().
| void kaldi::GetFeatureMeanAndVariance | ( | const std::string & | feat_rspecifier, |
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | inv_var_out, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | mean_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 33 of file gmm-init-model-flat.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), count, VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, VectorBase< Real >::InvertElements(), KALDI_ERR, VectorBase< Real >::Min(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value().
Referenced by main().
| EventMap* kaldi::GetFullBiphoneStubMap | ( | const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | phone_sets, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | phone2num_pdf_classes, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | ci_phones_list, | ||
| const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | bi_counts, | ||
| int32 | biphone_min_count, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | mono_counts, | ||
| int32 | mono_min_count | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 53 of file gmm-init-biphone.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSortedAndUniq(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_VLOG, and kPdfClass.
Referenced by BiphoneContextDependencyFull().
Definition at line 71 of file fmpe-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, DiagGmm::LogLikelihood(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by TestFmpe().
Definition at line 96 of file online2-tcp-nnet3-decode-faster.cc.
References LatticeStateTimes().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 345 of file ivector-extractor.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), KALDI_WARN, SpMatrix< Real >::LogPosDefDet(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by IvectorExtractor::GetPriorAuxf().
| void kaldi::GetOccs | ( | const BuildTreeStatsType & | stats, |
| const EventMap & | to_pdf_map, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | occs | ||
| ) |
Get state occupation counts.
Definition at line 92 of file gmm-init-model.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::MaxResult(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), SplitStatsByMap(), and SumNormalizer().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 130 of file simple-options.cc.
Referenced by SimpleOptions::GetOption().
| void kaldi::GetOutput | ( | OnlineFeatureInterface * | a, |
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | output | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 29 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References OnlineCacheFeature::ClearCache(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), OnlineFeatureInterface::Dim(), OnlineCacheFeature::GetFrame(), rnnlm::i, OnlineCacheFeature::IsLastFrame(), KALDI_ASSERT, OnlineFeatureInterface::NumFramesReady(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by PldaEstimator::Dim(), TestOnlineAppendFeature(), TestOnlineCmnInput(), TestOnlineDeltaFeature(), TestOnlineDeltaInput(), TestOnlineLdaInput(), TestOnlineMatrixCacheFeature(), TestOnlineMatrixInput(), TestOnlineMfcc(), TestOnlinePlp(), TestOnlineSpliceFrames(), and TestOnlineTransform().
| void kaldi::GetOutput | ( | OnlineFeatInputItf * | a, |
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | output | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 81 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References OnlineCacheInput::Compute(), OnlineFeatInputItf::Dim(), OnlineCacheInput::GetCachedData(), Rand(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
This function extracts the per-frame log likelihoods from a linear lattice (which we refer to as an 'nbest' lattice elsewhere in Kaldi code).
The dimension of *per_frame_loglikes will be set to the number of input symbols in 'nbest'. The elements of '*per_frame_loglikes' will be set to the .Value2() elements of the lattice weights, which represent the acoustic costs; you may want to scale this vector afterward by -1/acoustic_scale to get the original loglikes. If there are acoustic costs on input-epsilon arcs or the final-prob in 'nbest' (and this should not normally be the case in situations where it makes sense to call this function), they will be included to the cost of the preceding input symbol, or the following input symbol for input-epsilons encountered prior to any input symbol. If 'nbest' has no input symbols, 'per_frame_loglikes' will be set to the empty vector.
Definition at line 36 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by AlignUtteranceWrapper().
| char kaldi::GetRandChar | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References Rand().
Referenced by TestSplitStringToVector().
| char kaldi::GetRandDelim | ( | ) |
Definition at line 33 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References Rand().
Referenced by TestSplitStringToVector().
|
static |
Definition at line 1065 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References TransitionModel::GetNonSelfLoopLogProb(), TransitionModel::GetTransitionLogProb(), TransitionModel::GetTransitionLogProbIgnoringSelfLoops(), TransitionModel::IsSelfLoop(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToTransitionState().
Referenced by AddTransitionProbs().
| void kaldi::GetSeenPhones | ( | BuildTreeStatsType & | stats, |
| int | P, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | phones_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 32 of file build-tree-two-level.cc.
References CopySetToVector(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 63 of file kaldi-error.cc.
Referenced by MessageLogger::MessageLogger().
| void kaldi::GetSingleStatsDerivative | ( | double | ml_count, |
| double | ml_x_stats, | ||
| double | ml_x2_stats, | ||
| double | disc_count, | ||
| double | disc_x_stats, | ||
| double | disc_x2_stats, | ||
| double | model_mean, | ||
| double | model_var, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_variance, | ||
| double * | ml_x_stats_deriv, | ||
| double * | ml_x2_stats_deriv | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 25 of file indirect-diff-diag-gmm.cc.
References KALDI_VLOG.
Referenced by GetStatsDerivative().
| std::vector<bool> kaldi::GetSkipLayers | ( | const std::string & | skip_layers_str, |
| const int32 | first_layer_idx, | ||
| const int32 | last_layer_idx | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 58 of file nnet-am-average.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, and SplitStringToIntegers().
Referenced by main().
| void GetSplitTargets | ( | const Vector< BaseFloat > & | state_occs, |
| int32 | target_components, | ||
| BaseFloat | power, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_count, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | targets | ||
| ) |
Get Gaussian-mixture or substate-mixture splitting targets, according to a power rule (e.g.
typically power = 0.2). Returns targets for number of mixture components (Gaussians, or sub-states), allocating the Gaussians or whatever according to a power of occupancy in order to acheive the total supplied "target". During splitting we ensure that each Gaussian [or sub-state] would get a count of at least "min-count", assuming counts were evenly distributed between Gaussians in a state. The vector "targets" will be resized to the appropriate dimension; its value at input is ignored.
Definition at line 116 of file model-common.cc.
References CountStats::CountStats(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_WARN, CountStats::num_components, CountStats::occupancy, and CountStats::pdf_index.
Referenced by AmDiagGmm::MergeByCount(), LogisticRegression::MixUp(), SoftmaxComponent::MixUp(), AmDiagGmm::SplitByCount(), and AmSgmm2::SplitSubstates().
| void kaldi::GetStatsDerivative | ( | const DiagGmm & | gmm, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | num_acc, | ||
| const AccumDiagGmm & | den_acc, | ||
| const AccumDiagGmm & | ml_acc, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_variance, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_gaussian_occupancy, | ||
| AccumDiagGmm * | out_accs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 94 of file indirect-diff-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::AddStatsForComponent(), rnnlm::d, DiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), GetSingleStatsDerivative(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kGmmAll, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), DiagGmmNormal::means_, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), AccumDiagGmm::Resize(), AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator(), and DiagGmmNormal::vars_.
Referenced by GetStatsDerivative(), and main().
| void GetStatsDerivative | ( | const AmDiagGmm & | gmm, |
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | num_accs, | ||
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | den_accs, | ||
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | ml_accs, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_variance, | ||
| BaseFloat | min_gaussian_occupancy, | ||
| AccumAmDiagGmm * | out_accs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 157 of file indirect-diff-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), GetStatsDerivative(), AccumAmDiagGmm::Init(), KALDI_ASSERT, kGmmAll, AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), and AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs().
Definition at line 88 of file online2-tcp-nnet3-decode-faster.cc.
Referenced by main().
| EventMap* kaldi::GetToLengthMap | ( | const BuildTreeStatsType & | stats, |
| int32 | P, | ||
| const std::vector< EventValueType > * | phones, | ||
| int32 | default_length | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 760 of file build-tree-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, kPdfClass, and SplitStatsByKey().
|
inlinestatic |
This function gets the tree structure of the EventMap "map" in a convenient form.
If "map" corresponds to a tree structure (not necessarily binary) with leaves uniquely numbered from 0 to num_leaves-1, then the function will return true, output "num_leaves", and set "parent" to a vector of size equal to the number of nodes in the tree (nonleaf and leaf), where each index corresponds to a node and the leaf indices correspond to the values returned by the EventMap from that leaf; for an index i, parent[i] equals the parent of that node in the tree structure, where parent[i] > i, except for the last (root) node where parent[i] == i. If the EventMap does not have this structure (e.g. if multiple different leaf nodes share the same number), then it will return false.
Definition at line 429 of file event-map.cc.
References GetTreeStructureInternal(), rnnlm::i, IsLeafNode(), KALDI_ASSERT, and EventMap::Map().
Referenced by TestEventMap().
|
static |
Definition at line 375 of file event-map.cc.
References EventMap::GetChildren(), rnnlm::i, IsLeafNode(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, and EventMap::Map().
Referenced by GetTreeStructure().
| void kaldi::GetUtterancePairs | ( | const std::string & | reco2file_and_channel_rxfilename, |
| std::vector< std::vector< std::string > > * | utt_pairs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 34 of file compute-cmvn-stats-two-channel.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, PrintableRxfilename(), SplitStringToVector(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| void GetWeights | ( | const std::string & | weights_str, |
| int32 | num_inputs, | ||
| std::vector< BaseFloat > * | weights | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 30 of file nnet-am-average.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, and SplitStringToFloats().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
| std::string GmmFlagsToString | ( | GmmFlagsType | flags | ) |
Convert GMM flags to string.
Definition at line 43 of file model-common.cc.
References kGmmMeans, kGmmTransitions, kGmmVariances, and kGmmWeights.
Referenced by AccumFullGmm::Read(), AccumDiagGmm::Read(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), and UpdateEbwDiagGmm().
| void kaldi::HandleOutput | ( | bool | determinize, |
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| nnet3::NnetBatchDecoder * | decoder, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | clat_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lat_writer | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file nnet3-latgen-faster-batch.cc.
References NnetBatchDecoder::GetOutput(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::HouseBackward | ( | MatrixIndexT | dim, |
| const Real * | x, | ||
| Real * | v, | ||
| Real * | beta | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 102 of file qr.cc.
References cblas_Xscal(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_ISFINITE, KALDI_ISINF, and KALDI_ISNAN.
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::Tridiagonalize().
|
inline |
Definition at line 354 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by EigenvalueDecomposition< Real >::Tql2().
Definition at line 355 of file kaldi-math.h.
Definition at line 26 of file extend-transform-dim.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), rnnlm::d, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, kCopyData, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::InitAmGmm | ( | const BuildTreeStatsType & | stats, |
| const EventMap & | to_pdf_map, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| BaseFloat | var_floor | ||
| ) |
InitAmGmm initializes the GMM with one Gaussian per state.
Definition at line 35 of file gmm-init-model.cc.
References AmDiagGmm::AddPdf(), count, GaussClusterable::count(), DeletePointers(), GetPhonesForPdfs(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, EventMap::MaxResult(), SplitStatsByMap(), SumClusterable(), and SumStatsVec().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::InitAmGmmFromOld | ( | const BuildTreeStatsType & | stats, |
| const EventMap & | to_pdf_map, | ||
| int32 | N, | ||
| int32 | P, | ||
| const std::string & | old_tree_rxfilename, | ||
| const std::string & | old_model_rxfilename, | ||
| BaseFloat | var_floor, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm | ||
| ) |
InitAmGmmFromOld initializes the GMM based on a previously trained model and tree, which must require no more phonetic context than the current tree.
It does this by finding the closest PDF in the old model, to any given PDF in the new model. Here, "closest" is defined as: has the largest count in common from the tree stats.
Definition at line 116 of file gmm-init-model.cc.
References AmDiagGmm::AddPdf(), ContextDependency::CentralPosition(), ContextDependency::ContextWidth(), ConvertStats(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, EventMap::Map(), EventMap::MaxResult(), AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs(), AmDiagGmm::Read(), ContextDependency::Read(), TransitionModel::Read(), SplitStatsByMap(), Input::Stream(), SumStats(), and ContextDependency::ToPdfMap().
Referenced by main().
This function initializes the matrix to dimension 2 by (dim+1); 1st "dim" elements of 1st row are mean stats, 1st "dim" elements of 2nd row are var stats, last element of 1st row is count, last element of 2nd row is zero.
Definition at line 25 of file cmvn.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 161 of file fmllr-diag-gmm.h.
References ComputeFmllrDiagGmm(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit().
Definition at line 32 of file gmm-global-init-from-feats.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), DiagGmm::CopyFromNormal(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, VectorBase< Real >::Max(), DiagGmmNormal::means_, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), DiagGmm::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandInt(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), DiagGmmNormal::vars_, and DiagGmmNormal::weights_.
Referenced by main().
Initialize an opened stream for reading by detecting the binary header and.
InitKaldiInputStream initializes an opened stream for reading by detecting the binary header and setting the "binary" value appropriately; It will typically not be called by users directly.
Definition at line 306 of file io-funcs-inl.h.
Referenced by main(), Input::OpenInternal(), PosteriorHolder::Read(), KaldiObjectHolder< KaldiType >::Read(), GaussPostHolder::Read(), BasicHolder< BasicType >::Read(), BasicVectorHolder< BasicType >::Read(), BasicVectorVectorHolder< BasicType >::Read(), BasicPairVectorHolder< BasicType >::Read(), ReadBasicType(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix(), UnitTestGeneralMatrix(), UnitTestIo(), and UnitTestIoCross().
|
inline |
InitKaldiOutputStream initializes an opened stream for writing by writing an optional binary header and modifying the floating-point precision; it will typically not be called by users directly.
Definition at line 291 of file io-funcs-inl.h.
Referenced by Output::Open(), ReadBasicType(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix(), UnitTestGeneralMatrix(), UnitTestIo(), UnitTestIoCross(), KaldiObjectHolder< KaldiType >::Write(), PosteriorHolder::Write(), GaussPostHolder::Write(), BasicHolder< BasicType >::Write(), BasicVectorHolder< BasicType >::Write(), BasicVectorVectorHolder< BasicType >::Write(), and BasicPairVectorHolder< BasicType >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 42 of file cu-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::Cond(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and RandGauss().
|
static |
Definition at line 45 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, and RandGauss().
Referenced by Questions::Questions(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecToCols(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddVecToRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixDivRowsVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixInvertElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulColsVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsVec(), UnitTestCuVectorAddColSumMat(), UnitTestCuVectorAddColSumMatLarge(), UnitTestCuVectorAddRowSumMat(), UnitTestCuVectorAddRowSumMatLarge(), UnitTestCuVectorAddTpVec(), UnitTestCuVectorAddVec(), UnitTestCuVectorInvertElements(), UnitTestCuVectorMulTp(), UnitTestMatrixRandomizer(), and UnitTestVectorRandomizer().
|
static |
Definition at line 53 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Cond(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and RandGauss().
|
static |
Definition at line 53 of file cu-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, and RandGauss().
|
static |
Definition at line 56 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Cond(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and RandGauss().
Referenced by CholeskyUnitTestTr(), UnitTestAxpy(), UnitTestDeterminant(), UnitTestDeterminantSign(), UnitTestEig(), UnitTestEigSp(), UnitTestFloorChol(), UnitTestInverse(), UnitTestNonsymmetricPower(), UnitTestRow(), UnitTestSimpleForMat(), UnitTestTridiagonalize(), and UnitTestTridiagonalizeAndQr().
|
static |
Definition at line 69 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::Cond(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and RandGauss().
| void InitRandomGmm | ( | DiagGmm * | gmm_in | ) |
Definition at line 27 of file diag-gmm-test.cc.
References DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, DiagGmm::Perturb(), Rand(), RandGauss(), RandUniform(), DiagGmm::Resize(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), DiagGmm::SetInvVarsAndMeans(), DiagGmm::SetWeights(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
Referenced by UnitTestDiagGmmGenerate(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmm(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmDiagonal(), UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmOffset(), and UnitTestFmllrRaw().
Definition at line 354 of file event-map.cc.
References EventMap::GetChildren().
Referenced by GetTreeStructure(), and GetTreeStructureInternal().
| bool IsLine | ( | const std::string & | line | ) |
Returns true if "line" is free of
characters and unprintable characters, and does not contain leading or trailing whitespace.
Definition at line 154 of file text-utils.cc.
Referenced by ConvertStringToInteger(), and TestIsLine().
| void IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmm | ( | const AccumAmDiagGmm & | src_stats, |
| double | tau, | ||
| AccumAmDiagGmm * | dst_stats | ||
| ) |
Smooth "dst_stats" with "src_stats".
They don't have to be different.
Definition at line 358 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), IsmoothStatsDiagGmm(), KALDI_ASSERT, and AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs().
Referenced by main(), and EbwWeightOptions::Register().
| void IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmmFromModel | ( | const AmDiagGmm & | src_model, |
| double | tau, | ||
| AccumAmDiagGmm * | dst_stats | ||
| ) |
This version of the I-smoothing function takes a model as input.
Definition at line 367 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmmToStats(), AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), IsmoothStatsDiagGmm(), KALDI_ASSERT, kGmmAll, AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), and AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs().
Referenced by main(), and EbwWeightOptions::Register().
| void IsmoothStatsDiagGmm | ( | const AccumDiagGmm & | src_stats, |
| double | tau, | ||
| AccumDiagGmm * | dst_stats | ||
| ) |
I-Smooth the stats. src_stats and dst_stats do not have to be different.
Definition at line 318 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::AddStatsForComponent(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), AccumDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), KALDI_ASSERT, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), AccumDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator().
Referenced by IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmm(), IsmoothStatsAmDiagGmmFromModel(), EbwWeightOptions::Register(), and UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm().
|
static |
Definition at line 543 of file word-align-lattice.cc.
References rnnlm::i, TransitionModel::IsFinal(), TransitionModel::IsSelfLoop(), WordBoundaryInfo::kWordBeginAndEndPhone, WordBoundaryInfo::kWordBeginPhone, WordBoundaryInfo::kWordEndPhone, WordBoundaryInfo::reorder, TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone(), and WordBoundaryInfo::TypeOfPhone().
|
static |
Definition at line 745 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
References rnnlm::i, WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo::IsValidEntry(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, SplitToPhones(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by LatticeWordAligner::ComputationState::OutputArcForce(), and TestWordAlignedLattice().
|
static |
Definition at line 625 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i, TransitionModel::IsSelfLoop(), KALDI_ASSERT, and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToTransitionState().
Referenced by ConvertAlignmentInternal(), and SplitToPhones().
|
inline |
Returns true if the vector is sorted.
Definition at line 47 of file stl-utils.h.
Referenced by QuestionsForKey::Check(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::LatticeInfo::Check(), fst::CheckPhones(), PldaStats::Sort(), SplitEventMap::SplitEventMap(), TestIsSorted(), TestMergePairVectorSumming(), and Uniq().
|
inline |
Returns true if the vector is sorted and contains each element only once.
Definition at line 63 of file stl-utils.h.
Referenced by AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::AccumulateTreeStatsInfo(), AddTransitionProbs(), AutomaticallyObtainQuestions(), RegressionTree::BuildTree(), BuildTree(), BuildTreeTwoLevel(), ConvolutionModel::Check(), ComputationGraphBuilder::Check(), Compiler::CompileBackwardFromSubmatLocations(), ExampleMergingConfig::ComputeDerived(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeMatrixAccesses(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeVariableAccesses(), ComputationRenumberer::CreateRenumbering(), FeatureTransformEstimateMulti::Estimate(), FilterStatsByKey(), ComputationLoopedOptimizer::FindActiveMatrices(), GenRandContextDependency(), GenRandContextDependencyLarge(), GenRandTopology(), GetDefaultTopology(), GetFullBiphoneStubMap(), ContextDependency::GetPdfInfo(), GetPdfsForPhones(), GetPhonesForPdfs(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::GetRandomConvolutionIndexes(), GetStubMap(), SpliceComponent::Init(), TimeHeightConvolutionComponent::InitFromConfig(), KMeansClusterPhones(), LatticeActivePhones(), LatticeBoost(), main(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::MakeComputation(), ObtainSetsOfPhones(), HmmTopology::Read(), ReadRootsFile(), ReadSharedPhonesList(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::RegularizeTList(), DiagGmm::RemoveComponents(), FullGmm::RemoveComponents(), TestIsSortedAndUniq(), TrailingSilenceLength(), and TrainingGraphCompiler::TrainingGraphCompiler().
| bool IsToken | ( | const std::string & | token | ) |
Returns true if "token" is nonempty, and all characters are printable and whitespace-free.
Definition at line 105 of file text-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by ConvertStringToInteger(), RandomAccessTableReader< kaldi::TokenHolder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReaderScriptImpl< Holder >::HasKeyInternal(), IsNotToken(), Nnet::ProcessComponentConfigLine(), SplitArgOnEquals(), TestIsToken(), TokenHolder::Write(), TokenVectorHolder::Write(), TableWriterArchiveImpl< Holder >::Write(), TableWriterScriptImpl< Holder >::Write(), TableWriterBothImpl< Holder >::Write(), and WriteScriptFile().
| bool IsValidName | ( | const std::string & | name | ) |
Returns true if 'name' would be a valid name for a component or node in a nnet3Nnet.
This is a nonempty string beginning with A-Za-z_, and containing only '-', '_', '.', A-Z, a-z, or 0-9.
Definition at line 553 of file text-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by Nnet::AddComponent(), kaldi::nnet3::DescriptorTokenize(), ConfigLine::ParseLine(), Nnet::RemoveRedundantConfigLines(), and Nnet::SetNodeName().
| void JoinVectorToString | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | vec_in, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| bool | omit_empty_strings, | ||
| std::string * | str_out | ||
| ) |
Joins the elements of a vector of strings into a single string using "delim" as the delimiter.
If omit_empty_strings == true, any empty strings in the vector are skipped. A vector of empty strings results in an empty string on the output.
Definition at line 77 of file text-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by TestSplitStringToVector().
|
static |
Definition at line 133 of file kaldi-error.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by MessageLogger::LogMessage().
| void kaldi::LatticeAcousticRescore | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans_model, |
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | log_likes, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | state_times, | ||
| Lattice * | lat | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 31 of file lattice-rescore-mapped.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPdf().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::LatticeActivePhones | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | trans, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | sil_phones, | ||
| std::vector< std::set< int32 > > * | active_phones | ||
| ) |
Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, outputs for each frame the set of phones active on that frame.
If sil_phones (which must be sorted and uniq) is nonempty, it excludes phones in this list.
Definition at line 399 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, LatticeStateTimes(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
| void kaldi::LatticeActivePhones | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | trans, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | sil_phones, | ||
| std::vector< std::set< int32 > > * | active_phones | ||
| ) |
Given a lattice, and a transition model to map pdf-ids to phones, outputs for each frame the set of phones active on that frame.
If sil_phones (which must be sorted and uniq) is nonempty, it excludes phones in this list.
Definition at line 399 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, LatticeStateTimes(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
| bool LatticeBoost | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | alignment, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | silence_phones, | ||
| BaseFloat | b, | ||
| BaseFloat | max_silence_error, | ||
| Lattice * | lat | ||
| ) |
Boosts LM probabilities by b * [number of frame errors]; equivalently, adds -b*[number of frame errors] to the graph-component of the cost of each arc/path.
There is a frame error if a particular transition-id on a particular frame corresponds to a phone not matching transcription's alignment for that frame. This is used in "margin-inspired" discriminative training, esp. Boosted MMI. The TransitionModel is used to map transition-ids in the lattice input-side to phones; the phones appearing in "silence_phones" are treated specially in that we replace the frame error f (either zero or 1) for a frame, with the minimum of f or max_silence_error. For the normal recipe, max_silence_error would be zero. Returns true on success, false if there was some kind of mismatch. At input, silence_phones must be sorted and unique.
Definition at line 735 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, LatticeStateTimes(), TransitionModel::NumTransitionIds(), TopSortLatticeIfNeeded(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by DiscriminativeComputation::Compute(), NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::LatticeComputations(), and main().
| BaseFloat LatticeForwardBackward | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| Posterior * | arc_post, | ||
| double * | acoustic_like_sum = NULL |
||
| ) |
This function does the forward-backward over lattices and computes the posterior probabilities of the arcs.
It returns the total log-probability of the lattice. The Posterior quantities contain pairs of (transition-id, weight) on each frame. If the pointer "acoustic_like_sum" is provided, this value is set to the sum over the arcs, of the posterior of the arc times the acoustic likelihood [i.e. negated acoustic score] on that link. This is used in combination with other quantities to work out the objective function in MMI discriminative training.
Definition at line 314 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), fst::ConvertToCost(), Exp(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, kLogZeroDouble, LatticeStateTimes(), LogAdd(), and MergePairVectorSumming().
Referenced by SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::GetGaussianPosteriors(), LatticeForwardBackwardMmi(), main(), and TestWordAlignedLattice().
| BaseFloat LatticeForwardBackwardMmi | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans, |
| const Lattice & | lat, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | num_ali, | ||
| bool | drop_frames, | ||
| bool | convert_to_pdf_ids, | ||
| bool | cancel, | ||
| Posterior * | arc_post | ||
| ) |
This function can be used to compute posteriors for MMI, with a positive contribution for the numerator and a negative one for the denominator.
This function is not actually used in our normal MMI training recipes, where it's instead done using various command line programs that each do a part of the job. This function was written for use in neural-net MMI training.
| [in] | trans | The transition model. Used to map the transition-ids to phones or pdfs. |
| [in] | lat | The denominator lattice |
| [in] | num_ali | The numerator alignment |
| [in] | drop_frames | If "drop_frames" is true, it will not compute any posteriors on frames where the num and den have disjoint pdf-ids. |
| [in] | convert_to_pdf_ids | If "convert_to_pdfs_ids" is true, it will convert the output to be at the level of pdf-ids, not transition-ids. |
| [in] | cancel | If "cancel" is true, it will cancel out any positive and negative parts from the same transition-id (or pdf-id, if convert_to_pdf_ids == true). |
| [out] | arc_post | The output MMI posteriors of transition-ids (or pdf-ids if convert_to_pdf_ids == true) at each frame i.e. the difference between the numerator and denominator posteriors. |
It returns the forward-backward likelihood of the lattice.
Definition at line 1414 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References AlignmentToPosterior(), ConvertPosteriorToPdfs(), LatticeForwardBackward(), MergePosteriors(), and ScalePosterior().
Referenced by DiscriminativeComputation::ComputeObjfAndDeriv(), kaldi::nnet2::ExampleToPdfPost(), and NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::GetDiscriminativePosteriors().
| BaseFloat LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants | ( | const TransitionModel & | trans, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | silence_phones, | ||
| const Lattice & | lat, | ||
| const std::vector< int32 > & | num_ali, | ||
| std::string | criterion, | ||
| bool | one_silence_class, | ||
| Posterior * | post | ||
| ) |
This function implements either the MPFE (minimum phone frame error) or SMBR (state-level minimum bayes risk) forward-backward, depending on whether "criterion" is "mpfe" or "smbr".
It returns the MPFE criterion of SMBR criterion for this utterance, and outputs the posteriors (which may be positive or negative) into "post".
| [in] | trans | The transition model. Used to map the transition-ids to phones or pdfs. |
| [in] | silence_phones | A list of integer ids of silence phones. The silence frames i.e. the frames where num_ali corresponds to a silence phones are treated specially. The behavior is determined by 'one_silence_class' being false (traditional behavior) or true. Usually in our setup, several phones including the silence, vocalized noise, non-spoken noise and unk are treated as "silence phones" |
| [in] | lat | The denominator lattice |
| [in] | num_ali | The numerator alignment |
| [in] | criterion | The objective function. Must be "mpfe" or "smbr" for MPFE (minimum phone frame error) or sMBR (state minimum bayes risk) training. |
| [in] | one_silence_class | Determines how the silence frames are treated. Setting this to false gives the old traditional behavior, where the silence frames (according to num_ali) are treated as incorrect. However, this means that the insertions are not penalized by the objective. Setting this to true gives the new behaviour, where we treat silence as any other phone, except that all pdfs of silence phones are collapsed into a single class for the frame-error computation. This can possible reduce the insertions in the trained model. This is closer to the WER metric that we actually care about, since WER is generally computed after filtering out noises, but does penalize insertions. |
| [out] | post | The "MBR posteriors" i.e. derivatives w.r.t to the pseudo log-likelihoods of states at each frame. |
Definition at line 794 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), fst::ConvertToCost(), Exp(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_ISNAN, kLogZeroDouble, LatticeStateTimes(), LogAdd(), MergePairVectorSumming(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPdf(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by DiscriminativeComputation::ComputeObjfAndDeriv(), kaldi::nnet2::ExampleToPdfPost(), NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::GetDiscriminativePosteriors(), and main().
This function iterates over the states of a topologically sorted lattice and counts the time instance corresponding to each state.
The times are returned in a vector of integers 'times' which is resized to have a size equal to the number of states in the lattice. The function also returns the maximum time in the lattice (this will equal the number of frames in the file).
Definition at line 78 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by DiscriminativeSupervision::Check(), DiscriminativeExampleSplitter::CollapseTransitionIds(), ComputeAcousticScoresMap(), DiscriminativeExampleSplitter::ComputeFrameInfo(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::ComputeLatticeScores(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::CreateRangeLattice(), GetLatticeTimeSpan(), LatticeActivePhones(), LatticeBoost(), NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::LatticeComputations(), LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), DiscriminativeComputation::LookupNnetOutput(), main(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::PrepareLattice(), ReplaceAcousticScoresFromMap(), and RescoreLattice().
This function iterates over the states of a topologically sorted lattice and counts the time instance corresponding to each state.
The times are returned in a vector of integers 'times' which is resized to have a size equal to the number of states in the lattice. The function also returns the maximum time in the lattice (this will equal the number of frames in the file).
Definition at line 78 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by DiscriminativeSupervision::Check(), DiscriminativeExampleSplitter::CollapseTransitionIds(), ComputeAcousticScoresMap(), DiscriminativeExampleSplitter::ComputeFrameInfo(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::ComputeLatticeScores(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::CreateRangeLattice(), GetLatticeTimeSpan(), LatticeActivePhones(), LatticeBoost(), NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::LatticeComputations(), LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), DiscriminativeComputation::LookupNnetOutput(), main(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::PrepareLattice(), ReplaceAcousticScoresFromMap(), and RescoreLattice().
| std::string kaldi::LatticeToString | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| const fst::SymbolTable & | word_syms | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 70 of file online2-tcp-nnet3-decode-faster.cc.
References fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_WARN, and words.
Referenced by LatticeToString(), and main().
| std::string kaldi::LatticeToString | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| const fst::SymbolTable & | word_syms | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 102 of file online2-tcp-nnet3-decode-faster.cc.
References CompactLatticeShortestPath(), fst::ConvertLattice(), KALDI_WARN, and LatticeToString().
| I kaldi::Lcm | ( | I | m, |
| I | n | ||
| ) |
Returns the least common multiple of two integers.
Will crash unless the inputs are positive.
Definition at line 318 of file kaldi-math.h.
References Gcd(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by NnetSimpleComputationOptions::CheckAndFixConfigs(), DecodableNnetSimple::CheckAndFixConfigs(), LinearResample::GetNumOutputSamples(), SwitchingForwardingDescriptor::Modulus(), Nnet::Modulus(), BinarySumDescriptor::Modulus(), Descriptor::Modulus(), and UnitTestGcdLcmTpl().
| int32 LevenshteinAlignment | ( | const std::vector< T > & | a, |
| const std::vector< T > & | b, | ||
| T | eps_symbol, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< T, T > > * | output | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 130 of file edit-distance-inl.h.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, and ReverseVector().
Referenced by main(), and TestLevenshteinAlignment().
| int32 LevenshteinEditDistance | ( | const std::vector< T > & | a, |
| const std::vector< T > & | b | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 30 of file edit-distance-inl.h.
References rnnlm::i, and rnnlm::n.
Referenced by GetEditsDualHyp(), GetEditsSingleHyp(), main(), TestEditDistance(), TestEditDistance2(), TestEditDistance2String(), TestEditDistanceString(), and TestLevenshteinAlignment().
| int32 LevenshteinEditDistance | ( | const std::vector< T > & | ref, |
| const std::vector< T > & | hyp, | ||
| int32 * | ins, | ||
| int32 * | del, | ||
| int32 * | sub | ||
| ) |
| template int32 kaldi::LinearCgd< double > | ( | const LinearCgdOptions & | opts, |
| const SpMatrix< double > & | A, | ||
| const VectorBase< double > & | b, | ||
| VectorBase< double > * | x | ||
| ) |
Referenced by LinearCgd().
| template int32 kaldi::LinearCgd< float > | ( | const LinearCgdOptions & | opts, |
| const SpMatrix< float > & | A, | ||
| const VectorBase< float > & | b, | ||
| VectorBase< float > * | x | ||
| ) |
Referenced by LinearCgd().
Definition at line 252 of file interpolate-pitch.cc.
References rnnlm::i, and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
Definition at line 100 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::ApplyLog(), VectorBase< float >::ApplyLogAndCopy(), VectorBase< float >::ApplyLogSoftMax(), VectorBase< float >::ApplySoftMax(), MatrixBase< float >::ApplySoftMax(), CompactLatticeNormalize(), CuMatrix< float >::CompObjfAndDeriv(), AmSgmm2::ComponentPosteriors(), SpectrogramComputer::Compute(), MfccComputer::Compute(), FbankComputer::Compute(), PlpComputer::Compute(), PitchFrameInfo::ComputeBacktraces(), TransitionModel::ComputeDerivedOfProbs(), FullGmm::ComputeGconsts(), ComputeGconsts(), DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), NnetComputer::ComputeLastLayerDeriv(), ComputeLpc(), MleAmSgmm2Updater::ComputeMPrior(), AmSgmm2::ComputeNormalizersInternal(), DiscriminativeComputation::ConvertAnswersToLogLike(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyLog(), CuMatrixBase< float >::DiffXent(), DoRescalingUpdate(), EBWUpdateGaussian(), FbankComputer::FbankComputer(), FmllrInnerUpdate(), GetHmmAsFsa(), GetHmmAsFsaSimple(), GetLogLikeTest(), LogisticRegression::GetObjfAndGrad(), OnlineProcessPitch::GetRawLogPitchFeature(), Rbm::InitData(), TransitionModel::InitializeProbs(), SpMatrix< float >::Invert(), MatrixBase< float >::Invert(), KaldiAssertFailure_(), kaldi::nnet2::KlDivergence(), kaldi::nnet3::KlDivergence(), NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::LatticeComputations(), MatrixBase< float >::Log(), Log1p(), AmSgmm2::LogLikelihood(), SpMatrix< float >::LogPosDefDet(), LogSub(), VectorBase< float >::LogSumExp(), MatrixBase< float >::LogSumExp(), main(), TransitionModel::MapUpdate(), TransitionModel::MapUpdateShared(), DiagGmm::Merge(), DiagGmm::merged_components_logdet(), MfccComputer::MfccComputer(), SoftmaxComponent::MixUp(), TransitionModel::MleUpdate(), TransitionModel::MleUpdateShared(), PushSpecialClass::ModifyFst(), PitchInterpolator::MultiplyObsProb(), OnlinePaSource::OnlinePaSource(), PlpComputer::PlpComputer(), ProcessPovFeatures(), ProcessWindow(), LogSoftmaxComponent::Propagate(), RandGauss(), SpectrogramComputer::SpectrogramComputer(), VectorBase< float >::SumLog(), TakeLogOfPitch(), PushSpecialClass::TestAccuracy(), UnitTestCuDiffXent(), UnitTestDeterminantSign(), UnitTestDiagGmm(), UnitTestEig(), UnitTestFullGmm(), UnitTestLogAddSub(), UnitTestLogSpeed(), UnitTestTrain(), MlltAccs::Update(), OnlineProcessPitch::UpdateNormalizationStats(), MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateSubstateWeights(), and VectorToPosteriorEntry().
Definition at line 101 of file kaldi-math.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 104 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by Log1p(), LogAdd(), MatrixBase< float >::SoftHinge(), and UnitTestSoftHinge().
Definition at line 105 of file kaldi-math.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 184 of file kaldi-math.h.
References Exp(), and Log1p().
Referenced by ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas(), ComputeCompactLatticeBetas(), MinimumBayesRisk::EditDistance(), FullGmm::GaussianSelection(), DiagGmm::GaussianSelection(), FullGmm::GaussianSelectionPreselect(), DiagGmm::GaussianSelectionPreselect(), GetLogLikeTest(), LogisticRegression::GetLogPosteriors(), fst::InputDeterminizeSingleState(), GrammarFstPreparer::InsertEpsilonsForState(), LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), LogAddOrMax(), and UnitTestLogAddSub().
|
inlinestatic |
Definition at line 444 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References LogAdd().
Referenced by ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas().
|
inline |
Definition at line 228 of file kaldi-math.h.
References Exp(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_ISNAN, kLogZeroDouble, and Log().
Referenced by UnitTestLogAddSub().
Definition at line 247 of file kaldi-math.h.
References Exp(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_ISNAN, kLogZeroDouble, kLogZeroFloat, and Log().
This function returns the number of words in the longest sentence in a CompactLattice (i.e.
the the maximum of any path, of the count of olabels on that path).
Definition at line 1452 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, and LatticeWeightTpl< BaseFloat >::Zero().
Referenced by LongestSentenceLength(), and SentenceLevelConfidence().
| int32 LongestSentenceLength | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat | ) |
This function returns the number of words in the longest sentence in a CompactLattice, i.e.
the the maximum of any path, of the count of labels on that path... note, in CompactLattice, the ilabels and olabels are identical because it is an acceptor.
Definition at line 1489 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, LongestSentenceLength(), and CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Zero().
|
inline |
Definition at line 83 of file kaldi-utils.h.
References Sleep().
Referenced by SphinxMatrixHolder< kFeatDim >::Read(), ReadHtk(), SphinxMatrixHolder< kFeatDim >::Write(), WriteHtk(), and WriteSphinx().
|
inline |
Definition at line 62 of file event-map.h.
References EventTypeToString(), ReadEventType(), and WriteEventType().
Referenced by ShareEventMapLeaves(), and TestShareEventMapLeaves().
| void kaldi::MakeLatticeFromLinear | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | ali, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | words, | ||
| BaseFloat | lm_cost, | ||
| BaseFloat | ac_cost, | ||
| Lattice * | lat_out | ||
| ) |
|
inlinestatic |
This utility function, used in GetHTransducer(), creates an FSA (finite state acceptor, i.e.
an FST with ilabels equal to olabels) with a single successful path, with a single label on it.
Definition at line 239 of file hmm-utils.cc.
Referenced by GetHTransducer().
| void MapAmDiagGmmUpdate | ( | const MapDiagGmmOptions & | config, |
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | am_diag_gmm_acc, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | obj_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out | ||
| ) |
Maximum A Posteriori update.
Definition at line 237 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.cc.
References AmDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumAmDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MapDiagGmmUpdate(), AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), and AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs().
Referenced by main().
| std::string kaldi::MapCygwinPath | ( | const std::string & | filename | ) |
Definition at line 82 of file kaldi-cygwin-io-inl.h.
References KALDI_ERR, MapCygwinPathNoTmp(), and prefixp().
Referenced by UnitTestNativeFilename().
|
static |
Definition at line 52 of file kaldi-cygwin-io-inl.h.
References KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, and prefixp().
Referenced by MapCygwinPath().
| void MapDiagGmmUpdate | ( | const MapDiagGmmOptions & | config, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | diag_gmm_acc, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| DiagGmm * | gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | obj_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out | ||
| ) |
Maximum A Posteriori estimation of the model.
Definition at line 410 of file mle-diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), DiagGmmNormal::CopyToDiagGmm(), DiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), MapDiagGmmOptions::mean_tau, DiagGmmNormal::means_, MlObjective(), DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator(), MapDiagGmmOptions::variance_tau, DiagGmmNormal::vars_, MapDiagGmmOptions::weight_tau, and DiagGmmNormal::weights_.
Referenced by MapAmDiagGmmUpdate(), and AccumDiagGmm::Resize().
Definition at line 26 of file tree-accu.cc.
References KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by AccumulateTreeStats().
|
static |
Testing code; map word symbols in the lattice "lat" using the equivalence-classes obtained from the lexicon, using the function EquivalenceClassOf in the lexicon_info object.
Definition at line 912 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
References WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo::EquivalenceClassOf(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by TestWordAlignedLattice().
|
static |
Definition at line 257 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
|
static |
Definition at line 4592 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References KALDI_LOG, and UnitTestAddVecCross().
Definition at line 52 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Max(), and VectorBase< Real >::Min().
| void MaybeDoSanityCheck | ( | const KwsLexicographicFst & | index_transducer | ) |
Definition at line 325 of file kws-functions.cc.
References DifferenceWrapper(), fst::GetLinearSymbolSequence(), GetVerboseLevel(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_VLOG, and KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by DoFactorMerging(), main(), and MaybeDoSanityCheck().
| void MaybeDoSanityCheck | ( | const KwsProductFst & | product_transducer | ) |
Definition at line 365 of file kws-functions.cc.
References GetVerboseLevel(), and MaybeDoSanityCheck().
| std::string kaldi::MeanVariance | ( | const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | m | ) |
Definition at line 49 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), and ToString().
Referenced by CuRandGaussianMatrixBaseSpeedTest(), CuRandGaussianMatrixSpeedTest(), CuRandGaussianVectorSpeedTest(), CuRandUniformMatrixBaseSpeedTest(), CuRandUniformMatrixSpeedTest(), and CuRandUniformVectorSpeedTest().
| std::string kaldi::MeanVariance | ( | const CuVectorBase< Real > & | v | ) |
Definition at line 60 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::Add(), CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Dim(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Sum(), and ToString().
merges GMMs by appending Gaussians in "src" to "dst".
Renormalizes weights by allocating weight proportional to #Gauss.
Definition at line 28 of file fgmm-global-merge.cc.
References FullGmm::ComputeGconsts(), FullGmm::CopyFromFullGmm(), FullGmm::Dim(), rnnlm::i, FullGmm::inv_covars(), KALDI_ASSERT, FullGmm::means_invcovars(), FullGmm::NumGauss(), VectorBase< Real >::Range(), MatrixBase< Real >::Range(), FullGmm::Resize(), FullGmm::SetInvCovarsAndMeansInvCovars(), FullGmm::SetWeights(), and FullGmm::weights().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
For a vector of pair<I, F> where I is an integer and F a floating-point or integer type, this function sorts a vector of type vector<pair<I, F> > on the I value and then merges elements with equal I values, summing these over the F component and then removing any F component with zero value.
This is for where the vector of pairs represents a map from the integer to float component, with an "adding" type of semantics for combining the elements.
Definition at line 288 of file stl-utils.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT_IS_INTEGER_TYPE.
Referenced by LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), MergePosteriors(), TestMergePairVectorSumming(), and OnlineIvectorFeature::UpdateStatsForFrames().
| void MleAmDiagGmmUpdate | ( | const MleDiagGmmOptions & | config, |
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | amdiaggmm_acc, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | obj_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out | ||
| ) |
for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of an acoustic model that uses diagonal Gaussian mixture models as emission densities.
Definition at line 187 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.cc.
References count, AmDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumAmDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, MleDiagGmmOptions::min_gaussian_occupancy, MleDiagGmmUpdate(), AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), AmDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs(), MleDiagGmmOptions::remove_low_count_gaussians, and ResizeModel().
Referenced by main(), TestAmDiagGmmAccsIO(), and UnitTestRegtreeFmllrDiagGmm().
| void MleDiagGmmUpdate | ( | const MleDiagGmmOptions & | config, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | diag_gmm_acc, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| DiagGmm * | gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | obj_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out, | ||
| int32 * | floored_elements_out = NULL, |
||
| int32 * | floored_gauss_out = NULL, |
||
| int32 * | removed_gauss_out = NULL |
||
| ) |
for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model.
Update using the DiagGmm: exponential form. Sets, does not increment, objf_change_out, floored_elements_out and floored_gauss_out.
Definition at line 275 of file mle-diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), DiagGmmNormal::CopyToDiagGmm(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), DiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), DiagGmmNormal::means_, MleDiagGmmOptions::min_gaussian_occupancy, MleDiagGmmOptions::min_gaussian_weight, MleDiagGmmOptions::min_variance, MlObjective(), DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), MleDiagGmmOptions::remove_low_count_gaussians, DiagGmm::RemoveComponents(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator(), MleDiagGmmOptions::variance_floor_vector, DiagGmmNormal::vars_, and DiagGmmNormal::weights_.
Referenced by main(), MleAmDiagGmmUpdate(), AccumDiagGmm::Resize(), test_flags_driven_update(), test_io(), TestComponentAcc(), TrainOneIter(), UnitTestDiagGmmGenerate(), and UnitTestEstimateDiagGmm().
| void MleFullGmmUpdate | ( | const MleFullGmmOptions & | config, |
| const AccumFullGmm & | fullgmm_acc, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| FullGmm * | gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | obj_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out | ||
| ) |
for computing the maximum-likelihood estimates of the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model.
Update using the FullGmm exponential form
Definition at line 282 of file mle-full-gmm.cc.
References FullGmm::ComputeGconsts(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), FullGmmNormal::CopyToFullGmm(), AccumFullGmm::covariance_accumulator(), FullGmm::Dim(), AccumFullGmm::Flags(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, MleFullGmmOptions::max_condition, AccumFullGmm::mean_accumulator(), FullGmmNormal::means_, MleFullGmmOptions::min_gaussian_occupancy, MleFullGmmOptions::min_gaussian_weight, MlObjective(), FullGmm::NumGauss(), AccumFullGmm::occupancy(), MleFullGmmOptions::remove_low_count_gaussians, FullGmm::RemoveComponents(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), MleFullGmmOptions::variance_floor, FullGmmNormal::vars_, and FullGmmNormal::weights_.
Referenced by main(), AccumFullGmm::Resize(), test_flags_driven_update(), test_io(), TestComponentAcc(), UnitTestEstimateFullGmm(), and UnitTestFullGmmEst().
|
static |
Definition at line 308 of file regtree-mllr-diag-gmm.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), rnnlm::d, AffineXformStats::G_, AffineXformStats::K_, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), TraceMatMat(), and VecVec().
Referenced by RegtreeMllrDiagGmmAccs::Update().
| BaseFloat MlObjective | ( | const DiagGmm & | gmm, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | diag_gmm_acc | ||
| ) |
Calc using the DiagGMM exponential form.
Definition at line 261 of file mle-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), DiagGmm::gconsts(), DiagGmm::inv_vars(), kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, kTrans, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), DiagGmm::means_invvars(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), TraceMatMat(), AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator(), and VecVec().
Referenced by MapDiagGmmUpdate(), MleDiagGmmUpdate(), MleFullGmmUpdate(), AccumFullGmm::Resize(), and AccumDiagGmm::Resize().
| BaseFloat MlObjective | ( | const FullGmm & | gmm, |
| const AccumFullGmm & | fullgmm_acc | ||
| ) |
Calc using the DiagGMM exponential form.
Definition at line 261 of file mle-full-gmm.cc.
References AccumFullGmm::covariance_accumulator(), FullGmm::Dim(), AccumFullGmm::Flags(), FullGmm::gconsts(), rnnlm::i, FullGmm::inv_covars(), kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, kTrans, AccumFullGmm::mean_accumulator(), FullGmm::means_invcovars(), FullGmm::NumGauss(), AccumFullGmm::occupancy(), TraceMatMat(), TraceSpSp(), and VecVec().
| void ModifyGraphForCarefulAlignment | ( | fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | fst | ) |
This function modifies the decoding graph for what we call "careful alignment".
The problem we are trying to solve is that if the decoding eats up the words in the graph too fast, it can get stuck at the end, and produce what looks like a valid alignment even though there was really a failure. So what we want to do is to introduce, after the final-states of the graph, a "blind alley" with no final-probs reachable, where the decoding can go to get lost. Our basic idea is to append the decoding-graph to itself using the fst Concat operation; but in order that there should be final-probs at the end of the first but not the second FST, we modify the right-hand argument to the Concat operation so that it has none of the original final-probs, and add a "pre-initial" state that is final.
Definition at line 546 of file decoder-wrappers.cc.
References KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by AlignUtteranceWrapper(), and AlignConfig::Register().
| ContextDependency * MonophoneContextDependency | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | phones, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | phone2num_pdf_classes | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 331 of file context-dep.cc.
References ContextDependency::ContextDependency(), GetStubMap(), and rnnlm::i.
Referenced by main(), TestConvertAlignment(), and TestMonophoneContextDependency().
| ContextDependency * MonophoneContextDependencyShared | ( | const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | phone_sets, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | phone2num_pdf_classes | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 343 of file context-dep.cc.
References ContextDependency::ContextDependency(), and GetStubMap().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
This is not really a wrapper for CBLAS as CBLAS does not have this; in future we could extend this somehow.
Definition at line 341 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::MulElements().
|
inline |
Definition at line 224 of file parse-options.cc.
References rnnlm::d, KALDI_ASSERT, and kBash.
Referenced by ParseOptions::Escape().
| void kaldi::MyFunction1 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 27 of file kaldi-error-test.cc.
References MyFunction2().
Referenced by UnitTestError().
| void kaldi::MyFunction2 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file kaldi-error-test.cc.
References KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by MyFunction1().
| std::string NameOf | ( | ) |
Definition at line 30 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
This function processes the NCCF n to a reasonably accurate probability of voicing p by applying the formula:
n' = fabs(n) r = -5.2 + 5.4 * exp(7.5 * (n' - 1.0)) + 4.8 * n' - 2.0 * exp(-10.0 * n') + 4.2 * exp(20.0 * (n' - 1.0)); p = 1.0 / (1 + exp(-1.0 * r));
How did we get this formula? We plotted the empirical log-prob-ratio of voicing r = log( p[voiced] / p[not-voiced] ) [on the Keele database where voicing is marked], as a function of the NCCF at the delay picked by our algorithm. This was done on intervals of the NCCF, so we had enough statistics to get that ratio. The NCCF covers [-1, 1]; almost all of the probability mass is on [0, 1] but the empirical POV seems fairly symmetric with a minimum near zero, so we chose to make it a function of n' = fabs(n).
Then we manually tuned a function (the one you see above) that approximated the log-prob-ratio of voicing fairly well as a function of the absolute-value NCCF n'; however, wasn't a very exact match since we were also trying to make the transformed NCCF fairly Gaussian distributed, with a view to using it as a feature– an idea we later abandoned after a simpler formula worked better.
Definition at line 78 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References Exp(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by OnlineProcessPitch::UpdateNormalizationStats().
This function processes the NCCF n to a POV feature f by applying the formula f = (1.0001 - n)^0.15 - 1.0 This is a nonlinear function designed to make the output reasonably Gaussian distributed.
Before doing this, the NCCF distribution is in the range [-1, 1] but has a strong peak just before 1.0, which this function smooths out.
Definition at line 44 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by OnlineProcessPitch::GetPovFeature().
| CuCompressedMatrixBase * NewCuCompressedMatrix | ( | CuCompressedMatrixType | t, |
| BaseFloat | range, | ||
| bool | truncate = true |
||
| ) |
This function allocates a new CuCompressedMatrix with type determined by t, and with the 'range' and 'truncate' parameters provided to the constructor of class CuCompressedMatrix.
It will crash at runtime if called when CUDA is not compiled in, or not enabled.
Definition at line 119 of file cu-compressed-matrix.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, kCompressedMatrixInt16, kCompressedMatrixInt8, kCompressedMatrixUint16, and kCompressedMatrixUint8.
Referenced by CuCompressedMatrixTestNonnegative(), CuCompressedMatrixTestSign(), CuCompressedMatrixTestSymmetric(), and NnetComputer::ExecuteCommand().
|
static |
Definition at line 1550 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by UnitTestPca2().
|
static |
Definition at line 1538 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetUnit().
Referenced by UnitTestPca2().
|
static |
Definition at line 1567 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetUnit().
Referenced by UnitTestPca(), UnitTestTopEigs(), UnitTestTridiagonalize(), and UnitTestTridiagonalizeAndQr().
|
static |
ObtainSetsOfPhones is called by AutomaticallyObtainQuestions.
It processes the output of ClusterTopDown to obtain the sets of phones corresponding to both the leaf-level clusters and all the non-leaf-level clusters.
Definition at line 557 of file build-tree.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSortedAndUniq(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and RemoveDuplicates().
Referenced by AutomaticallyObtainQuestions().
| template void kaldi::OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > | ( | const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > & | decoder | ) |
| template void kaldi::OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > | ( | const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > > & | decoder | ) |
| template void kaldi::OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::GrammarFst > | ( | const LatticeFasterOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > & | decoder | ) |
| template void kaldi::OnlineSilenceWeighting::ComputeCurrentTraceback< fst::GrammarFst > | ( | const LatticeIncrementalOnlineDecoderTpl< fst::GrammarFst > & | decoder | ) |
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuBlockMatrix< Real > & | mat | ||
| ) |
Print the matrix to stream.
Definition at line 318 of file cu-block-matrix.cc.
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuBlockMatrix< float > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuBlockMatrix< double > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuArray< T > & | vec | ||
| ) |
Print the vector to stream.
I/O.
Definition at line 329 of file cu-array-inl.h.
References rnnlm::i.
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuPackedMatrix< Real > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuPackedMatrix< float > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuPackedMatrix< double > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| const kaldi::DiagGmm & | gmm | ||
| ) |
ostream operator that calls DiagGMM::Write()
Definition at line 722 of file diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmm::Write().
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out_stream, |
| const kaldi::FullGmm & | gmm | ||
| ) |
ostream operator that calls FullGmm::Write()
Definition at line 777 of file full-gmm.cc.
References FullGmm::Write().
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuVectorBase< Real > & | vec | ||
| ) |
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuVectorBase< float > & | vec | ||
| ) |
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuVectorBase< double > & | vec | ||
| ) |
| std::ostream & operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | mat | ||
| ) |
Print the matrix to stream.
I/O.
Definition at line 3464 of file cu-matrix.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuMatrixBase< float > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| template std::ostream& kaldi::operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | out, |
| const CuMatrixBase< double > & | mat | ||
| ) |
| bool kaldi::operator> | ( | const CompBotClustElem & | a, |
| const CompBotClustElem & | b | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 438 of file cluster-utils.cc.
References CompBotClustElem::dist.
| std::istream & operator>> | ( | std::istream & | is, |
| kaldi::DiagGmm & | gmm | ||
| ) |
istream operator that calls DiagGMM::Read()
Definition at line 758 of file diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmm::Read().
| std::istream & operator>> | ( | std::istream & | in_stream, |
| kaldi::FullGmm & | gmm | ||
| ) |
istream operator that calls FullGmm::Read()
Definition at line 848 of file full-gmm.cc.
References FullGmm::Read().
| void OptimizeFactorTransducer | ( | KwsLexicographicFst * | index_transducer, |
| int32 | max_states, | ||
| bool | allow_partial | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 116 of file kws-functions2.cc.
References fst::DeterminizeStar(), KALDI_VLOG, and KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by main().
| int PaCallback | ( | const void * | input, |
| void * | output, | ||
| long unsigned | frame_count, | ||
| const PaStreamCallbackTimeInfo * | time_info, | ||
| PaStreamCallbackFlags | status_flags, | ||
| void * | user_data | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 39 of file online-audio-source.cc.
References OnlinePaSource::Callback().
| void ParseConfigLines | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | lines, |
| std::vector< ConfigLine > * | config_lines | ||
| ) |
This function converts config-lines from a simple sequence of strings as output by ReadConfigLines(), into a sequence of first-tokens and name-value pairs.
The general format is: "command-type bar=baz xx=yyy" etc., although there are subtleties as to what exactly is allowed, see documentation for class ConfigLine for details. This function will die if there was a parsing failure.
Definition at line 579 of file text-utils.cc.
References rnnlm::i, and KALDI_ERR.
| bool kaldi::ParseMatrixRangeSpecifier | ( | const std::string & | range, |
| const int | rows, | ||
| const int | cols, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | row_range, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | col_range | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 33 of file kaldi-holder.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, KALDI_WARN, SplitStringToIntegers(), and SplitStringToVector().
Referenced by ExtractObjectRange().
| bool PhoneAlignLattice | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| const PhoneAlignLatticeOptions & | opts, | ||
| CompactLattice * | lat_out | ||
| ) |
Outputs a lattice in which the arcs correspond exactly to sequences of phones, so the boundaries between the arcs correspond to the boundaries between phones If remove-epsilon == false and replace-output-symbols == false, but an arc may have >1 phone on it, but the boundaries will still correspond with the boundaries between phones.
Note: it's possible to have arcs with words on them but no transition-ids at all. Returns true if everything was OK, false if some kind of error was detected (e.g. the "reorder" option was incorrectly specified.)
Definition at line 413 of file phone-align-lattice.cc.
References LatticePhoneAligner::AlignLattice().
Referenced by main(), PhoneAlignLatticeOptions::Register(), and WordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void kaldi::PlaceNansInGaps | ( | Matrix< Real > * | mat | ) |
Definition at line 1858 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::j, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), MatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Stride().
Referenced by UnitTestAddMatMatNans(), and UnitTestResizeCopyDataDifferentStrideType().
| template void kaldi::PosteriorToMatrix< double > | ( | const Posterior & | post, |
| const int32 | post_dim, | ||
| Matrix< double > * | mat | ||
| ) |
Referenced by PosteriorToMatrix().
| template void kaldi::PosteriorToMatrix< float > | ( | const Posterior & | post, |
| const int32 | post_dim, | ||
| Matrix< float > * | mat | ||
| ) |
Referenced by PosteriorToMatrix().
| template void kaldi::PosteriorToPdfMatrix< double > | ( | const Posterior & | post, |
| const TransitionModel & | model, | ||
| Matrix< double > * | mat | ||
| ) |
Referenced by PosteriorToPdfMatrix().
| template void kaldi::PosteriorToPdfMatrix< float > | ( | const Posterior & | post, |
| const TransitionModel & | model, | ||
| Matrix< float > * | mat | ||
| ) |
Referenced by PosteriorToPdfMatrix().
|
static |
Definition at line 45 of file kaldi-cygwin-io-inl.h.
References cygprefix().
Referenced by MapCygwinPath(), and MapCygwinPathNoTmp().
| void kaldi::PrepareMap | ( | const std::string & | map_rxfilename, |
| int32 | num_classes, | ||
| unordered_map< int32, int32 > * | map | ||
| ) |
PrepareMap creates a map that specifies the mapping between the input and output class labels.
If the string map_rxfilename is empty, then the mapping is the identity map (e.g., 0 maps to 0, 1 maps to 1, etc), based on the number of classes num_classes. If map_rxfilename is not empty, the mapping is created from that file. The file is expected to be two columns of integers with up to num_classes rows. If an input class is not specified in the file, then the output class label is the same as the input. The first column is the input class and the second column is the output class. For example: 0 0 1 1 2 0
Definition at line 42 of file compute-vad-from-frame-likes.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, SplitStringToVector(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::PrepareMap | ( | const std::string | map_rxfilename, |
| unordered_map< std::pair< int32, int32 >, int32, PairHasher< int32 > > * | map | ||
| ) |
PrepareMap creates a mapping between the pairs of VAD decisions and the output label.
If map_rxfilename is empty, we create a mapping in which a frame is only classified as speech (represented as "1") if both VAD decisions agree on speech, and nonspeech (represented as "0") otherwise. If map_rxfilename is not empty, then that table provides the mapping. If the first set of VAD decisions has N classes and the second has M classes, then the table needs to have NxM rows, and three columns. The first two columns correspond to the labels in the first and second VAD decisions respectively, and the last column is the resultant output label. For example: 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 1
Definition at line 45 of file merge-vads.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, SplitStringToVector(), and Input::Stream().
| void kaldi::PreparePriors | ( | const std::string & | priors_str, |
| int32 | num_classes, | ||
| std::vector< BaseFloat > * | priors | ||
| ) |
PreparePriors creates a table specifying the priors for each class.
If priors_str is empty, uniform priors are assumed. If priors_str is nonempty, the comma-separated floats are parsed out. If present, the input of priors_str is of the form: 0.5,0.25,0.25
Definition at line 80 of file compute-vad-from-frame-likes.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, and SplitStringToFloats().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 83 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_LOG.
Referenced by TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void PrintPartialResult | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | words, |
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| bool | line_break | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 60 of file onlinebin-util.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 95 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, and KALDI_LOG.
Referenced by TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
Definition at line 30 of file process-pitch-feats.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Log(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by main().
| int32 kaldi::ProcessTopo | ( | const HmmTopology & | topo, |
| const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | questions | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 27 of file compile-questions.cc.
References HmmTopology::GetPhones(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, HmmTopology::NumPdfClasses(), SortAndUniq(), and WriteIntegerVector().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::ProcessUtterance | ( | LatticeFasterDecoder & | decoder, |
| const AmSgmm2 & | am_sgmm, | ||
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| double | log_prune, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | features, | ||
| RandomAccessInt32VectorVectorReader & | gselect_reader, | ||
| RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReaderMapped & | spkvecs_reader, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| const std::string & | utt, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignments_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| double * | like_ptr | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 38 of file sgmm2-latgen-faster.cc.
References AmSgmm2::ComputePerSpkDerivedVars(), DecodeUtteranceLatticeFaster(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< Holder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars::SetSpeakerVector(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< Holder >::Value().
| void kaldi::ProcessUtterance | ( | const AmSgmm2 & | am_sgmm, |
| const TransitionModel & | trans_model, | ||
| double | log_prune, | ||
| double | acoustic_scale, | ||
| const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | features, | ||
| RandomAccessInt32VectorVectorReader & | gselect_reader, | ||
| RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReaderMapped & | spkvecs_reader, | ||
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| const std::string & | utt, | ||
| bool | determinize, | ||
| bool | allow_partial, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | alignments_writer, | ||
| Int32VectorWriter * | words_writer, | ||
| CompactLatticeWriter * | compact_lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeWriter * | lattice_writer, | ||
| LatticeFasterDecoder * | decoder, | ||
| double * | like_sum, | ||
| int64 * | frame_sum, | ||
| int32 * | num_done, | ||
| int32 * | num_err, | ||
| TaskSequencer< DecodeUtteranceLatticeFasterClass > * | sequencer | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 39 of file sgmm2-latgen-faster-parallel.cc.
References AmSgmm2::ComputePerSpkDerivedVars(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< Holder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), TaskSequencer< C >::Run(), Sgmm2PerSpkDerivedVars::SetSpeakerVector(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and RandomAccessTableReaderMapped< Holder >::Value().
Referenced by main().
Prunes a lattice or compact lattice.
Returns true on success, false if there was some kind of failure.
Definition at line 229 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References fst::ConvertToCost(), KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by fst::DeterminizeLatticePruned(), DeterminizeLatticeWrapper(), SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::GetGaussianPosteriors(), SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::GetLattice(), main(), and fst::TestDeterminizeLatticePruned().
| template bool kaldi::PruneLattice | ( | BaseFloat | beam, |
| CompactLattice * | lat | ||
| ) |
| void kaldi::QrInternal | ( | MatrixIndexT | n, |
| Real * | diag, | ||
| Real * | off_diag, | ||
| MatrixBase< Real > * | Q | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 331 of file qr.cc.
References rnnlm::d, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, rnnlm::n, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and QrStep().
Referenced by SpMatrix< float >::Qr().
| void kaldi::QrStep | ( | MatrixIndexT | n, |
| Real * | diag, | ||
| Real * | off_diag, | ||
| MatrixBase< Real > * | Q | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 245 of file qr.cc.
References cblas_Xrot(), rnnlm::d, MatrixBase< Real >::Data(), Givens(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ISFINITE, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Stride().
Referenced by QrInternal().
|
static |
Definition at line 263 of file parse-options.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and kBash.
Referenced by ParseOptions::Escape().
| int Rand | ( | struct RandomState * | state | ) |
Definition at line 45 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References RandomState::seed.
Referenced by CholeskyUnitTestTr(), ClusterKMeansOnce(), OnlineMatrixInput::Compute(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeExampleComputationRequestSimple(), CuVectorUnitTestAddColSumMat(), CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMat2(), CuVectorUnitTestAddDiagMatMat(), CuVectorUnitTestAddMatVec(), CuVectorUnitTestAddRowSumMat(), CuVectorUnitTestAddSpVec(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVec(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVecCross(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVecExtra(), CuVectorUnitTestAddVecVec(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeiling(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyCeilingNoCount(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloor(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyFloorNoCount(), CuVectorUnitTestApplyPow(), CuVectorUnitTestApplySoftMax(), CuVectorUnitTestApproxEqual(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyCross2(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromMat(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyDiagFromPacked(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyElements(), CuVectorUnitTestCopyFromMat(), CuVectorUnitTestInvertElements(), CuVectorUnitTestMax(), CuVectorUnitTestMin(), CuVectorUnitTestScale(), CuVectorUnitTestSum(), CuVectorUnitTestVecVec(), fst::GenAcceptorFromSequence(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceCnn(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceLstm(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceLstmType2(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceLstmWithTruncation(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceRnn(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceRnnClockwork(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceSimple(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceSimpleContext(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceSimplest(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateRandomComponentConfig(), GenRandContextDependency(), GenRandContextDependencyLarge(), kaldi::nnet3::GenRandDescriptor(), kaldi::nnet3::GenRandForwardingDescriptor(), fst::GenRandPhoneSeq(), GenRandStats(), kaldi::nnet3::GenRandSumDescriptor(), GetOutput(), GetRandChar(), GetRandDelim(), InitRandomGmm(), AmSgmm2::LogLikelihood(), main(), MyTaskClass::operator()(), kaldi::nnet2::PreconditionDirections(), fst::RandFst(), RandFstOptions::RandFstOptions(), RandInt(), fst::RandomCompactLatticeWeight(), RandomEventMap(), RandomizeVector(), fst::RandomLatticeWeight(), RandomState::RandomState(), fst::RandPairFst(), RandPosdefSpMatrix(), RandUniform(), kaldi::nnet1::RandUniform(), fst::TestAcceptorMinimize(), fst::TestAddSelfLoops(), TestAddToClustersOptimized(), TestBuildTree(), TestBuildTreeStatsIo(), TestClusterBottomUp(), TestClusterEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap2(), TestClusterEventMapRestricted(), TestClusterKMeans(), TestClusterKMeansVector(), TestClusterTopDown(), TestClusterUtils(), TestClusterUtilsVector(), TestContainsNullPointers(), TestContextDep(), fst::TestContextFst(), fst::TestConvert(), fst::TestConvert2(), fst::TestConvertPair(), TestCopyMapKeysToSet(), TestCopyMapKeysToVector(), TestCopyMapToVector(), TestCopyMapValuesToSet(), TestCopyMapValuesToVector(), TestCopySetToVector(), TestCuFindRowMaxId(), TestCuMatrixCompObjfAndDeriv(), TestCuMatrixLookup(), TestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), fst::TestDeterminize(), fst::TestDeterminize2(), fst::TestDeterminizeGeneral(), fst::TestDeterminizeLattice(), fst::TestDeterminizeLatticePruned(), TestEditDistance2(), TestEditDistance2String(), fst::TestEnsureEpsilonProperty(), fst::TestEqualAlign(), WordAlignedLatticeTester::TestEquivalent(), TestEventMap(), TestEventMapIo(), TestEventMapMapValues(), TestEventMapPrune(), TestEventTypeIo(), fst::TestFactor(), TestFmpe(), TestGenRandContextDependency(), TestGenRandStats(), TestHashList(), TestHmmTopology(), TestIsSorted(), TestIsSortedAndUniq(), TestIvectorExtractorIO(), TestIvectorExtractorStatsIO(), fst::TestLatticeStringRepository(), TestLatticeTableCross(), TestLevenshteinAlignment(), fst::TestMakeLinearAcceptor(), fst::TestMakeLoopFst(), fst::TestMakeSymbolsSame(), fst::TestMakeSymbolsSameClass(), TestMergePairVectorSumming(), fst::TestMinimize(), TestMinimizeCompactLattice(), TestMonophoneContextDependency(), kaldi::nnet3::TestNnetComponentIo(), TestOnlineCmnInput(), TestOnlineDeltaInput(), TestOnlineFeatureMatrix(), TestOnlineLdaInput(), TestOnlineMatrixInput(), fst::TestPreDeterminize(), fst::TestPruneSpecial(), fst::TestPush(), TestPushCompactLatticeStrings(), TestPushCompactLatticeWeights(), fst::TestPushInLog(), fst::TestPushSpecial(), TestQuestionsInitRand(), TestRefineClusters(), fst::TestRemoveEpsLocal(), fst::TestRemoveEpsLocalSpecial(), TestReverseVector(), fst::TestSafeDeterminizeWrapper(), fst::TestScalePair(), TestSetOfNumbers(), TestShareEventMapLeaves(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentDataDerivative(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentPropagateProperties(), TestSortAndUniq(), TestSplitDecisionTree(), TestSplitStatsByKey(), TestSplitStringToVector(), fst::TestStringRepository(), fst::TestTableMatcher(), fst::TestTableMatcherCacheLeft(), fst::TestTableMatcherCacheRight(), TestTaskSequencer(), TestTreeCluster(), TestUniq(), TestWordAlignedLattice(), UnitTestAddDiagMat2(), UnitTestAddDiagMatMat(), UnitTestAddDiagVecMat(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAdditiveNoiseComponent(), UnitTestAddMat2(), UnitTestAddMat2Sp(), UnitTestAddMatDiagVec(), UnitTestAddMatMatElements(), UnitTestAddMatSelf(), UnitTestAddMatSmat(), UnitTestAddOuterProductPlusMinus(), UnitTestAddRows(), UnitTestAddSp(), UnitTestAddToDiag(), UnitTestAddToDiagMatrix(), UnitTestAddToRows(), UnitTestAddVec2Sp(), UnitTestAddVecToCols(), UnitTestAddVecToRows(), UnitTestAddVecVec(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAffineComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAffineComponentPreconditioned(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAffineComponentPreconditionedOnline(), UnitTestAssertFunc(), UnitTestAxpy(), UnitTestBackpropLstmNonlinearity(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestBlockAffineComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestBlockAffineComponentPreconditioned(), UnitTestCholesky(), UnitTestComplexFft(), UnitTestComplexFt(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestComputationRequestIo(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestConvolutional1dComponent(), UnitTestCopyCols(), UnitTestCopyRows(), UnitTestCopyRowsAndCols(), UnitTestCopySp(), UnitTestCopyToRows(), UnitTestCuApproxEqual(), UnitTestCuArray(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatBlock(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatMat(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuCholesky(), UnitTestCuCopy(), UnitTestCuDiffNormalizePerRow(), UnitTestCuDiffXent(), UnitTestCuFindRowMaxId(), UnitTestCuLogSoftmax(), UnitTestCuMathComputeLstmNonlinearity(), UnitTestCuMathCopy(), UnitTestCuMathNormalizePerRow(), UnitTestCuMathRandomize(), UnitTestCuMathSplice(), UnitTestCuMatrixAdd(), UnitTestCuMatrixAdd2(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddCols(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddDiagVecMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatDiagVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatMatElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatTp(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddRowRanges(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToDiag(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddTpMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyCeiling(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExp(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExpLimited(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyExpSpecial(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyFloor(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyHeaviside(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyLog(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyPow(), UnitTestCuMatrixApplyPowAbs(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCols(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyColsFromVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross2(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyFromMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyFromTp(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyLowerToUpper(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyRowsFromVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyToRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixCopyUpperToLower(), UnitTestCuMatrixDiffGroupPnorm(), UnitTestCuMatrixDivElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixGroupMax(), UnitTestCuMatrixGroupMaxDeriv(), UnitTestCuMatrixGroupPnorm(), UnitTestCuMatrixHeaviside(), UnitTestCuMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuMatrixLookup(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulElements(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRows(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsGroupMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixMulRowsVec(), UnitTestCuMatrixObjfDeriv(), UnitTestCuMatrixReduceMax(), UnitTestCuMatrixReduceMin(), UnitTestCuMatrixReduceSum(), UnitTestCuMatrixScale(), UnitTestCuMatrixSet(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetMatMatDivMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetRandn(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetRandUniform(), UnitTestCuMatrixSetZeroAboveDiag(), UnitTestCuMatrixSigmoid(), UnitTestCuMatrixSoftHinge(), UnitTestCuMatrixSumColumnRanges(), UnitTestCuMatrixSymAddMat2(), UnitTestCuMatrixSymInvertPosDef(), UnitTestCuMatrixTraceMatMat(), UnitTestCuMatrixTranspose(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixAddToDiag(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixScale(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixScaleDiag(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixSetUnit(), UnitTestCuPackedMatrixTrace(), UnitTestCuSoftmax(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixConstructFromIndexes(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixCopyToSmat(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSelectRowsAndTranspose(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSum(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixSwap(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddMat2(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddSp(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddVec2(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixApproxEqual(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixCopyFromMat(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixInvert(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixSetUnit(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixTraceSpSp(), UnitTestCuSubMatrix(), UnitTestCuSubVector(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixCholesky(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixCopyFromMat(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixCopyFromTp(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixInvert(), UnitTestCuTpMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuVectorIO(), UnitTestCuVectorReplaceValue(), UnitTestDct(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestDctComponent(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestDescriptorIo(), UnitTestDeterminant(), UnitTestDeterminantSign(), UnitTestDotprod(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestDropoutComponent(), UnitTestEigSp(), UnitTestEigSymmetric(), UnitTestEnsureNonzero(), UnitTestEstimateDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), UnitTestExtractCompressedMatrix(), UnitTestFactorizeTpl(), UnitTestFFTbasedBlockConvolution(), UnitTestFFTbasedConvolution(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestFixedAffineComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestFixedBiasComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestFixedLinearComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestFixedScaleComponent(), UnitTestFloorCeiling(), UnitTestFloorChol(), UnitTestFloorUnit(), UnitTestFmllrRaw(), UnitTestFullGmmEst(), UnitTestGcdLcmTpl(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestGeneralDescriptor(), UnitTestGeneralMatrix(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestGenericComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestGenericComponentInternal(), UnitTestHeaviside(), UnitTestHtkIo(), UnitTestInnerProd(), UnitTestInverse(), UnitTestInvert(), UnitTestIo(), UnitTestIoCross(), UnitTestIoNew(), UnitTestIoPipe(), UnitTestIvectorExtractor(), UnitTestLbfgs(), UnitTestLimitCond(), UnitTestLimitCondInvert(), UnitTestLinearCgd(), UnitTestLogAddSub(), UnitTestMat2Vec(), UnitTestMatrix(), UnitTestMax2(), UnitTestMaxMin(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestMaxoutComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestMaxpoolingComponent(), UnitTestMmul(), UnitTestMmulSym(), UnitTestMul(), UnitTestMulElements(), UnitTestMulTp(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetComputationIo(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetIo(), UnitTestNonsymmetricPower(), UnitTestNorm(), UnitTestOnlineCmvn(), UnitTestOrthogonalizeRows(), UnitTestPca(), UnitTestPldaEstimation(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestPnormComponent(), UnitTestPosteriors(), UnitTestPower(), UnitTestPowerAbs(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestPreconditionDirections(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), UnitTestRand(), UnitTestRandCategorical(), UnitTestRange(), UnitTestRankNUpdate(), UnitTestRealFft(), UnitTestRegressionTree(), UnitTestRegtreeFmllrDiagGmm(), UnitTestRemoveRow(), UnitTestReplaceValue(), UnitTestResize(), UnitTestResizeCopyDataDifferentStrideType(), UnitTestRow(), UnitTestScale(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestScaleComponent(), UnitTestScaleDiag(), UnitTestSetDiag(), UnitTestSetRandn(), UnitTestSetRandUniform(), UnitTestSger(), UnitTestSigmoid(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestSigmoidComponent(), UnitTestSimple(), UnitTestSimpleForMat(), UnitTestSimpleForVec(), UnitTestSoftHinge(), UnitTestSolve(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestSolvePackingProblem(), UnitTestSpAddDiagVec(), UnitTestSpAddVecVec(), UnitTestSparseMatrixAddToMat(), UnitTestSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm(), UnitTestSparseMatrixSum(), UnitTestSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), UnitTestSparseVectorAddToVec(), UnitTestSparseVectorMax(), UnitTestSparseVectorSum(), UnitTestSparseVectorVecSvec(), UnitTestSpInvert(), UnitTestSpliceRows(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestSplitLocations(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestSplitLocationsBackward(), UnitTestSplitRadixComplexFft(), UnitTestSplitRadixComplexFft2(), UnitTestSplitRadixRealFft(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestSumGroupComponent(), UnitTestSvd(), UnitTestSvdJustvec(), UnitTestSvdNodestroy(), UnitTestSvdZero(), UnitTestSymAddMat2(), UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble(), UnitTestTableRandomBothDoubleMatrix(), UnitTestTableSequentialBaseFloatVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialBool(), UnitTestTableSequentialDouble(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleMatrixBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32PairVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32Script(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorVectorBoth(), UnitTestTanh(), UnitTestTp2(), UnitTestTp2Sp(), UnitTestTpInvert(), UnitTestTrace(), UnitTestTraceProduct(), UnitTestTraceSpSpLower(), UnitTestTrain(), UnitTestTranspose(), UnitTestTransposeScatter(), UnitTestTridiagonalize(), UnitTestTridiagonalizeAndQr(), UnitTestTriVecSolver(), UnitTestVecMatVec(), UnitTestVecmul(), UnitTestVector(), UnitTestVectorMax(), UnitTestVectorMin(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddMatSmat(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmat(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmatMat(), and WithProb().
| CompactLattice * RandCompactLattice | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file kaldi-lattice-test.cc.
References fst::ConvertLattice().
Referenced by TestCompactLatticeTable(), TestCompactLatticeTableCross(), TestPushCompactLatticeStrings(), and TestPushCompactLatticeWeights().
| CompactLattice* kaldi::RandDeterministicCompactLattice | ( | ) |
Definition at line 30 of file minimize-lattice-test.cc.
References RandFstOptions::acyclic, fst::DeterminizeLattice(), and KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by TestMinimizeCompactLattice().
Definition at line 30 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::Cond(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromSp(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by generate_features().
|
inline |
Definition at line 155 of file kaldi-math.h.
References Log(), M_PI, RandGauss2(), RandPoisson(), and RandUniform().
Referenced by _RandGauss(), Dither(), DiagGmm::Generate(), generate_features(), GenRandStats(), OnlineProcessPitch::GetDeltaPitchFeature(), init_rand_diag_gmm(), InitRand(), kaldi::unittest::InitRandDiagGmm(), kaldi::unittest::InitRandFullGmm(), InitRandNonsingular(), InitRandomGmm(), DiagGmm::Perturb(), PlaceNansInGaps(), rand_diag_gmm(), kaldi::unittest::RandDiagGaussFeatures(), kaldi::unittest::RandFullGaussFeatures(), fst::RandomLatticeWeight(), VectorBase< float >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< float >::SetRandn(), SparseVector< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< float >::SetRandn(), DiagGmm::Split(), TestAddToClustersOptimized(), TestAmDiagGmmIO(), TestClusterEventMapRestricted(), TestClustering(), TestClusterUtils(), TestContextDep(), TestFmpe(), TestSgmm2Fmllr(), TestSgmm2IncreaseDim(), TestSgmm2Init(), TestSgmm2IO(), TestSgmm2Substates(), TestShareEventMapLeaves(), TestSplitDecisionTree(), TestSplitStates(), UnitTestComplexPower(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix(), UnitTestCuSpMatrixAddVec2(), UnitTestDelay(), UnitTestDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateFullGmm(), UnitTestEstimateLda(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateSgmm2(), UnitTestFullGmm(), UnitTestGeneralMatrix(), UnitTestMleAmDiagGmm(), UnitTestNorm(), UnitTestPieces(), UnitTestRand(), UnitTestSearch(), UnitTestSparseMatrixConstructor(), UnitTestSpInvert(), UnitTestTableSequentialBaseFloatVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleMatrixBoth(), UnitTestTopEigs(), UnitTestTpInvert(), and UnitTestTransposeScatter().
| void RandGauss2 | ( | float * | a, |
| float * | b, | ||
| RandomState * | state | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 139 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, M_PI, and RandUniform().
Referenced by RandGauss(), RandGauss2(), VectorBase< float >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< float >::SetRandn(), and UnitTestRand().
| void RandGauss2 | ( | double * | a, |
| double * | b, | ||
| RandomState * | state | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 150 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and RandGauss2().
| int32 RandInt | ( | int32 | min_val, |
| int32 | max_val, | ||
| struct RandomState * | state | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 95 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, and Rand().
Referenced by ComputationGraphBuilder::Check(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::CheckModelAndIo(), ComputationGraphBuilder::Compute(), kaldi::nnet3::ConstrainOrthonormal(), CuCompressedMatrixTestNonnegative(), CuCompressedMatrixTestSign(), CuCompressedMatrixTestSymmetric(), fst::EqualAlign(), kaldi::nnet3::FindNStride(), GenerateCompactLatticeRandomly(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequence(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceCnnNew(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceCompositeBlock(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceDistribute(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceLstmType2(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceLstmWithTruncation(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceRestrictedAttention(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceRnn(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceSimple(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceSimpleContext(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateConfigSequenceStatistics(), GenerateLexicon(), GeneratePathThroughHmm(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateRandomComponentConfig(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateSimpleNnetTrainingExample(), GenerateWordAndPhoneSequence(), GenRandTopology(), GetBootstrapWERInterval(), GetBootstrapWERTwoSystemComparison(), UtteranceSplitter::GetChunkSizesForUtterance(), GeneralDropoutComponent::GetMemo(), SpecAugmentTimeMaskComponent::GetMemo(), kaldi::nnet3::GetNumNvalues(), NnetComputer::GetPointers(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::GetRandomConvolutionIndexes(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::GetRandomConvolutionModel(), InitGmmFromRandomFrames(), Questions::InitRand(), kaldi::nnet3::InsertCommands(), main(), PlaceNansInGaps(), TdnnComponent::PrecomputeIndexes(), kaldi::nnet3::ProcessFile(), kaldi::nnet3::SelectFromExample(), kaldi::nnet3::SetDerivTimesOptions(), NonlinearComponent::StoreBackpropStats(), RestrictedAttentionComponent::StoreStats(), SigmoidComponent::StoreStats(), TanhComponent::StoreStats(), RectifiedLinearComponent::StoreStats(), NnetDiscriminativeSupervision::Swap(), NnetChainSupervision::Swap(), TestAccumulateTreeStatsOptions(), TestAmDiagGmmAccsIO(), kaldi::nnet3::attention::TestAttentionForwardBackward(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::TestComputationIo(), TestConvertAlignment(), TestCuMatrixResize(), TestCuVectorApplyCeiling(), TestCuVectorApplyCeilingNoCount(), TestCuVectorApplyFloor(), TestCuVectorApplyFloorNoCount(), TestDoTableSplit(), TestFindAllKeys(), TestHmmTopology(), TestMllrAccsIO(), kaldi::nnet3::TestNnetDecodable(), TestOnlineMfcc(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::TestParamsBackprop(), TestPossibleValues(), TestPosteriorIo(), TestSgmm2Fmllr(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentDataDerivative(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentModelDerivative(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentPropagateProperties(), TestSplitToPhones(), TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon(), UnitTestAddMatMatNans(), UnitTestAmDiagGmm(), UnitTestApplyExpSpecial(), kaldi::nnet3::attention::UnitTestAttentionDotProductAndAddScales(), UnitTestBackpropLstmNonlinearity(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestCindexIo(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix(), UnitTestCompressedMatrix2(), UnitTestCuDiffLogSoftmax(), UnitTestCuDiffSoftmax(), UnitTestCuMathComputeLstmNonlinearity(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks1(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks1Trans(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddMatBlocks2(), UnitTestCuVectorSum(), UnitTestDiagGmm(), UnitTestDivideRoundingDown(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestEnsureContiguousProperty(), UnitTestEnsureNonzero(), UnitTestEstimateLda(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), UnitTestEstimateSgmm2(), UnitTestFullGmm(), UnitTestGeneralMatrix(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestHasContiguousProperty(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestIndexIo(), UnitTestIo(), UnitTestLstmNonlinearity(), UnitTestMatrixAddMatSmat(), UnitTestMatrixAddSmatMat(), UnitTestMleAmDiagGmm(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetAnalyze(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetCompileLooped(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetCompute(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetExample(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetInputDerivatives(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetMergeExamples(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetModelDerivatives(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetOptimizeInternal(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetOptimizeWithOptions(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), UnitTestRand(), UnitTestRangesMatrix(), UnitTestRegressionTree(), UnitTestRegtreeMllrDiagGmm(), UnitTestSgmm2(), UnitTestSparseMatrixConstructor(), UnitTestSparseVectorMax(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestSpliceComponent(), UnitTestTableSequentialBaseFloatVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialBool(), UnitTestTableSequentialDouble(), UnitTestTableSequentialDoubleBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32PairVectorBoth(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32Script(), UnitTestTableSequentialInt32VectorBoth(), and kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::UnitTestTimeHeightConvolutionIo().
| Lattice* kaldi::RandLattice | ( | ) |
Definition at line 36 of file kaldi-lattice-test.cc.
Referenced by TestLatticeTable(), and TestLatticeTableCross().
| EventMap* kaldi::RandomEventMap | ( | const std::vector< EventKeyType > & | keys | ) |
Definition at line 145 of file event-map-test.cc.
References CopySetToVector(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kMaxVal, Rand(), RandPoisson(), and RandUniform().
Referenced by TestEventMapIo(), TestEventMapMapValues(), and TestEventMapPrune().
| void kaldi::RandomizeVector | ( | std::vector< T > * | v | ) |
Definition at line 754 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), and swap().
Referenced by UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble(), and UnitTestTableRandomBothDoubleMatrix().
| bool kaldi::RandomSplit | ( | int32 | wav_dim, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | piece_dim, | ||
| int32 | num_pieces, | ||
| int32 | trials = 5 |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 57 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i.
Referenced by TestOnlineAppendFeature(), TestOnlineMfcc(), and TestOnlinePlp().
| int32 RandPoisson | ( | float | lambda, |
| struct RandomState * | state | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 126 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and RandUniform().
Referenced by RandGauss(), RandomEventMap(), and UnitTestRand().
| void kaldi::RandPosdefSpMatrix | ( | MatrixIndexT | dim, |
| SpMatrix< Real > * | matrix | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 36 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), TpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, and Rand().
Referenced by UnitTestFullGmm(), UnitTestLbfgs(), UnitTestLinearCgd(), and UnitTestSolve().
|
inline |
Definition at line 174 of file kaldi-math.h.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and RandUniform().
Referenced by NnetLdaStatsAccumulator::AccStatsFromOutput(), MlltAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), MleAmSgmm2Accs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), main(), and UnitTestRand().
|
inline |
Returns a random number strictly between 0 and 1.
Definition at line 151 of file kaldi-math.h.
References Rand().
Referenced by CuRand< float >::BinarizeProbs(), LstmNonlinearityComponent::ConsolidateMemory(), DiagGmm::Generate(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateRandomComponentConfig(), kaldi::nnet3::GenerateSimpleNnetTrainingExample(), GenRandContextDependency(), GenRandContextDependencyLarge(), fst::GenRandPhoneSeq(), GenRandStats(), GeneralDropoutComponent::GetMemo(), init_rand_diag_gmm(), kaldi::unittest::InitRandFullGmm(), InitRandomGmm(), PitchInterpolator::InitValues(), main(), kaldi::nnet3::PerturbImage(), DropoutMaskComponent::Propagate(), DropoutComponent::Propagate(), AdditiveNoiseComponent::Propagate(), rand_diag_gmm(), VectorBase< float >::RandCategorical(), RandGauss(), RandGauss2(), RandomEventMap(), RandPoisson(), RandPrune(), RandZeroToOneMatrix(), SigmoidComponent::RepairGradients(), TanhComponent::RepairGradients(), RectifiedLinearComponent::RepairGradients(), ClipGradientComponent::RepairGradients(), VectorBase< float >::SetRandUniform(), MatrixBase< float >::SetRandUniform(), TestBuildTree(), TestClusterBottomUp(), TestClusterEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap2(), TestClusterEventMapRestricted(), TestClustering(), TestClusterKMeans(), TestClusterTopDown(), TestClusterUtilsVector(), fst::TestContextFst(), TestCuMatrixCompObjfAndDeriv(), fst::TestFactor(), TestGenRandStats(), TestPosteriorIo(), TestRefineClusters(), fst::TestRemoveEpsLocal(), TestSgmm2AccsIO(), TestSgmm2Substates(), TestShareEventMapLeaves(), TestSplitStates(), TestTreeCluster(), TestVectorToPosteriorEntry(), UnitTestArbitraryResample(), UnitTestCuMatrixObjfDeriv(), UnitTestDiagGmm(), UnitTestFullGmm(), UnitTestIo(), UnitTestIoNew(), UnitTestIoPipe(), UnitTestLinearResample(), UnitTestRand(), UnitTestRegtreeFmllrDiagGmm(), UnitTestSimpleForVec(), and UnitTestVtln().
|
static |
Definition at line 64 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and RandUniform().
Referenced by UnitTestCuDiffLogSoftmax(), UnitTestCuDiffSigmoid(), UnitTestCuDiffSoftmax(), UnitTestCuDiffTanh(), and UnitTestCuDiffXent().
| void kaldi::ReadCommaSeparatedCommand | ( | const std::string & | s, |
| std::vector< BaseFloat > * | v | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 119 of file wav-reverberate.cc.
References ConvertStringToReal(), rnnlm::i, and SplitStringToVector().
Referenced by main().
| bool ReadCompactLattice | ( | std::istream & | is, |
| bool | binary, | ||
| CompactLattice ** | clat | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 304 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References ConvertToCompactLattice(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, and ReadCompactLatticeText().
Referenced by CompactLatticeHolder::Read(), and DiscriminativeNnetExample::Read().
| CompactLattice* kaldi::ReadCompactLatticeText | ( | std::istream & | is | ) |
Definition at line 277 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References ConvertToCompactLattice(), and LatticeReader::ReadText().
Referenced by ReadCompactLattice().
| void kaldi::ReadConfigFromFile | ( | const std::string & | config_filename, |
| C * | c | ||
| ) |
This template is provided for convenience in reading config classes from files; this is not the standard way to read configuration options, but may occasionally be needed.
This function assumes the config has a function "void Register(OptionsItf *opts)" which it can call to register the ParseOptions object.
Definition at line 237 of file parse-options.h.
References ParseOptions::Register().
Referenced by OnlineIvectorExtractionInfo::Init(), OnlineFeaturePipelineConfig::OnlineFeaturePipelineConfig(), and OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineInfo::OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineInfo().
| void ReadConfigLines | ( | std::istream & | is, |
| std::vector< std::string > * | lines | ||
| ) |
This function reads in a config file and *appends* its contents to a vector of lines; it is responsible for removing comments (anything after '#') and stripping out any lines that contain only whitespace after comment removal.
Definition at line 564 of file text-utils.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by Nnet::ReadConfig(), kaldi::nnet3::ReadEditConfig(), and UnitTestReadConfig().
| void kaldi::ReadConfigsFromFile | ( | const std::string & | conf, |
| C1 * | c1, | ||
| C2 * | c2 | ||
| ) |
This variant of the template ReadConfigFromFile is for if you need to read two config classes from the same file.
Definition at line 249 of file parse-options.h.
References ParseOptions::Register().
Referenced by OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineInfo::OnlineNnet2FeaturePipelineInfo().
| bool kaldi::ReadData | ( | SequentialBaseFloatMatrixReader & | feature_reader, |
| RandomAccessPosteriorReader & | target_reader, | ||
| RandomAccessBaseFloatVectorReader & | weights_reader, | ||
| int32 | length_tolerance, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | feats, | ||
| Posterior * | targets, | ||
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | weights, | ||
| int32 * | num_no_tgt_mat, | ||
| int32 * | num_other_error | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file nnet-train-multistream.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::IsOpen(), KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, kCopyData, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), VectorBase< Real >::Set(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value().
Referenced by main().
| fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > * ReadDecodeGraph | ( | const std::string & | filename | ) |
Definition at line 27 of file onlinebin-util.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 239 of file event-map.cc.
References ExpectToken(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and ReadBasicType().
Referenced by MakeEventPair(), ReadBuildTreeStats(), and TestEventTypeIo().
Referenced by ReadHtk().
ReadFromList attempts to read this list of integers, one per line, from the given file, in text format.
returns true if succeeded.
Definition at line 33 of file simple-io-funcs.cc.
References rnnlm::i, Input::OpenTextMode(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| bool ReadIntegerVectorVectorSimple | ( | const std::string & | rxfilename, |
| std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > * | list | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 62 of file simple-io-funcs.cc.
References Input::OpenTextMode(), SplitStringToIntegers(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main(), and ReadPhoneMap().
Definition at line 417 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References ConvertToLattice(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, and ReadLatticeText().
Referenced by LatticeHolder::Read(), and DiscriminativeSupervision::Read().
| Lattice* kaldi::ReadLatticeText | ( | std::istream & | is | ) |
Definition at line 291 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References ConvertToLattice(), and LatticeReader::ReadText().
Referenced by ReadLattice().
Read the lexicon in the special format required for word alignment.
Each line has a series of integers on it (at least two on each line), representing:
<old-word-id> <new-word-id> [<phone-id-1> [<phone-id-2> ... ] ]
Here, <old-word-id> is the word-id that appears in the lattice before alignment, and <new-word-id> is the word-is that should appear in the lattice after alignment. This is mainly useful when the lattice may have no symbol for the optional-silence arcs (so <old-word-id> would equal zero), but we want it to be output with a symbol on those arcs (so <new-word-id> would be nonzero). If the silence should not be added to the lattice, both <old-word-id> and <new-word-id> may be zero.
This function is very simple: it just reads in a series of lines from a text file, each with at least two integers on them.
Definition at line 1051 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
References KALDI_WARN, and SplitStringToIntegers().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 359 of file online-audio-client.cc.
References buffer_fill, buffer_offset, and rnnlm::i.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::ReadModels | ( | std::vector< std::pair< std::string, BaseFloat > > | models_and_weights, |
| nnet3::Nnet * | output_nnet, | ||
| int32 * | success | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 57 of file nnet3-average.cc.
References kaldi::nnet3::AddNnet(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::n, ReadKaldiObject(), and kaldi::nnet3::ScaleNnet().
Referenced by main().
| fst::Fst< fst::StdArc > * ReadNetwork | ( | std::string | filename | ) |
Definition at line 32 of file gmm-decode-biglm-faster.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| void ReadPhoneMap | ( | std::string | phone_map_rxfilename, |
| std::vector< int32 > * | phone_map | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 106 of file tree-accu.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, PrintableRxfilename(), and ReadIntegerVectorVectorSimple().
Referenced by AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::AccumulateTreeStatsInfo(), and main().
| void ReadSharedPhonesList | ( | std::string | rxfilename, |
| std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > * | list_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file gmm-init-biphone.cc.
References IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ERR, PrintableRxfilename(), SplitStringToIntegers(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::ReadSymbolList | ( | const std::string & | rxfilename, |
| fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| LabelPairVector * | lpairs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file lattice-oracle.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, PrintableRxfilename(), and Input::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| template void kaldi::RealFft | ( | VectorBase< float > * | v, |
| bool | forward | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::RealFft | ( | VectorBase< double > * | v, |
| bool | forward | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::RealFftInefficient | ( | VectorBase< float > * | v, |
| bool | forward | ||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::RealFftInefficient | ( | VectorBase< double > * | v, |
| bool | forward | ||
| ) |
|
inline |
Definition at line 87 of file cu-allocator.h.
References CuAllocatorOptions::Register().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 533 of file build-tree.cc.
References KALDI_VLOG.
Referenced by ObtainSetsOfPhones().
| void RemoveLongSilences | ( | int32 | max_silence_frames, |
| const std::vector< int32 > & | state_times, | ||
| KwsProductFst * | factor_transducer | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 265 of file kws-functions.cc.
Referenced by main().
| void ReplaceAcousticScoresFromMap | ( | const unordered_map< std::pair< int32, int32 >, std::pair< BaseFloat, int32 >, PairHasher< int32 > > & | acoustic_scores, |
| Lattice * | lat | ||
| ) |
This function restores acoustic scores computed using the function ComputeAcousticScoresMap into the lattice.
| [in] | acoustic_scores | A map from the pair (frame-index, transition-id) to a pair (sum-of-acoustic-scores, num-of-occurences) of the occurences of the transition-id in that frame. See the comments for ComputeAcousticScoresMap for details. |
| [out] | lat | Pointer to the output lattice. |
Definition at line 1709 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, LatticeStateTimes(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::SetValue2(), TopSortLatticeIfNeeded(), and LatticeWeightTpl< BaseFloat >::Zero().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 36 of file kws-functions2.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by DoFactorMerging().
| bool RescoreCompactLattice | ( | DecodableInterface * | decodable, |
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
This function *adds* the negated scores obtained from the Decodable object, to the acoustic scores on the arcs.
If you want to replace them, you should use ScaleCompactLattice to first set the acoustic scores to zero. Returns true on success, false on error (typically some kind of mismatched inputs).
Definition at line 1354 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References RescoreCompactLatticeInternal().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::RescoreCompactLatticeInternal | ( | const TransitionModel * | tmodel, |
| BaseFloat | speedup_factor, | ||
| DecodableInterface * | decodable, | ||
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
RescoreCompactLatticeInternal is the internal code for both RescoreCompactLattice and RescoreCompatLatticeSpeedup.
For RescoreCompactLattice, "tmodel" will be NULL and speedup_factor will be 1.0.
Definition at line 1216 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References CompactLatticeStateTimes(), rnnlm::i, DecodableInterface::IsLastFrame(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, DecodableInterface::LogLikelihood(), LatticeWeightTpl< FloatType >::SetValue2(), CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::SetWeight(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPdf(), CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Weight(), WithProb(), and CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Zero().
Referenced by RescoreCompactLattice(), and RescoreCompactLatticeSpeedup().
| bool RescoreCompactLatticeSpeedup | ( | const TransitionModel & | tmodel, |
| BaseFloat | speedup_factor, | ||
| DecodableInterface * | decodable, | ||
| CompactLattice * | clat | ||
| ) |
This function is like RescoreCompactLattice, but it is modified to avoid computing probabilities on most frames where all the pdf-ids are the same.
(it needs the transition-model to work out whether two transition-ids map to the same pdf-id, and it assumes that the lattice has transition-ids on it). The naive thing would be to just set all probabilities to zero on frames where all the pdf-ids are the same (because this value won't affect the lattice posterior). But this would become confusing when we compute corpus-level diagnostics such as the MMI objective function. Instead, imagine speedup_factor = 100 (it must be >= 1.0)... with probability (1.0 / speedup_factor) we compute those likelihoods and multiply them by speedup_factor; otherwise we set them to zero. This gives the right expected probability so our corpus-level diagnostics will be about right.
Definition at line 1346 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References RescoreCompactLatticeInternal().
Referenced by main().
| bool RescoreLattice | ( | DecodableInterface * | decodable, |
| Lattice * | lat | ||
| ) |
This function *adds* the negated scores obtained from the Decodable object, to the acoustic scores on the arcs.
If you want to replace them, you should use ScaleCompactLattice to first set the acoustic scores to zero. Returns true on success, false on error (e.g. some kind of mismatched inputs). The input labels, if nonzero, are interpreted as transition-ids or whatever other index the Decodable object expects.
Definition at line 1360 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References rnnlm::i, DecodableInterface::IsLastFrame(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, LatticeStateTimes(), and DecodableInterface::LogLikelihood().
Referenced by SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::GetLattice().
Definition at line 176 of file mle-am-diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs(), DiagGmm::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::Set(), and DiagGmm::SetInvVars().
Referenced by MleAmDiagGmmUpdate().
|
inline |
Reverses the contents of a vector.
Definition at line 264 of file stl-utils.h.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and swap().
Referenced by LevenshteinAlignment(), and TestReverseVector().
Definition at line 32 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ComputationGraphBuilder::AddDependencies(), AssertEqual(), FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals(), FFTbasedConvolveSignals(), FrameExtractionOptions::PaddedWindowSize(), and UnitTestRoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo().
|
static |
Definition at line 26 of file online-endpoint.cc.
References KALDI_VLOG, OnlineEndpointRule::max_relative_cost, OnlineEndpointRule::min_trailing_silence, OnlineEndpointRule::min_utterance_length, and OnlineEndpointRule::must_contain_nonsilence.
Referenced by EndpointDetected().
| void kaldi::RunMultiThreaded | ( | const C & | c_in | ) |
Here, class C should inherit from MultiThreadable.
Note: if you want to control the number of threads yourself, or need to do something in the main thread of the program while the objects exist, just initialize the MultiThreader<C> object yourself.
Definition at line 151 of file kaldi-thread.h.
Referenced by AmSgmm2::ComputeNormalizers(), TestThreads(), EbwAmSgmm2Updater::UpdatePhoneVectors(), MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdatePhoneVectors(), EbwAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateW(), and MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateW().
| int32 kaldi::RunPerSpeaker | ( | const std::string & | ivector_extractor_rxfilename, |
| const IvectorEstimationOptions & | opts, | ||
| bool | compute_objf_change, | ||
| const std::string & | spk2utt_rspecifier, | ||
| const std::string & | feature_rspecifier, | ||
| const std::string & | posterior_rspecifier, | ||
| const std::string & | ivector_wspecifier | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 92 of file ivector-extract.cc.
References IvectorEstimationOptions::acoustic_weight, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), IvectorExtractor::FeatDim(), IvectorExtractor::GetAuxf(), IvectorExtractor::GetIvectorDistribution(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), rnnlm::i, IvectorExtractor::IvectorDim(), KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), IvectorEstimationOptions::max_count, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), IvectorExtractor::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), IvectorExtractor::PriorOffset(), ReadKaldiObject(), ScalePosterior(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| bool kaldi::SameDim | ( | const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | M, |
| const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | N | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 949 of file cu-matrix.h.
| bool kaldi::SameDimAndStride | ( | const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | M, |
| const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | N | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 954 of file cu-matrix.h.
Referenced by ScaleAndOffsetComponent::Backprop(), and ScaleAndOffsetComponent::Propagate().
| bool kaldi::ScoringTest | ( | bool | seps, |
| const std::string & | infile, | ||
| const std::string & | sentence, | ||
| float | expected | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 156 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
References AddSelfLoops(), AddToChainFsa(), ApproxEqual(), Compile(), ArpaLmCompiler::Fst(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kBos, and kEos.
Referenced by RunAllTests().
| void kaldi::SelectLags | ( | const PitchExtractionOptions & | opts, |
| Vector< BaseFloat > * | lags | ||
| ) |
This function selects the lags at which we measure the NCCF: we need to select lags from 1/max_f0 to 1/min_f0, in a geometric progression with ratio 1 + d.
Definition at line 157 of file pitch-functions.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::Data(), PitchExtractionOptions::delta_pitch, PitchExtractionOptions::max_f0, PitchExtractionOptions::min_f0, and Vector< Real >::Resize().
Referenced by OnlinePitchFeatureImpl::OnlinePitchFeatureImpl().
| void kaldi::SendPartialResult | ( | const std::vector< int32 > & | words, |
| const fst::SymbolTable * | word_syms, | ||
| const bool | line_break, | ||
| const int32 | serv_sock, | ||
| const sockaddr_in & | client_addr | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 30 of file online-server-gmm-decode-faster.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, and KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by main().
| BaseFloat SentenceLevelConfidence | ( | const CompactLattice & | clat, |
| int32 * | num_paths, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | best_sentence, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | second_best_sentence | ||
| ) |
Caution: this function is not the only way to get confidences in Kaldi.
This only gives you sentence-level (utterance-level) confidence. You can get word-by-word confidence within a sentence, along with Minimum Bayes Risk decoding, by looking at sausages.h. Caution: confidences estimated using this type of method are not very accurate. This function will return the difference between the best path in clat and the second-best path in clat (a positive number), or zero if clat was equivalent to the empty FST (no successful paths), or infinity if there was only one path in "clat". It will output to "num_paths" (if non-NULL) a number n = 0, 1 or 2 saying how many n-best paths (up to two) were found. If n >= 1 it outputs to "best_sentence" (if non-NULL) the best word-sequence; if n == 2 it outputs to "second_best_sentence" (if non-NULL) the second best word-sequence (this may be useful for testing whether the two best word sequences are somehow equivalent for the task at hand). If you need more information than this or want to look deeper inside the n-best list, then look at the implementation of this function. This function requires that distinct paths in "lat" have distinct word sequences; this will automatically be the case if you generated "clat" in any normal way, such as from a decoder, because a deterministic FST has this property. This function assumes that any acoustic scaling you want to apply, has already been applied.
Definition at line 26 of file confidence.cc.
References fst::ConvertLattice(), fst::ConvertToCost(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, rnnlm::n, and fst::NbestAsFsts().
Referenced by main(), and SentenceLevelConfidence().
| BaseFloat SentenceLevelConfidence | ( | const Lattice & | lat, |
| int32 * | num_paths, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | best_sentence, | ||
| std::vector< int32 > * | second_best_sentence | ||
| ) |
This version of SentenceLevelConfidence takes as input a state-level lattice.
It needs to determinize it first, but it does so in a "smart" way that only generates about as many output paths as it needs.
Definition at line 85 of file confidence.cc.
References fst::DeterminizeLatticePruned(), LongestSentenceLength(), DeterminizeLatticePrunedOptions::max_arcs, and SentenceLevelConfidence().
| void kaldi::SetLinearAcceptorWeight | ( | double | cost, |
| fst::VectorFst< fst::StdArc > * | fst | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 27 of file transcripts-to-fsts.cc.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 69 of file simple-options.cc.
Referenced by SimpleOptions::SetOption().
Definition at line 84 of file process-pitch-feats.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::ShiftFeatureMatrix | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | src, |
| int32 | shift, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | rearranged | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 26 of file shift-feats.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by main().
| void Sleep | ( | float | seconds | ) |
Definition at line 45 of file kaldi-utils.cc.
Referenced by MachineIsLittleEndian(), main(), OnlineTimer::SleepUntil(), TimerTest(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAffineComponent(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAffineComponentPreconditioned(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestAffineComponentPreconditionedOnline(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestConvolutional1dComponent(), UnitTestIoPipe(), and UnitTestReadScriptFile().
| void kaldi::SlidingWindowCmnInternal | ( | const SlidingWindowCmnOptions & | opts, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | input, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | output | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 250 of file feature-functions.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), SlidingWindowCmnOptions::center, SlidingWindowCmnOptions::Check(), SlidingWindowCmnOptions::cmn_window, VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kTrans, SlidingWindowCmnOptions::max_warnings, SlidingWindowCmnOptions::min_window, VectorBase< Real >::MulElements(), SlidingWindowCmnOptions::normalize_variance, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), and VectorBase< Real >::Set().
Referenced by SlidingWindowCmn().
|
static |
Definition at line 169 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), rnnlm::i, and kNoTrans.
| template float kaldi::SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | G, |
| const SpMatrix< float > & | P1, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | P2, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | Q1, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | Q2, | ||
| const SolverOptions & | opts, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | M | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | G, |
| const SpMatrix< double > & | P1, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | P2, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | Q1, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | Q2, | ||
| const SolverOptions & | opts, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | M | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem | ( | const SpMatrix< float > & | Q, |
| const MatrixBase< float > & | Y, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | SigmaInv, | ||
| const SolverOptions & | opts, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | M | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem | ( | const SpMatrix< double > & | Q, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | Y, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | SigmaInv, | ||
| const SolverOptions & | opts, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | M | ||
| ) |
| double SolveQuadraticProblem | ( | const SpMatrix< double > & | H, |
| const VectorBase< double > & | g, | ||
| const SolverOptions & | opts, | ||
| VectorBase< double > * | x | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 635 of file sp-matrix.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2Sp(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), SolverOptions::Check(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromSp(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), SolverOptions::diagonal_precondition, VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), VectorBase< Real >::DivElements(), SolverOptions::eps, rnnlm::i, VectorBase< Real >::InvertElements(), SpMatrix< Real >::IsZero(), SolverOptions::K, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, kTrans, VectorBase< Real >::Max(), VectorBase< Real >::MulElements(), SolverOptions::name, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), SolverOptions::optimize_delta, SolverOptions::print_debug_output, SpMatrix< Real >::SymPosSemiDefEig(), VecSpVec(), and VecVec().
Referenced by LinearCgd(), SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem(), SolveQuadraticProblem(), SolverOptions::SolverOptions(), UnitTestSolve(), MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs::UpdateNoU(), EbwAmSgmm2Updater::UpdatePhoneVectorsInternal(), MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdatePhoneVectorsInternal(), EbwAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateU(), MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateU(), EbwAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateW(), MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateW(), IvectorExtractorStats::UpdateWeight(), and MleSgmm2SpeakerAccs::UpdateWithU().
| float SolveQuadraticProblem | ( | const SpMatrix< float > & | H, |
| const VectorBase< float > & | g, | ||
| const SolverOptions & | opts, | ||
| VectorBase< float > * | x | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 712 of file sp-matrix.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and SolveQuadraticProblem().
|
inline |
Sorts and uniq's (removes duplicates) from a vector.
Definition at line 39 of file stl-utils.h.
Referenced by ComputationGraphBuilder::AddDependencies(), AutomaticallyObtainQuestions(), HmmTopology::Check(), Nnet::Check(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeCommandAttributes(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeComputationGraph(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeComputationPhasesForEpoch(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeMatrixAccesses(), ComputationVariables::ComputeSplitPoints(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeVariableAccesses(), ConstIntegerSet< EventValueType >::ConstIntegerSet(), ContextDependency::EnumeratePairs(), WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo::FinalizeViabilityMap(), kaldi::nnet3::FindNStride(), GenerateLexicon(), GenRandStats(), GetHTransducer(), ContextDependency::GetPdfInfo(), GetPdfsForPhones(), GetPhonesForPdfs(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::GetRandomConvolutionIndexes(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::GetRandomConvolutionModel(), kaldi::nnet3::IndexesMultiToSubmatrixIndexes(), ConstIntegerSet< EventValueType >::Init(), TimeHeightConvolutionComponent::InitFromConfig(), Questions::InitRand(), InverseLeftBiphoneContextFst::InverseLeftBiphoneContextFst(), KMeansClusterPhones(), main(), kaldi::nnet3::MakeSccGraph(), SplitEventMap::MapValues(), kaldi::nnet3::NnetToDirectedGraph(), ProcessTopo(), ComputationGraphBuilder::PruneDependencies(), ReadSymbolTableAsIntegers(), RenumberEventMap(), ShareEventMapLeaves(), SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder(), Compiler::SplitByScale(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap(), TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap2(), TestEventMapPrune(), fst::TestMakeLinearAcceptor(), TestShareEventMapLeaves(), TestSortAndUniq(), TrainingGraphCompiler::TrainingGraphCompiler(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestSolvePackingProblem(), and WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo::UpdateEquivalenceMap().
| template void kaldi::SortSvd | ( | VectorBase< float > * | s, |
| MatrixBase< float > * | U, | ||
| MatrixBase< float > * | Vt, | ||
| bool | |||
| ) |
| template void kaldi::SortSvd | ( | VectorBase< double > * | s, |
| MatrixBase< double > * | U, | ||
| MatrixBase< double > * | Vt, | ||
| bool | |||
| ) |
Referenced by SortSvd().
| void kaldi::SparseMatrixUnitTest | ( | ) |
| void kaldi::SplitArgOnEquals | ( | const std::string & | arg, |
| std::string * | name, | ||
| std::string * | rspecifier | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 33 of file nnet3-get-egs-simple.cc.
References ClassifyRspecifier(), IsToken(), KALDI_ERR, and kNoRspecifier.
Referenced by main().
| void SplitStringOnFirstSpace | ( | const std::string & | line, |
| std::string * | first, | ||
| std::string * | rest | ||
| ) |
Removes leading and trailing white space from the string, then splits on the first section of whitespace found (if present), putting the part before the whitespace in "first" and the rest in "rest".
If there is no such space, everything that remains after removing leading and trailing whitespace goes in "first".
Definition at line 120 of file text-utils.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by ConvertStringToInteger(), SequentialTableReaderScriptImpl< Holder >::NextScpLine(), ReadScriptFile(), and TestSplitStringOnFirstSpace().
| bool SplitStringToFloats | ( | const std::string & | full, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| bool | omit_empty_strings, | ||
| std::vector< F > * | out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 30 of file text-utils.cc.
References ConvertStringToReal(), full, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and SplitStringToVector().
Referenced by GetWeights(), main(), PreparePriors(), SplitStringToIntegers(), SplitStringToWeights(), and TestSplitStringToFloats().
| template bool kaldi::SplitStringToFloats | ( | const std::string & | full, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| bool | omit_empty_strings, | ||
| std::vector< float > * | out | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::SplitStringToFloats | ( | const std::string & | full, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| bool | omit_empty_strings, | ||
| std::vector< double > * | out | ||
| ) |
| bool kaldi::SplitStringToIntegers | ( | const std::string & | full, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| bool | omit_empty_strings, | ||
| std::vector< I > * | out | ||
| ) |
Split a string (e.g.
1:2:3) into a vector of integers.
| [in] | delim | String containing a list of characters, any of which is allowed as a delimiter. |
| [in] | omit_empty_strings | If true, empty strings between delimiters are allowed and will not produce an output integer; if false, instances of characters in 'delim' that are consecutive or at the start or end of the string would be an error. You'll normally want this to be true if 'delim' consists of spaces, and false otherwise. |
| [out] | out | The output list of integers. |
Definition at line 68 of file text-utils.h.
References full, rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ASSERT_IS_INTEGER_TYPE, KALDI_STRTOLL, SplitStringToFloats(), and SplitStringToVector().
Referenced by AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::AccumulateTreeStatsInfo(), ExampleGenerationConfig::ComputeDerived(), DiscriminativeComputation::DiscriminativeComputation(), ExtractObjectRange(), GetSkipLayers(), ConfigLine::GetValue(), Splice::InitData(), BlockSoftmax::InitData(), CopyComponent::InitData(), TimeHeightConvolutionComponent::InitFromConfig(), TdnnComponent::InitFromConfig(), PermuteComponent::InitFromConfig(), main(), NnetDiscriminativeUpdater::NnetDiscriminativeUpdater(), OnlineCmvn::OnlineCmvn(), OnlineSilenceWeighting::OnlineSilenceWeighting(), kaldi::nnet2::ParseFromString(), ExampleMergingConfig::ParseIntSet(), ParseMatrixRangeSpecifier(), fst::ReadFstKaldi(), ReadIntegerVectorVectorSimple(), ReadLexiconForWordAlign(), ReadSharedPhonesList(), WordBoundaryInfo::SetOptions(), SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder(), kaldi::nnet3::SummarizeVector(), TestSplitStringToIntegers(), and TrailingSilenceLength().
| void SplitStringToVector | ( | const std::string & | full, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| bool | omit_empty_strings, | ||
| std::vector< std::string > * | out | ||
| ) |
Split a string using any of the single character delimiters.
If omit_empty_strings == true, the output will contain any nonempty strings after splitting on any of the characters in the delimiter. If omit_empty_strings == false, the output will contain n+1 strings if there are n characters in the set "delim" within the input string. In this case the empty string is split to a single empty string.
Definition at line 63 of file text-utils.cc.
Referenced by ClassifyRspecifier(), ClassifyWspecifier(), ExampleMergingConfig::ComputeDerived(), CopyExcludedFeats(), CopyIncludedFeats(), CopySubsetLattices(), ExtractObjectRange(), ExtractRangeSpecifier(), GetUtterancePairs(), WordBoundaryInfo::Init(), TimeHeightConvolutionComponent::InitFromConfig(), MultiTaskLoss::InitFromString(), main(), kaldi::nnet2::ParseFromString(), ExampleMergingConfig::ParseIntSet(), ParseMatrixRangeSpecifier(), PrepareMap(), kaldi::nnet3::ProcessRangeFile(), ArpaFileParser::Read(), TokenVectorHolder::Read(), ReadCommaSeparatedCommand(), fst::ReadFstKaldi(), LatticeReader::ReadText(), Fmpe::SetContexts(), SplitStringToFloats(), SplitStringToIntegers(), and TestSplitStringToVector().
| void kaldi::SplitStringToWeights | ( | const string & | full, |
| const char * | delim, | ||
| vector< BaseFloat > * | out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 91 of file lattice-combine.cc.
References KALDI_WARN, and SplitStringToFloats().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 659 of file hmm-utils.cc.
References TransitionModel::GetTopo(), rnnlm::i, TransitionModel::IsFinal(), TransitionModel::IsSelfLoop(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoPdf, HmmTopology::TopologyForPhone(), TransitionModel::TransitionIdToTransitionState(), TransitionModel::TransitionStateToHmmState(), and TransitionModel::TransitionStateToPhone().
Referenced by SplitToPhones().
| bool StringsApproxEqual | ( | const std::string & | a, |
| const std::string & | b, | ||
| int32 | decimal_places_check = 2 |
||
| ) |
This function returns true when two text strings are approximately equal, and false when they are not.
The definition of 'equal' is normal string equality, except that two substrings like "0.31134" and "0.311341" would be considered equal. 'decimal_places_tolerance' controls how many digits after the '.' have to match up. E.g. StringsApproxEqual("hello 0.23 there", "hello 0.24 there", 2) would return false because there is a difference in the 2nd decimal, but with an argument of 1 it would return true.
Definition at line 335 of file text-utils.cc.
References StringsApproxEqualInternal().
Referenced by kaldi::nnet3::CheckStringsApproxEqual(), ConvertStringToInteger(), kaldi::nnet3::TestNnetComponentCopy(), kaldi::nnet3::TestNnetComponentUpdatable(), and TestStringsApproxEqual().
| bool kaldi::StringsApproxEqualInternal | ( | const char * | a, |
| const char * | b, | ||
| int32 | decimal_places_tolerance, | ||
| int32 | places_into_number | ||
| ) |
| GmmFlagsType StringToGmmFlags | ( | std::string | str | ) |
Convert string which is some subset of "mSwa" to flags.
Definition at line 26 of file model-common.cc.
References CharToString(), KALDI_ERR, kGmmAll, kGmmMeans, kGmmTransitions, kGmmVariances, and kGmmWeights.
Referenced by main().
| SgmmUpdateFlagsType StringToSgmmUpdateFlags | ( | std::string | str | ) |
Definition at line 64 of file model-common.cc.
References CharToString(), KALDI_ERR, kSgmmAll, kSgmmCovarianceMatrix, kSgmmPhoneProjections, kSgmmPhoneVectors, kSgmmPhoneWeightProjections, kSgmmSpeakerProjections, kSgmmSpeakerWeightProjections, kSgmmSubstateWeights, and kSgmmTransitions.
Referenced by main().
| SgmmWriteFlagsType StringToSgmmWriteFlags | ( | std::string | str | ) |
Definition at line 86 of file model-common.cc.
References CharToString(), KALDI_ERR, kSgmmAll, kSgmmBackgroundGmms, kSgmmGlobalParams, kSgmmNormalizers, and kSgmmStateParams.
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 49 of file process-pitch-feats.cc.
References rnnlm::i, and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
Definition at line 275 of file basic-filebuf.h.
References basic_filebuf< CharT, Traits >::swap().
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::AddDiagMatMat(), CuMatrixBase< float >::AddDiagVecMat(), MatrixBase< float >::AddDiagVecMat(), CuMatrixBase< float >::AddMatBlock(), CuMatrixBase< float >::AddMatDiagVec(), MatrixBase< float >::AddMatDiagVec(), CuBlockMatrix< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< float >::AddMatMatMat(), ChangeReorderingOfAlignment(), kaldi::nnet3::CheckComputationOnline(), PosteriorHolder::Clear(), GaussPostHolder::Clear(), fst::ComposeDeterministicOnDemandInverse(), fst::ConvertLattice(), DiscriminativeSupervisionSplitter::CreateRangeLattice(), DeterminizerStar< F >::Debug(), GeneralDropoutComponent::GetMemo(), GeneralDescriptor::Normalize(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::operator()(), SpMatrix< float >::operator()(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::operator()(), LatticeDeterminizer< Weight, IntType >::Output(), LatticeLexiconWordAligner::ProcessFinalForceOut(), RandomizeVector(), BottomUpClusterer::ReconstructQueue(), CompartmentalizedBottomUpClusterer::ReconstructQueue(), CompartmentalizedBottomUpClusterer::Renumber(), DctComponent::Reorder(), ReverseVector(), CRnnLM::sortVocab(), RowOpsSplitter::SplitCommand(), basic_filebuf< CharT, Traits >::swap(), SparseVector< Real >::Swap(), SpMatrix< float >::Swap(), TpMatrix< float >::Swap(), IoSpecification::Swap(), CompactLatticeHolder::Swap(), KaldiObjectHolder< KaldiType >::Swap(), CuBlockMatrix< Real >::Swap(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::Swap(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Swap(), DiscriminativeSupervision::Swap(), LatticeHolder::Swap(), VectorFstTplHolder< Arc >::Swap(), GenericHolder< SomeType >::Swap(), WaveData::Swap(), PackedMatrix< float >::Swap(), CuArray< Int32Pair >::Swap(), CompressedMatrix::Swap(), BasicHolder< BasicType >::Swap(), WaveInfoHolder::Swap(), CuVector< float >::Swap(), NnetComputation::MatrixDebugInfo::Swap(), Vector< float >::Swap(), OnlineNaturalGradient::Swap(), HtkMatrixHolder::Swap(), Matrix< BaseFloat >::Swap(), CuMatrix< float >::Swap(), TestClusterBottomUp(), TestEditDistance2(), TestEditDistance2String(), TestHashList(), TestSetOfNumbers(), TraceMatMatMat(), TraceMatMatMatMat(), MatrixBase< float >::Transpose(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatBlock(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixAddMatMat(), UnitTestCuBlockMatrixIO(), UnitTestCuMatrixIO(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddMatSmat(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmat(), UnitTextCuMatrixAddSmatMat(), and WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo::UpdateEquivalenceMap().
| void SynchronizeGpu | ( | ) |
The function SynchronizeGpu(), which for convenience is defined whether or not we have compiled for CUDA, is intended to be called in places where threads need to be synchronized.
It just launches a no-op kernel into the legacy default stream. This will have the effect that it will run after any kernels previously launched from any stream(*), and before kernels that will later be launched from any stream(*). (*) does not apply to non-blocking streams.
Note: at the time of writing we never call SynchronizeGpu() from binary-level code because it hasn't become necessary yet; the only program that might have multiple threads actually using the GPU is rnnlm-train (if the user were to invoke it with the ,bg option for loading training examples); but the only CUDA invocation the RnnlmExample::Read() function uses (via CuMatrix::Read()), is cudaMemcpy, which is synchronous already.
Definition at line 638 of file cu-device.cc.
Referenced by NnetBatchComputer::Compute(), and NnetBatchComputer::FormatOutputs().
Definition at line 39 of file process-pitch-feats.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Log(), and MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestAccumulateTreeStatsOptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 188 of file hmm-utils-test.cc.
References AccumulateTreeStatsOptions::central_position, AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::central_position, AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::ci_phones, AccumulateTreeStatsOptions::ci_phones_str, AccumulateTreeStatsOptions::context_width, AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::context_width, KALDI_ASSERT, AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::phone_map, AccumulateTreeStatsOptions::phone_map_rxfilename, RandInt(), AccumulateTreeStatsOptions::var_floor, and AccumulateTreeStatsInfo::var_floor.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 156 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AddToClusters(), AssertEqual(), ScalarClusterable::Copy(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and ScalarClusterable::Mean().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 183 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References ScalarClusterable::Add(), AddToClusters(), AddToClustersOptimized(), AssertEqual(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), RandGauss(), SumClusterable(), and SumClusterableNormalizer().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestBuildTree | ( | ) |
Definition at line 90 of file build-tree-test.cc.
References BuildTree(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), GenRandStats(), Questions::GetKeysWithQuestions(), Questions::GetQuestionsOf(), Questions::HasQuestionsForKey(), rnnlm::i, QuestionsForKey::initial_questions, Questions::InitRand(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_VLOG, kAllKeysUnion, EventMap::Map(), Rand(), RandUniform(), EventMap::Write(), WriteBasicType(), WriteBuildTreeStats(), and WriteIntegerVector().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestBuildTreeStatsIo | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 838 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), ReadBuildTreeStats(), Input::Stream(), and WriteBuildTreeStats().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 232 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterBottomUp(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), RandUniform(), and swap().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestClusterEventMap | ( | ) |
Definition at line 376 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterEventMap(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), DoTableSplit(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::Map(), rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandUniform(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap | ( | ) |
Definition at line 256 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterEventMapGetMapping(), EventMap::Copy(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), DeletePointers(), DoTableSplit(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::MaxResult(), EventMap::MultiMap(), rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandUniform(), RenumberEventMap(), SortAndUniq(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestClusterEventMapGetMappingAndRenumberEventMap2 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 315 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterEventMapGetMapping(), EventMap::Copy(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), DeletePointers(), DoTableSplit(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::MultiMap(), rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandUniform(), RenumberEventMap(), SortAndUniq(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestClusterEventMapRestricted | ( | ) |
Definition at line 437 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterEventMap(), ClusterEventMapRestrictedByKeys(), ClusterEventMapRestrictedByMap(), CopySetToVector(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), DoTableSplitMultiple(), rnnlm::i, Questions::InitRand(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kAllKeysInsistIdentical, Rand(), RandGauss(), RandUniform(), SplitDecisionTree(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 329 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterKMeans(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandUniform(), and SumClusterableObjf().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 388 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ClusterKMeans(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, ClusterKMeansOptions::num_tries, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SumClusterableObjf().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 509 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References ClusterTopDown(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandUniform(), SumClusterableObjf(), and TreeClusterOptions::thresh.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 25 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References Clusterable::Add(), Clusterable::Copy(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, Clusterable::Normalizer(), Clusterable::Objf(), Rand(), and RandGauss().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 56 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References Clusterable::Add(), VectorClusterable::Add(), Clusterable::Copy(), kaldi::cu::Copy(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, Clusterable::Normalizer(), Clusterable::Objf(), VectorClusterable::Objf(), Rand(), RandUniform(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCompactLatticeTable | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 41 of file kaldi-lattice-test.cc.
References TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, RandCompactLattice(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCompactLatticeTableCross | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 69 of file kaldi-lattice-test.cc.
References TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), fst::ConvertLattice(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, RandCompactLattice(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestContainsNullPointers | ( | ) |
Definition at line 190 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References ContainsNullPointers(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestContextDep | ( | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file context-dep-test.cc.
References Clusterable::Add(), Clusterable::Copy(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Clusterable::Normalizer(), Clusterable::Objf(), Rand(), and RandGauss().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestConvertAlignment | ( | ) |
Definition at line 232 of file hmm-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertAlignment(), ContextDependencyInterface::Copy(), GenerateRandomAlignment(), GenRandContextDependencyLarge(), GenRandTopology(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, MonophoneContextDependency(), RandInt(), SplitToPhones(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestConvertPhnxToProns | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file hmm-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertPhnxToProns(), KALDI_ASSERT, and words.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestConvertStats | ( | ) |
Definition at line 72 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertStats(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestConvertStringToInteger | ( | ) |
Definition at line 145 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertStringToInteger(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestConvertStringToReal | ( | ) |
Definition at line 165 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertStringToReal(), rnnlm::d, and KALDI_ASSERT.
| void kaldi::TestCopyMapKeysToSet | ( | ) |
Definition at line 158 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapKeysToSet(), CopyMapKeysToVector(), CopyVectorToSet(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCopyMapKeysToVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 130 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapKeysToVector(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCopyMapToVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 116 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapToVector(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCopyMapValuesToSet | ( | ) |
Definition at line 174 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapValuesToSet(), CopyMapValuesToVector(), CopyVectorToSet(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCopyMapValuesToVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 142 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapValuesToVector(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestCopySetToVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 103 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References CopySetToVector(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 368 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuArrayBase< T >::CopyToVec(), Timer::Elapsed(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::FindRowMaxId(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixAddDiagVecMat | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 265 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddDiagVecMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTrans, and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Definition at line 169 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Definition at line 192 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixAddRowRanges | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 958 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixAddRows1 | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 886 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixAddRows2 | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 910 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixAddToRows | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 934 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCholesky | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 652 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddToDiag(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Cholesky(), Timer::Elapsed(), and KALDI_LOG.
|
static |
Definition at line 308 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyLog(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrix< Real >::CompObjfAndDeriv(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, CuMatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kTrans, Rand(), RandUniform(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetZero(), and TraceMatMat().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyFromSp | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 712 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromSp(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyFromTp | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 688 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromTp(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyLowerToUpper | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 670 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyLowerToUpper(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTrans, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyRows1 | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 814 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyRows2 | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 838 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyToRows | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 862 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixCopyUpperToLower | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 736 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyUpperToLower(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTrans, kUndefined, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and TestCuMatrixResize().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixDiffGroupPnorm | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 553 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupPnorm(), KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixDiffLogSoftmax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 482 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixDiffSoftmax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 464 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixDivRowsVec | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 97 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::DivRowsVec(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixGroupMax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 573 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupMax(), and KALDI_LOG.
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixGroupMaxAllGroupSizes | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 589 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupMax(), KALDI_LOG, kUndefined, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixGroupMaxDeriv | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 612 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupMaxDeriv(), and KALDI_LOG.
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixGroupPnorm | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 536 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupPnorm(), and KALDI_LOG.
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixHeaviside | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 427 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyHeaviside(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixLogSoftmax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 518 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::LogSoftMaxPerRow(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixLookup | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 782 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), Int32Pair::first, rnnlm::j, KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Lookup(), Rand(), Int32Pair::second, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixMatMat | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 212 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and kNoTrans.
Definition at line 229 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References AddMatMatBatched(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixMax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 63 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Max(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixMin | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 80 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Min(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixMulRowsGroupMat | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 445 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void TestCuMatrixResize | ( | int32 | size_multiple | ) |
Definition at line 41 of file cu-device-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kUndefined, and RandInt().
Referenced by TestCuMatrixCopyUpperToLower().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixSetZeroAboveDiag | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 767 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetZeroAboveDiag().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixSigmoid | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 410 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sigmoid().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixSoftmax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 500 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SoftMaxPerRow().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixSum | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 46 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixTraceMatMat | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 630 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and TraceMatMat().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixTransposeCross | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 148 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and kTrans.
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixTransposeNS | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 116 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Transpose().
| void kaldi::TestCuMatrixTransposeS | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 132 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Transpose().
| void kaldi::TestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 983 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and TraceMatSmat().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorAddColSumMat | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 266 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorAddDiagMat2 | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 222 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorAddDiagMat2OnVariousShapes | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 196 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorAddDiagMatMat | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transN, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transO | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 170 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMatMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorAddDiagMatMatShape | ( | int32 | num_rows, |
| int32 | num_cols, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transM, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transN | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 372 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMatMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorAddRowSumMat | ( | int32 | dim, |
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 244 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorApplyCeiling | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 330 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, RandInt(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorApplyCeilingNoCount | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 351 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, RandInt(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorApplyFloor | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 288 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, RandInt(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorApplyFloorNoCount | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 309 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, RandInt(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorCopyFromVec | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 79 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CU1DBLOCK, CuVectorBase< Real >::Data(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Dim(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kUndefined, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorSoftmax | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 44 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::ApplySoftMax(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorSum | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 62 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::TestCuVectorVecVecOne | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 148 of file cu-vector-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, CuVectorBase< Real >::Set(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 117 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), and ScalarClusterable::Objf().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestDoTableSplit | ( | ) |
Definition at line 206 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References DoTableSplit(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::Lookup(), EventMap::Map(), RandInt(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEditDistance | ( | ) |
Definition at line 26 of file edit-distance-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and LevenshteinEditDistance().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEditDistance2 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 112 of file edit-distance-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, LevenshteinEditDistance(), Rand(), and swap().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEditDistance2String | ( | ) |
Definition at line 172 of file edit-distance-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, LevenshteinEditDistance(), Rand(), and swap().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEditDistanceString | ( | ) |
Definition at line 68 of file edit-distance-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and LevenshteinEditDistance().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 147 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References DeletePointers(), EnsureClusterableVectorNotNull(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEventMap | ( | ) |
Definition at line 27 of file event-map-test.cc.
References GetTreeStructure(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, TableEventMap::Map(), EventMap::MaxResult(), and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEventMapIo | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 178 of file event-map-test.cc.
References CopySetToVector(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), RandomEventMap(), EventMap::Read(), and EventMap::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEventMapMapValues | ( | ) |
Definition at line 270 of file event-map-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kMaxVal, EventMap::Map(), EventMap::MapValues(), Rand(), and RandomEventMap().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEventMapPrune | ( | ) |
Definition at line 210 of file event-map-test.cc.
References EventMap::Copy(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, EventMap::Map(), EventMap::MultiMap(), EventMap::Prune(), Rand(), RandomEventMap(), and SortAndUniq().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestEventTypeIo | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 110 of file event-map-test.cc.
References Output::Close(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), ReadEventType(), Output::Stream(), Input::Stream(), and WriteEventType().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestFindAllKeys | ( | ) |
Definition at line 148 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapKeysToSet(), CopyMapToVector(), CopySetToVector(), FindAllKeys(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kAllKeysInsistIdentical, kAllKeysIntersection, kAllKeysUnion, and RandInt().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestFmpe | ( | ) |
Definition at line 79 of file fmpe-test.cc.
References Fmpe::AccStats(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), Fmpe::ComputeFeatures(), GetFeatDeriv(), GetGmmLike(), rnnlm::i, kaldi::unittest::InitRandDiagGmm(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsZero(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kTrans, FmpeUpdateOptions::learning_rate, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), DiagGmm::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), RandGauss(), Fmpe::Read(), Output::Stream(), Input::Stream(), TraceMatMat(), Fmpe::Update(), and Fmpe::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestGenRandContextDependency | ( | ) |
Definition at line 74 of file context-dep-test.cc.
References Output::Close(), CopySetToVector(), GenRandContextDependency(), ContextDependency::GetPdfInfo(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), ContextDependency::Read(), Output::Stream(), Input::Stream(), and ContextDependency::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestGenRandStats | ( | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file build-tree-test.cc.
References DeleteBuildTreeStats(), GenRandStats(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_VLOG, kPdfClass, EventMap::Lookup(), Rand(), RandUniform(), WriteBasicType(), WriteBuildTreeStats(), and WriteIntegerVector().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestHashList | ( | ) |
Definition at line 29 of file hash-list-test.cc.
References HashList< I, T >::Clear(), count, HashList< I, T >::Delete(), HashList< I, T >::Find(), HashList< I, T >::GetList(), rnnlm::i, HashList< I, T >::Insert(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), HashList< I, T >::SetSize(), and swap().
| void kaldi::TestHmmTopology | ( | ) |
Definition at line 27 of file hmm-topology-test.cc.
References GenRandTopology(), GetDefaultTopology(), KALDI_ASSERT, HmmTopology::MinLength(), Rand(), RandInt(), HmmTopology::Read(), and HmmTopology::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestInf | ( | ) |
Definition at line 242 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertStringToReal(), rnnlm::d, and KALDI_ASSERT.
| void kaldi::TestIsLine | ( | ) |
Definition at line 304 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References IsLine(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 26 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSorted(), KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 38 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSortedAndUniq(), KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestIsToken | ( | ) |
Definition at line 288 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References IsToken(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestIvectorExtraction | ( | const IvectorExtractor & | extractor, |
| const MatrixBase< BaseFloat > & | feats, | ||
| const FullGmm & | fgmm | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 85 of file ivector-extractor-test.cc.
References IvectorExtractorUtteranceStats::AccStats(), OnlineIvectorEstimationStats::AccStats(), FullGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), IvectorExtractor::GetAuxf(), OnlineIvectorEstimationStats::GetIvector(), IvectorExtractor::GetIvectorDistribution(), rnnlm::i, IvectorExtractor::IvectorDependentWeights(), IvectorExtractor::IvectorDim(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kUndefined, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), IvectorExtractorUtteranceStats::NumFrames(), FullGmm::NumGauss(), IvectorExtractor::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), OnlineIvectorEstimationStats::ObjfChange(), IvectorExtractor::PriorOffset(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Row().
Referenced by UnitTestIvectorExtractor().
| void kaldi::TestIvectorExtractorIO | ( | const IvectorExtractor & | extractor | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file ivector-extractor-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), IvectorExtractor::Read(), and IvectorExtractor::Write().
Referenced by UnitTestIvectorExtractor().
| void kaldi::TestIvectorExtractorStatsIO | ( | IvectorExtractorStats & | stats | ) |
Definition at line 39 of file ivector-extractor-test.cc.
References IvectorExtractorStats::Add(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), IvectorExtractorStats::Read(), and IvectorExtractorStats::Write().
Referenced by UnitTestIvectorExtractor().
| void kaldi::TestLatticeTable | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 99 of file kaldi-lattice-test.cc.
References TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, RandLattice(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestLatticeTableCross | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 128 of file kaldi-lattice-test.cc.
References TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), fst::ConvertLattice(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), RandLattice(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestLevenshteinAlignment | ( | ) |
Definition at line 231 of file edit-distance-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, LevenshteinAlignment(), LevenshteinEditDistance(), and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestLocateSymbolRange | ( | ) |
Definition at line 52 of file kaldi-error-test.cc.
References VerifySymbolRange().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestMergePairVectorSumming | ( | ) |
Definition at line 220 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, IsSorted(), KALDI_ASSERT, MergePairVectorSumming(), and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestMinimizeCompactLattice | ( | ) |
Definition at line 47 of file minimize-lattice-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, fst::MinimizeCompactLattice(), fst::PushCompactLatticeStrings(), fst::PushCompactLatticeWeights(), Rand(), and RandDeterministicCompactLattice().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestMonophoneContextDependency | ( | ) |
Definition at line 56 of file context-dep-test.cc.
References CopySetToVector(), ContextDependency::GetPdfInfo(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MonophoneContextDependency(), and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestNan | ( | ) |
Definition at line 236 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References ConvertStringToReal(), rnnlm::d, and KALDI_ASSERT.
|
static |
Definition at line 107 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), and ScalarClusterable::Objf().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 95 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), KALDI_LOG, and ScalarClusterable::Objf().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineAppendFeature | ( | ) |
Definition at line 290 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::AcceptWaveform(), OfflineFeatureTpl< F >::Compute(), WaveData::Data(), FrameExtractionOptions::dither, MfccOptions::frame_opts, PlpOptions::frame_opts, GetOutput(), PlpOptions::htk_compat, rnnlm::i, OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::InputFinished(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MelBanksOptions::low_freq, PlpOptions::mel_opts, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), FrameExtractionOptions::preemph_coeff, RandomSplit(), WaveData::Read(), FrameExtractionOptions::remove_dc_offset, FrameExtractionOptions::round_to_power_of_two, FrameExtractionOptions::samp_freq, WaveData::SampFreq(), PlpOptions::use_energy, and FrameExtractionOptions::window_type.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineCmnInput | ( | ) |
Definition at line 193 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), OnlineCacheInput::GetCachedData(), GetOutput(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineDeltaFeature | ( | ) |
Definition at line 97 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), ComputeDeltas(), GetOutput(), KALDI_ASSERT, DeltaFeaturesOptions::order, and DeltaFeaturesOptions::window.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineDeltaInput | ( | ) |
Definition at line 168 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), ComputeDeltas(), GetOutput(), KALDI_ASSERT, DeltaFeaturesOptions::order, Rand(), and DeltaFeaturesOptions::window.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineFeatureMatrix | ( | ) |
Definition at line 110 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References OnlineFeatureMatrix::GetFrame(), OnlineFeatureMatrix::IsValidFrame(), KALDI_ASSERT, OnlineFeatureMatrixOptions::num_tries, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineLdaInput | ( | ) |
Definition at line 131 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), GetOutput(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SpliceFrames().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineMatrixCacheFeature | ( | ) |
Definition at line 83 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), GetOutput(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineMatrixInput | ( | ) |
Definition at line 96 of file online-feat-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), GetOutput(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineMfcc | ( | ) |
Definition at line 146 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::AcceptWaveform(), AssertEqual(), OfflineFeatureTpl< F >::Compute(), WaveData::Data(), FrameExtractionOptions::dither, MfccOptions::frame_opts, GetOutput(), rnnlm::i, OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::InputFinished(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandInt(), RandomSplit(), WaveData::Read(), and WaveData::SampFreq().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlinePlp | ( | ) |
Definition at line 198 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::AcceptWaveform(), AssertEqual(), OfflineFeatureTpl< F >::Compute(), WaveData::Data(), FrameExtractionOptions::dither, PlpOptions::frame_opts, GetOutput(), rnnlm::i, OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::InputFinished(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandomSplit(), WaveData::Read(), and WaveData::SampFreq().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineSpliceFrames | ( | ) |
Definition at line 121 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), GetOutput(), KALDI_ASSERT, OnlineSpliceOptions::left_context, OnlineSpliceOptions::right_context, and SpliceFrames().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestOnlineTransform | ( | ) |
Definition at line 247 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::AcceptWaveform(), ApplyAffineTransform(), AssertEqual(), WaveData::Data(), OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::Dim(), FrameExtractionOptions::dither, MfccOptions::frame_opts, GetOutput(), rnnlm::i, OnlineGenericBaseFeature< C >::InputFinished(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), WaveData::Read(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), WaveData::SampFreq(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestPossibleValues | ( | ) |
Definition at line 38 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References CopyMapToVector(), CopySetToVector(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, PossibleValues(), and RandInt().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestPosteriorIo | ( | ) |
Definition at line 53 of file posterior-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), RandUniform(), ReadPosterior(), and WritePosterior().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestPushCompactLatticeStrings | ( | ) |
Definition at line 39 of file push-lattice-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, fst::PushCompactLatticeStrings(), Rand(), RandCompactLattice(), and CompactLatticeWeightTpl< WeightType, IntType >::Zero().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestPushCompactLatticeWeights | ( | ) |
Definition at line 77 of file push-lattice-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, LatticeWeightTpl< BaseFloat >::One(), fst::Plus(), fst::PushCompactLatticeWeights(), Rand(), and RandCompactLattice().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestQuestionsInitRand | ( | ) |
Definition at line 640 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References EventMap::Check(), CopySetToVector(), Questions::GetQuestionsOf(), Questions::HasQuestionsForKey(), rnnlm::i, QuestionsForKey::initial_questions, Questions::InitRand(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, kAllKeysIntersection, kAllKeysUnion, Rand(), Questions::Read(), and Questions::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestRecyclingVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 378 of file online-feature-test.cc.
References RecyclingVector::At(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, RecyclingVector::PushBack(), VectorBase< Real >::Set(), and RecyclingVector::Size().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 286 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, RefineClustersOptions::num_iters, Rand(), RandUniform(), RefineClusters(), SumClusterableObjf(), and RefineClustersOptions::top_n.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestReverseVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 204 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and ReverseVector().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSetOfNumbers | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 30 of file const-integer-set-test.cc.
References ConstIntegerSet< I >::begin(), ConstIntegerSet< I >::count(), ConstIntegerSet< I >::end(), rnnlm::i, ConstIntegerSet< I >::Init(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), ConstIntegerSet< I >::Read(), ConstIntegerSet< I >::size(), Input::Stream(), swap(), and ConstIntegerSet< I >::Write().
| void kaldi::TestShareEventMapLeaves | ( | ) |
Definition at line 535 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References CopySetToVector(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), DoTableSplitMultiple(), rnnlm::i, Questions::InitRand(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, kAllKeysInsistIdentical, MakeEventPair(), EventMap::MultiMap(), PossibleValues(), Rand(), RandGauss(), RandUniform(), ShareEventMapLeaves(), SortAndUniq(), SplitDecisionTree(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 79 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, Rand(), and SortAndUniq().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitDecisionTree | ( | ) |
Definition at line 730 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References EventMap::Check(), CopySetToVector(), DeleteBuildTreeStats(), Questions::GetQuestionsOf(), Questions::HasQuestionsForKey(), rnnlm::i, QuestionsForKey::initial_questions, Questions::InitRand(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kAllKeysIntersection, ObjfGivenMap(), Rand(), RandGauss(), SplitDecisionTree(), SplitStatsByMap(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitStatsByKey | ( | ) |
Definition at line 123 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::Lookup(), Rand(), and SplitStatsByKey().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitStringOnFirstSpace | ( | ) |
Definition at line 266 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and SplitStringOnFirstSpace().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitStringToFloats | ( | ) |
Definition at line 123 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and SplitStringToFloats().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitStringToIntegers | ( | ) |
Definition at line 98 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and SplitStringToIntegers().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitStringToVector | ( | ) |
Definition at line 41 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References full, GetRandChar(), GetRandDelim(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, JoinVectorToString(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and SplitStringToVector().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSplitToPhones | ( | ) |
Definition at line 203 of file hmm-utils-test.cc.
References GenerateRandomAlignment(), GenRandTransitionModel(), TransitionModel::GetPhones(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), SplitToPhones(), and TransitionModel::TransitionIdToPhone().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestStringsApproxEqual | ( | ) |
Definition at line 313 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and StringsApproxEqual().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 137 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Clusterable::Objf(), and SumClusterable().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 125 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ScalarClusterable::Objf(), SumClusterableNormalizer(), and SumClusterableObjf().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestSymInvertPosDef | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 286 of file cu-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymAddMat2(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymInvertPosDef().
| void kaldi::TestTaskSequencer | ( | ) |
Definition at line 105 of file kaldi-thread-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, TaskSequencerConfig::num_threads, TaskSequencerConfig::num_threads_total, Rand(), and TaskSequencer< C >::Run().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestThreads | ( | ) |
Definition at line 62 of file kaldi-thread-test.cc.
References g_num_threads, KALDI_ASSERT, and RunMultiThreaded().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestTransitionModel | ( | ) |
Definition at line 26 of file transition-model-test.cc.
References TransitionModel::Compatible(), GenRandTransitionModel(), KALDI_ASSERT, TransitionModel::Read(), and TransitionModel::Write().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 461 of file cluster-utils-test.cc.
References DeletePointers(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandUniform(), SumClusterableObjf(), TreeClusterOptions::thresh, and TreeCluster().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestTrim | ( | ) |
Definition at line 256 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and TrimTmp().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestTrivialTree | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file build-tree-utils-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, EventMap::Map(), and TrivialTree().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 58 of file stl-utils-test.cc.
References count, rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and Uniq().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TestVectorToPosteriorEntry | ( | ) |
Definition at line 26 of file posterior-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Max(), rnnlm::n, RandUniform(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorToPosteriorEntry().
Referenced by main().
| void TestWordAlignedLattice | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| const WordBoundaryInfo & | info, | ||
| const CompactLattice & | aligned_lat | ||
| ) |
You should only test a lattice if WordAlignLattice returned true (i.e.
This function is designed to crash if something went wrong with the word-alignment of the lattice.
it succeeded and it wasn't a forced-out lattice); otherwise the test will most likely fail.
It verifies that arcs are of 4 types: properly-aligned word arcs, with a word label. partial-word arcs, with the partial-word label. silence arcs, with the silence label.
Definition at line 918 of file word-align-lattice.cc.
References WordAlignedLatticeTester::Test().
|
static |
Check equivalence.
Definition at line 927 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
References fst::ConvertLattice(), GetVerboseLevel(), IsPlausibleWord(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_WARN, LatticeForwardBackward(), MapSymbols(), and Rand().
Referenced by main(), and WordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void kaldi::TestWordAlignedLatticeLexicon | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | lexicon, | ||
| const CompactLattice & | aligned_lat, | ||
| bool | allow_duplicate_paths | ||
| ) |
This function is designed to crash if something went wrong with the word-alignment of the lattice.
If was_ok==true (was_ok is the return status of WordAlignLattice), it tests that, after removing any silence and partial-word labels that may have been inserted by WordAlignLattice, the word-aligned lattice is equivalent to the input. It also verifies that arcs are of 4 types: properly-aligned word arcs, with a word label. partial-word arcs, with the partial-word label. silence arcs, with the silence label.
Referenced by WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::Register().
| void kaldi::TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon | ( | ) |
Definition at line 173 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon-test.cc.
References WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::allow_duplicate_paths, fst::ConvertLattice(), fst::ConvertNbestToVector(), GenerateCompactLatticeRandomly(), GenerateLexicon(), GenerateRandomAlignment(), GenerateWordAndPhoneSequence(), GenRandTransitionModel(), TransitionModel::GetPhones(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, PrintLexicon(), PrintWordsAndPhones(), RandInt(), WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::reorder, WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::test, WordAlignLatticeLexicon(), and WriteCompactLattice().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 207 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
References Compile().
Referenced by RunAllTests().
| void kaldi::TimerTest | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file timer-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_ERR, and Sleep().
Referenced by main().
| std::string TimeToTimecode | ( | float | time | ) |
| void TopSortCompactLatticeIfNeeded | ( | CompactLattice * | clat | ) |
Topologically sort the compact lattice if not already topologically sorted.
Will crash if the lattice cannot be topologically sorted.
Definition at line 608 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by LatticeIncrementalDeterminizer::AcceptRawLatticeChunk(), CompactLatticeLimitDepth(), PrunedCompactLatticeComposer::Compose(), and main().
| void TopSortLatticeIfNeeded | ( | Lattice * | clat | ) |
Topologically sort the lattice if not already topologically sorted.
Will crash if lattice cannot be topologically sorted.
Definition at line 616 of file lattice-functions.cc.
References KALDI_ERR.
Referenced by SingleUtteranceGmmDecoder::GetGaussianPosteriors(), LatticeBoost(), and ReplaceAcousticScoresFromMap().
| std::string kaldi::ToString | ( | const T & | t | ) |
Definition at line 42 of file cu-rand-speed-test.cc.
Referenced by MeanVariance().
|
static |
Definition at line 878 of file compose-lattice-pruned.cc.
Referenced by PrunedCompactLatticeComposer::Compose().
| Real TraceMatMat | ( | const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | A, |
| const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 2145 of file cu-matrix.cc.
References CU1DBLOCK, CuVectorBase< Real >::Data(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Data(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kUndefined, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Mat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::num_rows_, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Stride(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), and TraceMatMat().
| template float kaldi::TraceMatMat | ( | const CuMatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| const CuMatrixBase< float > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatMat | ( | const CuMatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| const CuMatrixBase< double > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Referenced by CuMatrixBase< float >::IsUnit(), and TraceMatMat().
| Real TraceMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< Real > & | A, |
| const MatrixBase< Real > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans = kNoTrans |
||
| ) |
We need to declare this here as it will be a friend function.
tr(A B), or tr(A B^T).
Definition at line 2692 of file kaldi-matrix.cc.
References cblas_Xdot(), MatrixBase< Real >::data_, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::stride_, and TraceMatMat().
Referenced by CalBasisFmllrStepSize(), CalcFmllrStepSize(), DiscriminativeComputation::Compute(), kaldi::nnet3::ComputeObjectiveFunction(), BasisFmllrEstimate::ComputeTransform(), LstmNonlinearityComponent::ConsolidateMemory(), kaldi::nnet3::ConstrainOrthonormalInternal(), ConvolutionComponent::DotProduct(), TimeHeightConvolutionComponent::DotProduct(), LstmNonlinearityComponent::DotProduct(), TdnnComponent::DotProduct(), RepeatedAffineComponent::DotProduct(), AffineComponent::DotProduct(), LinearComponent::DotProduct(), BlockAffineComponent::DotProduct(), Convolutional1dComponent::DotProduct(), FmllrAuxfGradient(), FmllrAuxFuncDiagGmm(), FmllrSgmm2Accs::FmllrObjGradient(), MatrixBase< float >::FrobeniusNorm(), LogisticRegression::GetObjfAndGrad(), AffineComponent::Info(), AffineComponentPreconditioned::Info(), AffineComponentPreconditionedOnline::Info(), FixedLinearComponent::Info(), FixedAffineComponent::Info(), Convolutional1dComponent::Info(), main(), NnetComputer::MatrixStddev(), MllrAuxFunction(), MlObjective(), OnlineNaturalGradient::PreconditionDirections(), kaldi::nnet2::PreconditionDirectionsAlpha(), kaldi::nnet2::PreconditionDirectionsAlphaRescaled(), OnlinePreconditionerSimple::PreconditionDirectionsCpu(), OnlineNaturalGradientSimple::PreconditionDirectionsCpu(), OnlinePreconditioner::PreconditionDirectionsInternal(), kaldi::nnet3::PrintParameterStats(), NnetDiscriminativeComputeObjf::ProcessOutputs(), NnetChainTrainer::ProcessOutputs(), NnetChainComputeProb::ProcessOutputs(), NnetDiscriminativeTrainer::ProcessOutputs(), NnetUpdater::Propagate(), SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem(), kaldi::nnet3::attention::TestAttentionForwardBackward(), TestCuMatrixCompObjfAndDeriv(), TestCuMatrixTraceMatMat(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::TestDataBackprop(), TestFmpe(), kaldi::nnet3::time_height_convolution::TestParamsBackprop(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentDataDerivative(), kaldi::nnet3::TestSimpleComponentModelDerivative(), TraceMatSpMatSp(), UnitTestCuMatrixObjfDeriv(), UnitTestCuMatrixTraceMatMat(), UnitTestCuSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), UnitTestDeterminant(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestGenericComponentInternal(), UnitTestLstmNonlinearity(), UnitTestMatrixAddMatSmat(), UnitTestMatrixAddSmatMat(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetInputDerivatives(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestNnetModelDerivatives(), kaldi::nnet2::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), kaldi::nnet3::UnitTestPreconditionDirectionsOnline(), UnitTestSolve(), UnitTestSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat(), UnitTestTrace(), UnitTestTraceProduct(), FmllrSgmm2Accs::Update(), and MleAmSgmm2Updater::UpdateW().
| template float kaldi::TraceMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| const MatrixBase< float > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceMatMat(), and TraceMatMatMat().
| template float kaldi::TraceMatMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceMatMatMat(), and TraceMatMatMatMat().
| template float kaldi::TraceMatMatMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | D, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transD | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatMatMatMat | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transB, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | D, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transD | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceMatMatMatMat().
| Real TraceMatSmat | ( | const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | A, |
| const CuSparseMatrix< Real > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 524 of file cu-sparse-matrix.cc.
References CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CsrColIdx(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CsrRowPtr(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CsrVal(), CU1DBLOCK, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Data(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Mat(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumElements(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::Smat(), and CuSparseMatrix< Real >::TraceMatSmat.
| template float kaldi::TraceMatSmat | ( | const CuMatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| const CuSparseMatrix< float > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatSmat | ( | const CuMatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| const CuSparseMatrix< double > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::TraceMatSmat | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| const SparseMatrix< float > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatSmat | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| const SparseMatrix< double > & | B, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | trans | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceMatSmat().
| template float kaldi::TraceMatSpMat | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | B, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatSpMat | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | B, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::TraceMatSpMatSp | ( | const MatrixBase< float > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | B, | ||
| const MatrixBase< float > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC, | ||
| const SpMatrix< float > & | D | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceMatSpMatSp | ( | const MatrixBase< double > & | A, |
| MatrixTransposeType | transA, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | B, | ||
| const MatrixBase< double > & | C, | ||
| MatrixTransposeType | transC, | ||
| const SpMatrix< double > & | D | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::TraceSpMat | ( | const SpMatrix< float > & | A, |
| const MatrixBase< float > & | B | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceSpMat | ( | const SpMatrix< double > & | A, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | B | ||
| ) |
| Real TraceSpSp | ( | const CuSpMatrix< Real > & | A, |
| const CuSpMatrix< OtherReal > & | B | ||
| ) |
C++ templatd wrapper of ANSI-C CUBLAS function GEMM (matrix multiply)
TraceSpSp returns tr(A B)
Definition at line 168 of file cu-sp-matrix.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromPacked(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Data(), KALDI_ASSERT, kUndefined, CuSpMatrix< Real >::Mat(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), TraceSpSp(), and VecVec().
| template float kaldi::TraceSpSp | ( | const CuSpMatrix< float > & | A, |
| const CuSpMatrix< float > & | B | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::TraceSpSp | ( | const CuSpMatrix< float > & | A, |
| const CuSpMatrix< double > & | B | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceSpSp | ( | const CuSpMatrix< double > & | A, |
| const CuSpMatrix< float > & | B | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceSpSp | ( | const CuSpMatrix< double > & | A, |
| const CuSpMatrix< double > & | B | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::TraceSpSp< double, float > | ( | const SpMatrix< double > & | A, |
| const SpMatrix< float > & | B | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceSpSp().
| template float kaldi::TraceSpSp< float, double > | ( | const SpMatrix< float > & | A, |
| const SpMatrix< double > & | B | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceSpSp().
| template double kaldi::TraceSpSpLower | ( | const SpMatrix< double > & | A, |
| const SpMatrix< double > & | B | ||
| ) |
| void kaldi::TrainOneIter | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | feats, |
| const MleDiagGmmOptions & | gmm_opts, | ||
| int32 | iter, | ||
| int32 | num_threads, | ||
| DiagGmm * | gmm | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 61 of file gmm-global-init-from-feats.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::AccumulateFromDiagMultiThreaded(), count, KALDI_LOG, kGmmAll, kUndefined, MleDiagGmmUpdate(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and VectorBase< Real >::Set().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::TransformIvectors | ( | const Matrix< BaseFloat > & | ivectors_in, |
| const PldaConfig & | plda_config, | ||
| const Plda & | plda, | ||
| Matrix< BaseFloat > * | ivectors_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 87 of file ivector-plda-scoring-dense.cc.
References Plda::Dim(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and Plda::TransformIvector().
Referenced by main().
| void Trim | ( | std::string * | str | ) |
Removes the beginning and trailing whitespaces from a string.
Definition at line 92 of file text-utils.cc.
Referenced by ConvertStringToInteger(), ParseOptions::Read(), ParseOptions::ReadConfigFile(), TrimTmp(), and UnitTestRangesMatrix().
| std::string kaldi::TrimTmp | ( | std::string | s | ) |
Definition at line 251 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References Trim().
Referenced by TestTrim().
| void kaldi::TrimTrailingWhitespace | ( | std::string * | str | ) |
Definition at line 41 of file arpa-file-parser.cc.
Referenced by ArpaFileParser::Read().
| int32 kaldi::TypeOneUsage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po, |
| BaseFloat | scale1, | ||
| BaseFloat | scale2 | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 30 of file matrix-sum.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), DeletePointers(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::FreeCurrent(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), kNoTrans, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), ParseOptions::NumArgs(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), SameDim(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| int32 kaldi::TypeOneUsage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po | ) |
Definition at line 36 of file vector-sum.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), DeletePointers(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::FreeCurrent(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), ParseOptions::NumArgs(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
| int32 kaldi::TypeOneUsageAverage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po | ) |
Definition at line 106 of file matrix-sum.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), DeletePointers(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::FreeCurrent(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), kNoTrans, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), ParseOptions::NumArgs(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), SameDim(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| int32 kaldi::TypeThreeUsage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po, |
| bool | binary | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 151 of file vector-sum.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ClassifyRspecifier(), ClassifyWspecifier(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, kCopyData, kNoRspecifier, kNoWspecifier, ParseOptions::NumArgs(), PrintableWxfilename(), ReadKaldiObject(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), and WriteKaldiObject().
| int32 kaldi::TypeThreeUsage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po, |
| bool | binary, | ||
| bool | average | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 226 of file matrix-sum.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), ClassifyRspecifier(), ClassifyWspecifier(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, kCopyData, kNoRspecifier, kNoWspecifier, ParseOptions::NumArgs(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), PrintableWxfilename(), ReadKaldiObject(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and WriteKaldiObject().
Referenced by main().
| int32 kaldi::TypeTwoUsage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po, |
| bool | binary, | ||
| bool | average = false |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 103 of file vector-sum.cc.
References ClassifyRspecifier(), ClassifyWspecifier(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kNoRspecifier, kNoWspecifier, ParseOptions::NumArgs(), PrintableWxfilename(), and WriteKaldiObject().
| int32 kaldi::TypeTwoUsage | ( | const ParseOptions & | po, |
| bool | binary | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 179 of file matrix-sum.cc.
References ClassifyRspecifier(), ClassifyWspecifier(), ParseOptions::GetArg(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kNoRspecifier, kNoTrans, kNoWspecifier, ParseOptions::NumArgs(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), PrintableWxfilename(), and WriteKaldiObject().
Referenced by main().
|
inline |
Removes duplicate elements from a sorted list.
Definition at line 78 of file stl-utils.h.
References IsSorted(), KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_PARANOID_ASSERT.
Referenced by TestUniq(), UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble(), and UnitTestTableRandomBothDoubleMatrix().
|
static |
Definition at line 151 of file cu-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymInvertPosDef().
|
static |
Definition at line 166 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1986 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), diag, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2020 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), rnnlm::d, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 190 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 2944 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromSp(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTakeLower, kTrans, Rand(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SymAddMat2().
|
static |
Definition at line 2903 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatSp(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddSmat2Sp(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 220 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 248 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 4503 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, PlaceNansInGaps(), RandInt(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 112 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, kNoTrans, and kTrans.
|
static |
Definition at line 2932 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AssertEqual(), kTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2880 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddSmatMat(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 1136 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AddOuterProductPlusMinus(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, fst::Plus(), Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 779 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 136 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 266 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddSp(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2831 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References PackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 177 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 818 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddToRows(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 3519 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2Sp(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromVec(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestAddVecCross | ( | ) |
Definition at line 3814 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by MatrixUnitTest().
|
static |
Definition at line 3540 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Set(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 227 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToCols(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 3500 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Set(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 196 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1749 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2800 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExpSpecial(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), AssertEqual(), KALDI_LOG, RandInt(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestApproxEqual | ( | ) |
Definition at line 255 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestAssertFunc | ( | ) |
Definition at line 220 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, and Rand().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 1020 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 321 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), kaldi::cu::BackpropLstmNonlinearity(), kaldi::cu::CpuBackpropLstmNonlinearity(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), RandInt(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestCheck | ( | ) |
Definition at line 2519 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_LOG, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 87 of file cu-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Cholesky(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, and Rand().
| void kaldi::UnitTestClassifyRspecifier | ( | ) |
Definition at line 177 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References ClassifyRspecifier(), KALDI_ASSERT, kArchiveRspecifier, kNoRspecifier, kScriptRspecifier, RspecifierOptions::once, and RspecifierOptions::sorted.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestClassifyRxfilename | ( | ) |
Definition at line 31 of file kaldi-io-test.cc.
References ClassifyRxfilename(), KALDI_ASSERT, kFileInput, kNoInput, kOffsetFileInput, kPipeInput, and kStandardInput.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestClassifyWspecifier | ( | ) |
Definition at line 91 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References WspecifierOptions::binary, ClassifyWspecifier(), WspecifierOptions::flush, KALDI_ASSERT, kArchiveWspecifier, kBothWspecifier, kNoWspecifier, and kScriptWspecifier.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestClassifyWxfilename | ( | ) |
Definition at line 52 of file kaldi-io-test.cc.
References ClassifyWxfilename(), KALDI_ASSERT, kFileOutput, kNoOutput, kPipeOutput, and kStandardOutput.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 3422 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ComplexFft(), ComplexFt(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 3559 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), ComplexFft(), ComplexFt(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
|
static |
Definition at line 3395 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ComplexFt(), rnnlm::d, Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
| void kaldi::UnitTestComplexPower | ( | ) |
Definition at line 3701 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), AttemptComplexPower(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and RandGauss().
|
static |
Definition at line 4057 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AssertEqual(), CompressedMatrix::CopyColToVec(), CompressedMatrix::CopyRowToVec(), CompressedMatrix::CopyToMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), rnnlm::i, InitKaldiInputStream(), InitKaldiOutputStream(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kAutomaticMethod, kOneByteAuto, kSpeechFeature, kTwoByteAuto, rnnlm::n, CompressedMatrix::NumCols(), CompressedMatrix::NumRows(), Rand(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), CompressedMatrix::Read(), Matrix< Real >::Read(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), CompressedMatrix::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CompressedMatrix::Write(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 4013 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kOneByteZeroOne, kTwoByteSignedInteger, and RandInt().
|
static |
Definition at line 327 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ConvertIntToString(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_LOG, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), and Matrix< Real >::Read().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
| void kaldi::UnitTestConfigLineParse | ( | ) |
Definition at line 328 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References ConfigLine::FirstToken(), ConfigLine::GetValue(), ConfigLine::HasUnusedValues(), KALDI_ASSERT, ConfigLine::ParseLine(), and ConfigLine::UnusedValues().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 216 of file cu-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_LOG, and kTakeLower.
|
static |
Definition at line 853 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 294 of file cu-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_LOG, kTakeLower, kTakeMean, and kTakeUpper.
|
static |
Definition at line 713 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 317 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromVec(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
CuSpMatrix<Real> E(dim);
Definition at line 242 of file cu-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_LOG, kTakeLower, kUndefined, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Stride().
|
static |
Definition at line 1051 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), kTakeLower, kTakeMean, kTakeMeanAndCheck, kTakeUpper, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 746 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyToRows(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2157 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 53 of file cu-array-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuArrayBase< T >::CopyToHost(), CuArrayBase< T >::CopyToVec(), CuArrayBase< T >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kSetZero, Rand(), CuArray< T >::Resize(), and CuArrayBase< T >::Set().
|
static |
Definition at line 76 of file cu-block-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatBlock(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuBlockMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), CuBlockMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and swap().
|
static |
Definition at line 116 of file cu-block-matrix-test.cc.
References CuBlockMatrix< Real >::AddMatMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), ApproxEqual(), CuBlockMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuBlockMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), CuBlockMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), and swap().
|
static |
Definition at line 46 of file cu-block-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuBlockMatrix< Real >::Read(), swap(), and CuBlockMatrix< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 112 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Cholesky(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyLowerToUpper(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymAddMat2().
|
static |
Definition at line 2195 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2325 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DiffLogSoftmaxPerRow(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), rnnlm::n, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandInt(), RandZeroToOneMatrix(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 593 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMat2(), VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddDiagVecMat(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::Data(), kaldi::cu::DiffNormalizePerRow(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, kUndefined, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2251 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DiffSigmoid(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandZeroToOneMatrix(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2281 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddDiagMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddDiagVecMat(), ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DiffSoftmaxPerRow(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), rnnlm::n, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandInt(), RandZeroToOneMatrix(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2593 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DiffTanh(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandZeroToOneMatrix(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2483 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuArray< T >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DiffXent(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Log(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and RandZeroToOneMatrix().
|
static |
Definition at line 2444 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuArrayBase< T >::CopyToVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::FindRowMaxId(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2407 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, CuMatrixBase< Real >::LogSoftMaxPerRow(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 166 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), kaldi::cu::ComputeLstmNonlinearity(), kaldi::cu::CpuComputeLstmNonlinearity(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), RandInt(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 97 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), kaldi::cu::Copy(), CuArray< T >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 479 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyColFromVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::Data(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kaldi::cu::NormalizePerRow(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 550 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), kaldi::cu::NormalizePerRow(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 46 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuArray< T >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), kaldi::cu::Randomize(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 124 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuArray< T >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and kaldi::cu::Splice().
|
static |
Definition at line 254 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1803 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 886 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1236 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Row(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Scale(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Sum(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 2822 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddElements(), ApproxEqual(), Int32Pair::first, rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), Int32Pair::second, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1367 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kSetZero, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Range(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1425 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatBlocks(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1452 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatBlocks(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, RandInt(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1482 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatBlocks(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1273 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuMatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1660 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1715 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References AddMatMatBatched(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1301 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, CuMatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 1849 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatTp(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatTp(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 713 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddRowRanges(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 517 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1789 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddToDiag(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddToDiag(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2867 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddToElements(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and WithProb().
|
static |
Definition at line 594 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddToRows(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1891 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddTpMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddTpMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1538 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToCols(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1561 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1691 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 933 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 181 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 198 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExpLimited(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 165 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExpSpecial(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExpSpecial(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 912 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 954 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyHeaviside(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyHeaviside(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 143 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyLog(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyLog(), ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform().
|
static |
Definition at line 349 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 373 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPowAbs(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPowAbs(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 753 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 422 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyColsFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyColsFromVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross | ( | ) |
Definition at line 636 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestCuMatrixCopyCross2 | ( | ) |
Definition at line 658 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1818 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1833 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromTp(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromTp(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2718 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyLowerToUpper(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 447 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 395 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 483 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToRows(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2759 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyUpperToLower(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 1164 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DiffGroupPnorm(), MatrixBase< Real >::GroupPnorm(), MatrixBase< Real >::GroupPnormDeriv(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsGroupMat(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1018 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::DivElements(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DivElements(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform().
|
static |
Definition at line 1342 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DivRowsVec(), InitRand(), VectorBase< Real >::InvertElements(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2920 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), KALDI_ASSERT, kSetZero, CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 313 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupMax(), MatrixBase< Real >::GroupMax(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1204 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::GroupMax(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupMaxDeriv(), MatrixBase< Real >::GroupMaxDeriv(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 288 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::GroupPnorm(), MatrixBase< Real >::GroupPnorm(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 974 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyHeaviside(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Heaviside(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, kUndefined, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2093 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), InitRand(), MatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
|
static |
Definition at line 2111 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrix< Real >::Read(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), swap(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 2889 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References Int32Pair::first, rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, CuMatrixBase< Real >::Lookup(), Rand(), Int32Pair::second, and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1045 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::Max(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Max(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1067 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::Min(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Min(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1090 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 993 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 558 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1138 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsGroupMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsGroupMat(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1113 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2781 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyLog(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrix< Real >::CompObjfAndDeriv(), rnnlm::i, CuMatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), RandUniform(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Set(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and TraceMatMat().
|
static |
Definition at line 1520 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::Max(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Max(), Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1529 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::Min(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Min(), Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1511 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 239 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 334 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Set(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Set().
|
static |
Definition at line 1319 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMatElements(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::DivElements(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 2627 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), ApproxEqual(), DoubleFactorial(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 2677 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 2738 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetZeroAboveDiag().
|
static |
Definition at line 219 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sigmoid(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sigmoid().
|
static |
Definition at line 270 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SoftHinge(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SoftHinge().
|
static |
Definition at line 673 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kUndefined, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SumColumnRanges().
|
static |
Definition at line 1583 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymAddMat2(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 1613 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTakeLower, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymAddMat2(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymInvertPosDef(), SpMatrix< Real >::Trace(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 76 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::Add(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform(), MatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), and TraceMatMat().
|
static |
Definition at line 1873 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 195 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References CuPackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), AssertDiagEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 114 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 127 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::CopyFromPacked(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::CopyToPacked(), rnnlm::i, and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 161 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 177 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::ScaleDiag(), PackedMatrix< Real >::ScaleDiag(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 211 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, CuPackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetUnit().
|
static |
Definition at line 148 of file cu-packed-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Trace(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 2224 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sigmoid().
|
static |
Definition at line 2370 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SoftMaxPerRow().
|
static |
Definition at line 34 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), SparseMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), SparseMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 202 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToSmat(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 181 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 82 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, kTrans, CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::SelectRows(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SelectRows(), and SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 160 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::Sum(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 226 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), SparseMatrix< Real >::NumCols(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), SparseMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), CuMatrix< Real >::Resize(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuSparseMatrix< Real >::Swap().
|
static |
Definition at line 126 of file cu-sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), TraceMatMat(), and TraceMatSmat().
|
static |
Definition at line 206 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), AssertEqual(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, kTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 232 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), AssertEqual(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 323 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 110 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuPackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), PackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), AssertEqual(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 183 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2(), AssertEqual(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), RandGauss(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 73 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), SpMatrix< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 44 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kTakeLower, PackedMatrix< Real >::SetDiag(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 84 of file cu-sp-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), Timer::Elapsed(), KALDI_LOG, kTakeLower, and kTakeUpper.
|
static |
Definition at line 132 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, kTakeLower, kTakeMean, kTakeUpper, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SpMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 43 of file cu-sp-matrix-speed-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), AssertEqual(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyToSp(), Timer::Elapsed(), CuSpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kTrans, CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 152 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), PackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, CuSpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), SpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 302 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Read(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 96 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuSpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromSp(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestCuSpMatrixSetUnit | ( | ) |
Definition at line 275 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuPackedMatrix< Real >::AddToDiag(), AssertEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetUnit(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 257 of file cu-sp-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and TraceSpSp().
|
static |
Definition at line 2029 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Range(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 85 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Range(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestCuTanh | ( | ) |
Definition at line 2574 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Tanh(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Tanh().
|
static |
Definition at line 134 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), CuTpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), TpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 112 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuTpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), TpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 95 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References CuTpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromTp(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 79 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 159 of file cu-tp-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Read(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 2000 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 2048 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 1941 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 1972 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddRowSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 122 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddTpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddTpVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2131 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddTpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddTpVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1917 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 67 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2076 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::InvertElements(), VectorBase< Real >::InvertElements(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
|
static |
Definition at line 48 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuVector< Real >::Read(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuVector< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 102 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::MulTp(), VectorBase< Real >::MulTp(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2173 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), InitRand(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::MulTp(), VectorBase< Real >::MulTp(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 298 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::ReplaceValue(), VectorBase< Real >::ReplaceValue(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 313 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, RandInt(), and VectorBase< Real >::Range().
|
static |
Definition at line 3409 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), ComputeDctMatrix(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, and Rand().
| void kaldi::UnitTestDefines | ( | ) |
Definition at line 190 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References DBL_EPSILON, Exp(), FLT_EPSILON, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ISFINITE, KALDI_ISINF, KALDI_ISNAN, kLogZeroDouble, kLogZeroFloat, M_2PI, M_LOG_2PI, and M_PI.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 219 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References OnlinePitchFeature::AcceptWaveform(), ApproxEqual(), ProcessPitchOptions::delay, ProcessPitchOptions::delta_pitch_noise_stddev, VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), OnlineProcessPitch::Dim(), OnlineProcessPitch::GetFrame(), rnnlm::i, OnlinePitchFeature::InputFinished(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, M_2PI, rnnlm::n, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast_online, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), OnlineProcessPitch::NumFramesReady(), pitch_use_naive_search, RandGauss(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), and PitchExtractionOptions::samp_freq.
Referenced by UnitTestFeatNoKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 1181 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsZero(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, SpMatrix< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), SpMatrix< Real >::LogPosDefDet(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero(), TraceMatMat(), and TraceSpSp().
|
static |
Definition at line 1211 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Log(), SpMatrix< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), SpMatrix< Real >::LogPosDefDet(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Svd().
| void kaldi::UnitTestDiagGmm | ( | ) |
Definition at line 86 of file diag-gmm-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), DiagGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), DiagGmm::CopyFromDiagGmm(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::d, DiagGmm::Dim(), Exp(), DiagGmm::GetComponentMean(), DiagGmm::GetMeans(), DiagGmm::GetVars(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), Log(), DiagGmm::LogLikelihood(), DiagGmm::LogLikelihoods(), DiagGmm::LogLikelihoodsPreselect(), VectorBase< Real >::LogSumExp(), M_LOG_2PI, DiagGmm::Merge(), DiagGmm::MergeKmeans(), DiagGmm::NumGauss(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), RandUniform(), DiagGmm::Read(), DiagGmm::Resize(), DiagGmm::SetInvVars(), DiagGmm::SetInvVarsAndMeans(), DiagGmm::SetMeans(), DiagGmm::SetWeights(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero(), DiagGmm::Split(), Input::Stream(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), DiagGmm::weights(), and DiagGmm::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestDiagGmmGenerate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 54 of file diag-gmm-test.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::AccumulateFromDiag(), AssertEqual(), count, DiagGmm::Dim(), DiagGmm::Generate(), rnnlm::i, InitRandomGmm(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kGmmAll, MleDiagGmmUpdate(), and DiagGmm::NumGauss().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestDiffSampleRate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 528 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::lowpass_cutoff, PitchExtractionOptions::max_f0, WaveData::Read(), and PitchExtractionOptions::samp_freq.
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
| void kaldi::UnitTestDivideRoundingDown | ( | ) |
Definition at line 60 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References DivideRoundingDown(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and RandInt().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 1838 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 1432 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), CreateEigenvalueMatrix(), MatrixBase< Real >::Eig(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), MatrixBase< Real >::Invert(), kNoTrans, Log(), and MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet().
|
static |
Definition at line 1479 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Vec(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddSp(), SpMatrix< Real >::ApproxEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 1413 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::Eig(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 73 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References kaldi::cu::EnsureNonzero(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kUndefined, Rand(), RandInt(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestError | ( | ) |
| void kaldi::UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm | ( | ) |
Definition at line 30 of file ebw-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References AccumDiagGmm::AccumulateFromDiag(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec2(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyRowFromMat(), count, rnnlm::d, DiagGmm::Dim(), Exp(), GmmFlagsToString(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), IsmoothStatsDiagGmm(), KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, kGmmWeights, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), Rand(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), DiagGmm::Resize(), AccumDiagGmm::Resize(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), DiagGmm::SetInvVarsAndMeans(), DiagGmm::SetWeights(), AccumDiagGmm::SetZero(), DiagGmm::Split(), UpdateEbwDiagGmm(), UpdateEbwWeightsDiagGmm(), and DiagGmm::weights().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestExpSpeed | ( | ) |
Definition at line 276 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and KALDI_LOG.
|
static |
Definition at line 4435 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), CompressedMatrix::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_VLOG, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFactorize | ( | ) |
Definition at line 249 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFactorizeTpl | ( | ) |
Definition at line 232 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References Factorize(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 596 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References UnitTestDelay(), UnitTestPieces(), UnitTestSearch(), UnitTestSimple(), and UnitTestSnipEdges().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 604 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References UnitTestComputeGPE(), UnitTestDiffSampleRate(), UnitTestKeele(), UnitTestKeeleNccfBallast(), UnitTestPenaltyFactor(), UnitTestPitchExtractionSpeed(), UnitTestPitchExtractorCompareKeele(), and UnitTestProcess().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFFTbasedBlockConvolution | ( | ) |
Definition at line 26 of file signal-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), FFTbasedBlockConvolveSignals(), FFTbasedConvolveSignals(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFFTbasedConvolution | ( | ) |
Definition at line 41 of file signal-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ConvolveSignals(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), FFTbasedConvolveSignals(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 2284 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApplyCeiling(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyFloor(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::d, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2223 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), SpMatrix< Real >::ApplyFloor(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecSpVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 2261 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), SpMatrix< Real >::ApplyFloor(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, VectorBase< Real >::Min(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SpMatrix< Real >::SymPosSemiDefEig().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFmllrDiagGmm | ( | ) |
Definition at line 50 of file fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), ApplyAffineTransform(), ApplyFeatureTransformToStats(), ApproxEqual(), DiagGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), count, DiagGmm::Dim(), DiagGmm::Generate(), rnnlm::i, InitRandomGmm(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit(), and FmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmDiagonal | ( | ) |
Definition at line 107 of file fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), ApplyAffineTransform(), ApplyModelTransformToStats(), ApproxEqual(), DiagGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), count, DiagGmm::Dim(), DiagGmm::Generate(), rnnlm::i, InitRandomGmm(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), and FmllrOptions::update_type.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFmllrDiagGmmOffset | ( | ) |
Definition at line 167 of file fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateFromPosteriors(), ApplyAffineTransform(), ApplyModelTransformToStats(), ApproxEqual(), DiagGmm::ComponentPosteriors(), count, DiagGmm::Dim(), DiagGmm::Generate(), rnnlm::i, InitRandomGmm(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit(), FmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), and FmllrOptions::update_type.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestFmllrRaw | ( | bool | use_offset | ) |
Definition at line 50 of file fmllr-raw-test.cc.
References FmllrRawAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), ApplyAffineTransform(), count, DiagGmm::Dim(), rnnlm::i, InitRandomGmm(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit(), FmllrRawAccs::SetZero(), and FmllrRawAccs::Update().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestGcdLcm | ( | ) |
Definition at line 71 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestGcdLcmTpl | ( | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References Gcd(), KALDI_ASSERT, Lcm(), and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 4305 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), AssertEqual(), GeneralMatrix::Clear(), GeneralMatrix::Compress(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), ExtractRowRangeWithPadding(), MatrixBase< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), GeneralMatrix::GetMatrix(), InitKaldiInputStream(), InitKaldiOutputStream(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, kNoTrans, rnnlm::n, GeneralMatrix::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), GeneralMatrix::NumRows(), Rand(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), GeneralMatrix::Read(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), GeneralMatrix::SwapSparseMatrix(), and GeneralMatrix::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 1117 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyHeaviside(), KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2614 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, HtkHeader::mNSamples, HtkHeader::mSampleKind, HtkHeader::mSamplePeriod, HtkHeader::mSampleSize, Rand(), ReadHtk(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and WriteHtk().
|
static |
Definition at line 2814 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecSpVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 1802 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 185 of file cu-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, Rand(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SymInvertPosDef().
| void kaldi::UnitTestIo | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 24 of file io-funcs-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ExpectToken(), rnnlm::i, InitKaldiInputStream(), InitKaldiOutputStream(), KALDI_ASSERT, Peek(), PeekToken(), Rand(), RandInt(), RandUniform(), ReadBasicType(), ReadIntegerPairVector(), ReadIntegerVector(), ReadToken(), WriteBasicType(), WriteIntegerPairVector(), WriteIntegerVector(), and WriteToken().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 2486 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, InitKaldiInputStream(), InitKaldiOutputStream(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Read(), Vector< Real >::Read(), Matrix< Real >::Read(), SpMatrix< Real >::Resize(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), VectorBase< Real >::Write(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 2552 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromSp(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, InitKaldiInputStream(), InitKaldiOutputStream(), KALDI_ERR, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Read(), Vector< Real >::Read(), Matrix< Real >::Read(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Write(), VectorBase< Real >::Write(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
| void kaldi::UnitTestIoNew | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 71 of file kaldi-io-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Output::Close(), ExpectToken(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Peek(), Rand(), RandUniform(), ReadBasicType(), ReadIntegerVector(), ReadToken(), Output::Stream(), Input::Stream(), WriteBasicType(), WriteIntegerVector(), and WriteToken().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestIoPipe | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 169 of file kaldi-io-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Output::Close(), ExpectToken(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Peek(), PeekToken(), Rand(), RandUniform(), ReadBasicType(), ReadIntegerVector(), ReadToken(), Sleep(), Output::Stream(), Input::Stream(), WriteBasicType(), WriteIntegerVector(), and WriteToken().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestIoStandard | ( | ) |
Definition at line 283 of file kaldi-io-test.cc.
References Output::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestIvectorExtractor | ( | ) |
Definition at line 145 of file ivector-extractor-test.cc.
References IvectorExtractorStats::AccStatsForUtterance(), IvectorExtractorStats::AuxfPerFrame(), IvectorExtractorEstimationOptions::gaussian_min_count, kaldi::unittest::InitRandFullGmm(), IvectorExtractorOptions::ivector_dim, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, IvectorExtractorStatsOptions::num_samples_for_weights, Rand(), FullGmmNormal::Rand(), Matrix< Real >::Swap(), TestIvectorExtraction(), TestIvectorExtractorIO(), TestIvectorExtractorStatsIO(), IvectorExtractorStats::Update(), IvectorExtractorStatsOptions::update_variances, and IvectorExtractorOptions::use_weights.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 366 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast, WaveData::Read(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 430 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast, WaveData::Read(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 3170 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), OptimizeLbfgs< Real >::DoStep(), Exp(), g_kaldi_verbose_level, OptimizeLbfgs< Real >::GetProposedValue(), OptimizeLbfgs< Real >::GetValue(), SpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_VLOG, LbfgsOptions::minimize, VectorBase< Real >::Norm(), Rand(), RandPosdefSpMatrix(), OptimizeLbfgs< Real >::RecentStepLength(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), VecSpVec(), and VecVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 2345 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SpMatrix< Real >::LimitCond(), and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2202 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, SpMatrix< Real >::LimitCond(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 3230 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, LinearCgd(), LinearCgdOptions::max_error, LinearCgdOptions::max_iters, SpMatrix< Real >::MaxAbsEig(), VectorBase< Real >::Norm(), Rand(), RandPosdefSpMatrix(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestLogAddSub | ( | ) |
Definition at line 171 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References Exp(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Log(), LogAdd(), LogSub(), and Rand().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestLogSpeed | ( | ) |
Definition at line 297 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, and Log().
| void kaldi::UnitTestLstmNonlinearity | ( | ) |
Definition at line 213 of file cu-math-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), ApproxEqual(), kaldi::cu::BackpropLstmNonlinearity(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::ColRange(), kaldi::cu::ComputeLstmNonlinearity(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, kTrans, RandInt(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Row(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), and TraceMatMat().
Referenced by CudaMathUnitTest().
|
static |
Definition at line 2317 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Vec(), AssertEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromSp(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SpMatrix< Real >::SymPosSemiDefEig().
|
static |
Definition at line 338 of file cu-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestMatrixAddMatSmat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 229 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatSmat(), AssertEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, RandInt(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), TraceMatMat(), and TraceMatSmat().
| void kaldi::UnitTestMatrixAddSmatMat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 272 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddSmatMat(), AssertEqual(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, RandInt(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), TraceMatMat(), and TraceMatSmat().
|
static |
Definition at line 3143 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::Max(), and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 3158 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), rnnlm::i, VectorBase< Real >::Max(), SpMatrix< Real >::MaxAbsEig(), VectorBase< Real >::Min(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 3280 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, PackedMatrix< Real >::Max(), MatrixBase< Real >::Max(), VectorBase< Real >::Max(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Min(), MatrixBase< Real >::Min(), VectorBase< Real >::Min(), Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1693 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 1718 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddSpSp(), AssertEqual(), kNoTrans, kTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2750 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddTpVec(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromTp(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1822 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 385 of file cu-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), kNoTrans, kTrans, CuVectorBase< Real >::MulTp(), VectorBase< Real >::MulTp(), Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestNativeFilename | ( | ) |
Definition at line 309 of file kaldi-io-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and MapCygwinPath().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestNonsymmetricPower | ( | ) |
Definition at line 3754 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), InitRandNonsingular(), MatrixBase< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::Power(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 674 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), ApproxEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), MatrixBase< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Norm(), Rand(), RandGauss(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestOnlineCmvn | ( | ) |
Definition at line 32 of file feature-functions-test.cc.
References SlidingWindowCmnOptions::center, SlidingWindowCmnOptions::cmn_window, rnnlm::d, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, SlidingWindowCmnOptions::min_window, SlidingWindowCmnOptions::normalize_variance, Rand(), and SlidingWindowCmn().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 2052 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestParseOptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 46 of file parse-options-test.cc.
References ParseOptions::GetArg(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, DummyOptions::my_bool, DummyOptions::my_string, ParseOptions::NumArgs(), ParseOptions::PrintUsage(), ParseOptions::Read(), DummyOptions::Register(), and ParseOptions::Register().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 3854 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), ComputePca(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::IsUnit(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, NonUnitness(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 3901 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), AssertEqual(), ComputePca(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::IsDiagonal(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, NonDiagonalness(), NonOrthogonality(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SortSvd(), and SpMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 397 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::penalty_factor, WaveData::Read(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 154 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References OnlinePitchFeature::AcceptWaveform(), ApproxEqual(), AssertEqual(), ComputeKaldiPitch(), ProcessPitchOptions::delta_pitch_noise_stddev, VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), OnlineProcessPitch::Dim(), OnlinePitchFeature::GetFrame(), OnlineProcessPitch::GetFrame(), rnnlm::i, OnlinePitchFeature::InputFinished(), KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, M_2PI, rnnlm::n, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast_online, OnlinePitchFeature::NumFramesReady(), ProcessPitch(), RandGauss(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), and PitchExtractionOptions::samp_freq.
Referenced by UnitTestFeatNoKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 465 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::lowpass_cutoff, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast, and WaveData::Read().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 499 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast, and WaveData::Read().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
| void kaldi::UnitTestPldaEstimation | ( | int32 | dim | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file plda-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), PldaStats::AddSamples(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddTp2Sp(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecToRows(), TpMatrix< Real >::Cholesky(), MatrixBase< Real >::Cond(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), PldaEstimator::Estimate(), TpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PldaStats::Sort(), and SpMatrix< Real >::Trace().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestPosteriors | ( | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file logistic-regression-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyRowFromMat(), LogisticRegression::GetLogPosteriors(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, LogisticRegressionConfig::max_steps, LogisticRegressionConfig::normalizer, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), LogisticRegression::SetWeights(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 1074 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::ApplyPow(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), AssertEqual(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), kNoTrans, kTrans, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 1100 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::ApplyPowAbs(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), KALDI_LOG, and Rand().
| void kaldi::UnitTestProcess | ( | ) |
Definition at line 561 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeKaldiPitch(), ConvertIntToString(), ProcessPitchOptions::delta_pitch_noise_stddev, rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, PitchExtractionOptions::lowpass_cutoff, ProcessPitch(), WaveData::Read(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Write().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatWithKeele().
| void kaldi::UnitTestRand | ( | ) |
Definition at line 77 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, Rand(), RandGauss(), RandGauss2(), RandInt(), RandPoisson(), RandPrune(), RandUniform(), and WithProb().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 4481 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, rnnlm::n, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::RandCategorical(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 2653 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::Range(), MatrixBase< Real >::Range(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::UnitTestRangesMatrix | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 842 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), rnnlm::n, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), RandInt(), Output::Stream(), Input::Stream(), Trim(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 2140 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestReadConfig | ( | ) |
Definition at line 479 of file text-utils-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, and ReadConfigLines().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestReadScriptFile | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References Output::Close(), KALDI_ASSERT, ReadScriptFile(), Sleep(), and Output::Stream().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 3611 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), Rand(), RealFft(), RealFftInefficient(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 38 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, and RealFft().
|
static |
Definition at line 3676 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, and RealFft().
Definition at line 140 of file regtree-fmllr-diag-gmm-test.cc.
References AccumAmDiagGmm::AccumulateForGmm(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::AccumulateForGmm(), AmDiagGmm::AddPdf(), RegressionTree::BuildTree(), DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), MatrixBase< Real >::Cond(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::d, DeletePointers(), generate_features(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::GetLogDets(), rnnlm::i, AccumAmDiagGmm::Init(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Init(), MatrixBase< Real >::InvertElements(), rnnlm::j, kGmmAll, RegtreeFmllrOptions::min_count, MleAmDiagGmmUpdate(), rnnlm::n, RegressionTree::NumBaseclasses(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::NumBaseClasses(), AmDiagGmm::NumGaussInPdf(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::NumRegClasses(), Rand(), RandUniform(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::Read(), DiagGmm::Resize(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), DiagGmm::SetInvVarsAndMeans(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), DiagGmm::SetWeights(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::SetZero(), AmDiagGmm::SplitPdf(), Input::Stream(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::TransformFeature(), RegtreeFmllrDiagGmmAccs::Update(), RegtreeFmllrOptions::use_regtree, RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::Validate(), and RegtreeFmllrDiagGmm::Write().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 389 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), Vector< Real >::RemoveElement(), Matrix< Real >::RemoveRow(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 657 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::ReplaceValue(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1899 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::IsZero(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsZero(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kCopyData, kSetZero, Rand(), SpMatrix< Real >::Resize(), Vector< Real >::Resize(), Matrix< Real >::Resize(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Make sure that when Resize() is called with resize_type = kCopyData and a stride_type different from this's stride_type, the resized matrix is equivalent to the original matrix (modulo the stride).
Definition at line 1879 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, kCopyData, kDefaultStride, kSetZero, kStrideEqualNumCols, PlaceNansInGaps(), Rand(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
| void kaldi::UnitTestRoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo | ( | ) |
Definition at line 47 of file kaldi-math-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, and RoundUpToNearestPowerOfTwo().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 984 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyRowFromMat(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), rnnlm::j, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 2712 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::MulColsVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::MulRowsVec(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 2842 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::ScaleDiag(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 289 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ComputeKaldiPitch(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, M_2PI, rnnlm::n, PitchExtractionOptions::nccf_ballast_online, RandGauss(), and PitchExtractionOptions::samp_freq.
Referenced by UnitTestFeatNoKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 2854 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetDiag().
|
static |
Definition at line 449 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), DoubleFactorial(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 481 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyPow(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandUniform(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 60 of file cu-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_LOG, MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetZeroAboveDiag().
|
static |
Definition at line 1161 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, rnnlm::n, Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2383 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::DiffSigmoid(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sigmoid().
|
static |
Definition at line 52 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ComputeAndProcessKaldiPitch(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, and KALDI_LOG.
|
static |
Definition at line 2427 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApplyExp(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyLogAndCopy(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, MatrixBase< Real >::IsDiagonal(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsSymmetric(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsZero(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetUnit(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero().
Referenced by UnitTestFeat(), and UnitTestFeatNoKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 878 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::Add(), SpMatrix< Real >::AddVec2(), MatrixBase< Real >::ApplySoftMax(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, MatrixBase< Real >::LogDet(), MatrixBase< Real >::LogSumExp(), MatrixBase< Real >::MulElements(), rnnlm::n, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::RowData(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetZero(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
|
static |
Definition at line 517 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddColSumMat(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVecDivVec(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyLogSoftMax(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, VectorBase< Real >::IsZero(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, VectorBase< Real >::MulElements(), VectorBase< Real >::Norm(), Rand(), RandUniform(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Set(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSimpleOptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 24 of file simple-options-test.cc.
References SimpleOptions::GetOptionType(), KALDI_ASSERT, SimpleOptions::kInt32, SimpleOptions::Register(), and SimpleOptions::SetOption().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 71 of file pitch-functions-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), AssertEqual(), ComputeAndProcessKaldiPitch(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), WaveData::Data(), PitchExtractionOptions::frame_length_ms, PitchExtractionOptions::frame_shift_ms, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_LOG, KALDI_WARN, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), WaveData::Read(), WaveData::SampFreq(), PitchExtractionOptions::snip_edges, and VecVec().
Referenced by UnitTestFeatNoKeele().
|
static |
Definition at line 2406 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, Log1p(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SoftHinge().
|
static |
Definition at line 3017 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatSp(), VectorBase< Real >::AddSpVec(), AssertEqual(), SolverOptions::diagonal_precondition, rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, SolverOptions::optimize_delta, Rand(), RandPosdefSpMatrix(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SolveDoubleQuadraticMatrixProblem(), SolveQuadraticMatrixProblem(), SolveQuadraticProblem(), TraceMatMat(), TraceMatSpMat(), TraceMatSpMatSp(), VecSpVec(), and VecVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 279 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddDiagVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 297 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddVecVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddVecVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseMatrixAddToMat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 152 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMat(), SparseMatrix< Real >::AddToMat(), AssertEqual(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseMatrixConstructor | ( | ) |
Definition at line 175 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseMatrixFrobeniusNorm | ( | ) |
Definition at line 133 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), SparseMatrix< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), MatrixBase< Real >::FrobeniusNorm(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseMatrixSum | ( | ) |
Definition at line 114 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::Sum(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseMatrixTraceMatSmat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 198 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SparseMatrix< Real >::CopyToMat(), rnnlm::i, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), TraceMatMat(), and TraceMatSmat().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseVectorAddToVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 44 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References SparseVector< Real >::AddToVec(), VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), AssertEqual(), SparseVector< Real >::CopyElementsToVec(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SparseVector< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseVectorMax | ( | ) |
Definition at line 66 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SparseVector< Real >::CopyElementsToVec(), rnnlm::i, SparseVector< Real >::Max(), VectorBase< Real >::Max(), Rand(), RandInt(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and SparseVector< Real >::SetRandn().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseVectorSum | ( | ) |
Definition at line 26 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SparseVector< Real >::CopyElementsToVec(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseVector< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseVector< Real >::Sum(), and VectorBase< Real >::Sum().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSparseVectorVecSvec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 92 of file sparse-matrix-test.cc.
References SparseVector< Real >::CopyElementsToVec(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseVector< Real >::SetRandn(), VecSvec(), and VecVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 2160 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), SpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromSp(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), SpMatrix< Real >::InvertDouble(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and RandGauss().
|
static |
Definition at line 339 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyColFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyColsFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyColsFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyRowFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowsFromVec(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 3453 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), ComplexFt(), SplitRadixComplexFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 3591 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), SplitRadixComplexFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), KALDI_ASSERT, and Rand().
|
static |
Definition at line 3639 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), SplitRadixRealFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), Rand(), RealFftInefficient(), and VectorBase< Real >::Scale().
|
static |
Definition at line 50 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References SplitRadixRealFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, and KALDI_LOG.
|
static |
Definition at line 3688 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SplitRadixRealFft< Real >::Compute(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), rnnlm::i, and KALDI_LOG.
|
static |
Definition at line 1265 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::CopyFromVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 430 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), rnnlm::i, and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1292 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMatMat(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero().
|
static |
Definition at line 1318 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, MatrixBase< Real >::Set(), MatrixBase< Real >::Svd(), and SpMatrix< Real >::SymPosSemiDefEig().
|
static |
Definition at line 1398 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Svd().
|
static |
Definition at line 1360 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::Dim(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SortSvd(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Svd().
|
static |
Definition at line 64 of file matrix-lib-speed-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), Timer::Elapsed(), rnnlm::i, PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Svd().
|
static |
Definition at line 3953 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Svd().
|
static |
Definition at line 1341 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::SetZero().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSwapCu2Cu | ( | ) |
Definition at line 2533 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Swap().
| void kaldi::UnitTestSwapCu2M | ( | ) |
Definition at line 2554 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::CopyToMat(), KALDI_ASSERT, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuMatrix< Real >::Swap().
|
static |
Definition at line 2980 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), AssertEqual(), TpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::Sum(), MatrixBase< Real >::SymAddMat2(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTableRandomBothDouble | ( | bool | binary, |
| bool | read_scp, | ||
| bool | sorted, | ||
| bool | called_sorted, | ||
| bool | once | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 768 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CharToString(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), RandomizeVector(), Uniq(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTableRandomBothDoubleMatrix | ( | bool | binary, |
| bool | read_scp, | ||
| bool | sorted, | ||
| bool | called_sorted, | ||
| bool | once | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 972 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::ApproxEqual(), CharToString(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::HasKey(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, Rand(), RandomizeVector(), Uniq(), RandomAccessTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 704 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandGauss(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTableSequentialBool | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 356 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTableSequentialDouble | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 390 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 431 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 652 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References ApproxEqual(), CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandGauss(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTableSequentialInt32 | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 323 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 518 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTableSequentialInt32Script | ( | bool | binary | ) |
Definition at line 600 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), ReadScriptFile(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), TableWriter< Holder >::Write(), and WriteScriptFile().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 477 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), RandInt(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 558 of file kaldi-table-test.cc.
References CharToString(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Close(), TableWriter< Holder >::Close(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Done(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Key(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Next(), Rand(), SequentialTableReader< Holder >::Value(), and TableWriter< Holder >::Write().
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 2356 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::DiffTanh(), Exp(), rnnlm::i, Rand(), and MatrixBase< Real >::Tanh().
|
static |
Definition at line 4518 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), VectorBase< Real >::ApplyAbs(), AssertEqual(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyDiagFromMat(), VectorBase< Real >::Data(), SpMatrix< Real >::Eig(), rnnlm::i, SpMatrix< Real >::IsUnit(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, NonUnitness(), RandGauss(), and SpMatrix< Real >::TopEigs().
|
static |
Definition at line 1968 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2(), AssertEqual(), kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 1943 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), and PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 2180 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), TpMatrix< Real >::CopyFromTp(), rnnlm::i, TpMatrix< Real >::Invert(), MatrixBase< Real >::IsUnit(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), and RandGauss().
|
static |
Definition at line 119 of file cu-test.cc.
References KALDI_LOG, PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), CuPackedMatrix< Real >::Trace(), and SpMatrix< Real >::Trace().
|
static |
Definition at line 3327 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMatMat(), approx_equal(), AssertEqual(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::Trace(), TraceMat(), TraceMatMat(), TraceMatMatMat(), TraceMatMatMatMat(), TraceMatSpMat(), TraceMatSpMatSp(), and TraceSpMat().
|
static |
Definition at line 1277 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and TraceMatMat().
|
static |
Definition at line 2865 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), Rand(), PackedMatrix< Real >::Scale(), PackedMatrix< Real >::ScaleDiag(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), TraceSpSp(), and TraceSpSpLower().
| void kaldi::UnitTestTrain | ( | ) |
Definition at line 67 of file logistic-regression-test.cc.
References MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromMat(), LogisticRegression::GetObjfAndGrad(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Log(), LogisticRegressionConfig::max_steps, LogisticRegressionConfig::normalizer, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), LogisticRegression::Train(), and LogisticRegression::weights_.
Referenced by main().
|
static |
Definition at line 3491 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 2076 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyFromSp(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, MatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), MatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), PackedMatrix< Real >::NumRows(), Rand(), RandGauss(), and Matrix< Real >::Resize().
|
static |
Definition at line 4468 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::IsTridiagonal(), and KALDI_ASSERT.
|
static |
Definition at line 1579 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), AssertEqual(), cblas_Xspmv(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, SpMatrix< Real >::LogDet(), NonUnitness(), Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::Set(), SpMatrix< Real >::Trace(), and SpMatrix< Real >::Tridiagonalize().
|
static |
Definition at line 1640 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References SpMatrix< Real >::AddMat2Sp(), AssertEqual(), cblas_Xspmv(), rnnlm::i, InitRandNonsingular(), SpMatrix< Real >::IsDiagonal(), rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, SpMatrix< Real >::LogDet(), NonUnitness(), SpMatrix< Real >::Qr(), Rand(), SpMatrix< Real >::Trace(), and SpMatrix< Real >::Tridiagonalize().
|
static |
Definition at line 4563 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddTpVec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_LOG, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), PackedMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and VectorBase< Real >::Solve().
| void kaldi::UnitTestVecMatVec | ( | ) |
Definition at line 234 of file cu-vector-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and VecMatVec().
|
static |
Definition at line 1770 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddMatSvec(), AssertEqual(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and Matrix< Real >::Transpose().
|
static |
Definition at line 406 of file cu-test.cc.
References AssertEqual(), CuVectorBase< Real >::CopyToVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::MulElements(), VectorBase< Real >::MulElements(), Rand(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::Scale(), VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn(), and CuVectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 631 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Max(), Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 644 of file matrix-lib-test.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, VectorBase< Real >::Min(), Rand(), and VectorBase< Real >::SetRandn().
|
static |
Definition at line 810 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddMatSmat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddMatSmat(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and swap().
|
static |
Definition at line 778 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddSmat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddSmat(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and swap().
|
static |
Definition at line 848 of file cu-matrix-test.cc.
References CuMatrixBase< Real >::AddSmatMat(), MatrixBase< Real >::AddSmatMat(), ApproxEqual(), rnnlm::i, KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, rnnlm::n, Rand(), MatrixBase< Real >::SetRandn(), SparseMatrix< Real >::SetRandn(), and swap().
| void UpdateEbwAmDiagGmm | ( | const AccumAmDiagGmm & | num_stats, |
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | den_stats, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| const EbwOptions & | opts, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | auxf_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out, | ||
| int32 * | num_floored_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 278 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), KALDI_ASSERT, AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs(), and UpdateEbwDiagGmm().
Referenced by main(), and EbwWeightOptions::Register().
| void UpdateEbwDiagGmm | ( | const AccumDiagGmm & | num_stats, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | den_stats, | ||
| GmmFlagsType | flags, | ||
| const EbwOptions & | opts, | ||
| DiagGmm * | gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | auxf_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out, | ||
| int32 * | num_floored_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 94 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References VectorBase< Real >::AddVec(), DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), DiagGmmNormal::CopyFromDiagGmm(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), MatrixBase< Real >::CopyRowFromVec(), DiagGmmNormal::CopyToDiagGmm(), DiagGmm::Dim(), AccumDiagGmm::Dim(), EbwOptions::E, EBWUpdateGaussian(), AccumDiagGmm::Flags(), GmmFlagsToString(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_ERR, KALDI_VLOG, KALDI_WARN, kGmmMeans, kGmmVariances, kGmmWeights, AccumDiagGmm::mean_accumulator(), DiagGmmNormal::means_, DiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::NumGauss(), AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), MatrixBase< Real >::Row(), EbwOptions::tau, AccumDiagGmm::variance_accumulator(), and DiagGmmNormal::vars_.
Referenced by EbwWeightOptions::Register(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), and UpdateEbwAmDiagGmm().
| void UpdateEbwWeightsAmDiagGmm | ( | const AccumAmDiagGmm & | num_stats, |
| const AccumAmDiagGmm & | den_stats, | ||
| const EbwWeightOptions & | opts, | ||
| AmDiagGmm * | am_gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | auxf_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 300 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References AccumAmDiagGmm::GetAcc(), AmDiagGmm::GetPdf(), KALDI_ASSERT, AccumAmDiagGmm::NumAccs(), AmDiagGmm::NumPdfs(), and UpdateEbwWeightsDiagGmm().
Referenced by main(), and EbwWeightOptions::Register().
| void UpdateEbwWeightsDiagGmm | ( | const AccumDiagGmm & | num_stats, |
| const AccumDiagGmm & | den_stats, | ||
| const EbwWeightOptions & | opts, | ||
| DiagGmm * | gmm, | ||
| BaseFloat * | auxf_change_out, | ||
| BaseFloat * | count_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 207 of file ebw-diag-gmm.cc.
References DiagGmm::ComputeGconsts(), DiagGmmNormal::CopyFromDiagGmm(), VectorBase< Real >::CopyFromVec(), DiagGmmNormal::CopyToDiagGmm(), KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_LOG, kGmmAll, EbwWeightOptions::min_gaussian_weight, EbwWeightOptions::min_num_count_weight_update, AccumDiagGmm::occupancy(), VectorBase< Real >::Sum(), EbwWeightOptions::tau, and DiagGmmNormal::weights_.
Referenced by EbwWeightOptions::Register(), UnitTestEstimateMmieDiagGmm(), and UpdateEbwWeightsAmDiagGmm().
| Real VecMatVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< Real > & | v1, |
| const CuMatrixBase< Real > & | M, | ||
| const CuVectorBase< Real > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
Returns 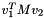 .
.
Definition at line 83 of file cu-vector.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::AddMatVec(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, kNoTrans, kTrans, CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumCols(), CuMatrixBase< Real >::NumRows(), VecMatVec(), and VecVec().
| template float kaldi::VecMatVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< float > & | v1, |
| const CuMatrixBase< float > & | M, | ||
| const CuVectorBase< float > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecMatVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< double > & | v1, |
| const CuMatrixBase< double > & | M, | ||
| const CuVectorBase< double > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::VecMatVec | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | v1, |
| const MatrixBase< float > & | M, | ||
| const VectorBase< float > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecMatVec | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | v1, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | M, | ||
| const VectorBase< double > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
Referenced by VecMatVec().
| template float kaldi::VecSpVec | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | v1, |
| const SpMatrix< float > & | M, | ||
| const VectorBase< float > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecSpVec | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | v1, |
| const SpMatrix< double > & | M, | ||
| const VectorBase< double > & | v2 | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::VecSvec | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | vec, |
| const SparseVector< float > & | svec | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecSvec | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | vec, |
| const SparseVector< double > & | svec | ||
| ) |
Referenced by TraceMatSmat().
| template float kaldi::VecVec | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | a, |
| const VectorBase< float > & | b | ||
| ) |
| Real VecVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< Real > & | a, |
| const CuVectorBase< Real > & | b | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 47 of file cu-vector.cc.
References CuVectorBase< Real >::Data(), CuVectorBase< Real >::Dim(), KALDI_ASSERT, CuVectorBase< Real >::Vec(), and VecVec().
| template double kaldi::VecVec | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | a, |
| const VectorBase< double > & | b | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::VecVec | ( | const VectorBase< float > & | ra, |
| const VectorBase< double > & | rb | ||
| ) |
| template float kaldi::VecVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< float > & | a, |
| const CuVectorBase< float > & | b | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< double > & | a, |
| const CuVectorBase< double > & | b | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecVec | ( | const VectorBase< double > & | ra, |
| const VectorBase< float > & | rb | ||
| ) |
Referenced by VecMatVec().
| Real VecVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< Real > & | A, |
| const CuVectorBase< OtherReal > & | B | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 73 of file cu-vector.cc.
References VecVec().
| template float kaldi::VecVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< float > & | A, |
| const CuVectorBase< double > & | B | ||
| ) |
| template double kaldi::VecVec | ( | const CuVectorBase< double > & | A, |
| const CuVectorBase< float > & | B | ||
| ) |
Referenced by CuVectorBase< float >::ApproxEqual().
| void kaldi::VerifySymbolRange | ( | const std::string & | trace, |
| const bool | want_found, | ||
| const std::string & | want_symbol | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 36 of file kaldi-error-test.cc.
References KALDI_ERR, and kaldi::internal::LocateSymbolRange().
Referenced by TestLocateSymbolRange().
| bool WithProb | ( | BaseFloat | prob, |
| struct RandomState * | state | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 72 of file kaldi-math.cc.
References KALDI_ASSERT, KALDI_COMPILE_TIME_ASSERT, and Rand().
Referenced by GetCount(), kaldi::nnet2::GetCount(), kaldi::nnet3::GetCount(), SpecAugmentTimeMaskComponent::GetMemo(), main(), kaldi::nnet3::PerturbImage(), RescoreCompactLatticeInternal(), SparseVector< Real >::SetRandn(), UnitTestCuMatrixAddToElements(), and UnitTestRand().
| bool WordAlignLattice | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| const WordBoundaryInfo & | info, | ||
| int32 | max_states, | ||
| CompactLattice * | lat_out | ||
| ) |
Align lattice so that each arc has the transition-ids on it that correspond to the word that is on that arc.
[May also have epsilon arcs for optional silences.] Returns true if everything was OK, false if some kind of error was detected (e.g. the words didn't have the kinds of sequences we would expect if the WordBoundaryInfo was correct). Note: we don't expect silence inside words, or empty words (words with no phones), and we expect the word to start with a wbegin_phone, to end with a wend_phone, and to possibly have winternal_phones inside (or to consist of just one wbegin_and_end_phone). Note: if it returns false, it doesn't mean the lattice that the output is necessarily bad: it might just be that the lattice was "forced out" as the end-state was not reached during decoding, and in this case the output might be usable. If max_states > 0, if this code detects that the #states of the output will be greater than max_states, it will abort the computation, return false and produce an empty lattice out.
Definition at line 723 of file word-align-lattice.cc.
References LatticeWordAligner::AlignLattice().
Referenced by main().
| bool WordAlignLatticeLexicon | ( | const CompactLattice & | lat, |
| const TransitionModel & | tmodel, | ||
| const WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo & | lexicon_info, | ||
| const WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts & | opts, | ||
| CompactLattice * | lat_out | ||
| ) |
Align lattice so that each arc has the transition-ids on it that correspond to the word that is on that arc.
[May also have epsilon arcs for optional silences.] Returns true if everything was OK, false if there was any kind of error including when the the lattice seems to have been "forced out" (did not reach end state, resulting in partial word at end).
Definition at line 1001 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
References LatticeLexiconWordAligner::AlignLattice(), WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::allow_duplicate_paths, KALDI_WARN, WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::max_expand, WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::partial_word_label, PhoneAlignLattice(), PhoneAlignLatticeOptions::remove_epsilon, PhoneAlignLatticeOptions::reorder, WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::reorder, PhoneAlignLatticeOptions::replace_output_symbols, WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::test, and TestWordAlignedLattice().
Referenced by main(), WordAlignLatticeLexiconOpts::Register(), and TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon().
| void kaldi::WriteAsKaldiVector | ( | const std::vector< double > & | counts, |
| std::string & | wxfilename, | ||
| bool | binary | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 53 of file compare-int-vector.cc.
References rnnlm::i, and WriteKaldiObject().
Referenced by main().
| bool WriteCompactLattice | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| bool | binary, | ||
| const CompactLattice & | t | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 62 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by TestWordAlignLatticeLexicon(), CompactLatticeHolder::Write(), and DiscriminativeNnetExample::Write().
Definition at line 228 of file event-map.cc.
References rnnlm::i, WriteBasicType(), and WriteToken().
Referenced by MakeEventPair(), TestEventTypeIo(), and WriteBuildTreeStats().
| template bool kaldi::WriteHtk | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| const MatrixBase< float > & | M, | ||
| HtkHeader | htk_hdr | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::WriteHtk | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | M, | ||
| HtkHeader | htk_hdr | ||
| ) |
Referenced by WriteHtk().
WriteToList attempts to write this list of integers, one per line, to the given file, in text format.
returns true if succeeded.
Definition at line 24 of file simple-io-funcs.cc.
References Output::Close(), rnnlm::i, Output::Open(), and Output::Stream().
Referenced by main().
| bool WriteIntegerVectorVectorSimple | ( | const std::string & | wxfilename, |
| const std::vector< std::vector< int32 > > & | list | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 46 of file simple-io-funcs.cc.
References Output::Close(), rnnlm::i, rnnlm::j, Output::Open(), and Output::Stream().
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 388 of file kaldi-lattice.cc.
References KALDI_WARN.
Referenced by LatticeHolder::Write(), and DiscriminativeSupervision::Write().
| template bool kaldi::WriteSphinx | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| const MatrixBase< float > & | M | ||
| ) |
| template bool kaldi::WriteSphinx | ( | std::ostream & | os, |
| const MatrixBase< double > & | M | ||
| ) |
Referenced by WriteSphinx().
|
static |
Definition at line 100 of file wave-reader.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, and KALDI_SWAP2.
Referenced by WaveData::Write().
|
static |
Definition at line 86 of file wave-reader.cc.
References rnnlm::i, KALDI_ERR, and KALDI_SWAP4.
Referenced by WaveData::Write().
|
inline |
Definition at line 199 of file cblas-wrappers.h.
References cblas_Xaxpy(), cblas_Xscal(), rnnlm::i, and kNoTrans.
Referenced by MatrixBase< float >::AddMatSmat(), VectorBase< float >::AddMatSvec(), SpMatrix< float >::AddSmat2Sp(), and MatrixBase< float >::AddSmatMat().
|
static |
Definition at line 43 of file kaldi-math.cc.
| int32 buffer_fill = 0 |
Definition at line 356 of file online-audio-client.cc.
Referenced by ReadLine().
| int32 buffer_offset = 0 |
Definition at line 355 of file online-audio-client.cc.
Referenced by ReadLine().
| CuAllocatorOptions g_allocator_options |
Definition at line 644 of file cu-allocator.cc.
Referenced by CuAllocatorOptions::Check().
| int32 g_num_threads = 8 |
Definition at line 25 of file kaldi-thread.cc.
Referenced by IvectorExtractor::ComputeDerivedVars(), kaldi::nnet2::DoBackpropParallel(), main(), TestThreads(), IvectorExtractorStats::UpdateProjections(), and IvectorExtractorStats::UpdateWeights().
| ProfileStats g_profile_stats |
| const float kFramesPerSecond = 100.0f |
Definition at line 65 of file online-audio-server-decode-faster.cc.
Referenced by main().
Definition at line 130 of file kaldi-math.h.
| const double kLogZeroDouble = -std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity() |
Definition at line 129 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by ComputeCompactLatticeAlphas(), ComputeCompactLatticeBetas(), ComputeLatticeAlphasAndBetas(), MinimumBayesRisk::EditDistance(), LatticeForwardBackward(), LatticeForwardBackwardMpeVariants(), LogSub(), VectorBase< float >::LogSumExp(), MatrixBase< float >::LogSumExp(), and UnitTestDefines().
Definition at line 128 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by LogSub(), VectorBase< float >::LogSumExp(), MatrixBase< float >::LogSumExp(), and UnitTestDefines().
| const int32 kMaxVal = 20 |
Definition at line 143 of file event-map-test.cc.
Referenced by RandomEventMap(), and TestEventMapMapValues().
|
static |
Definition at line 124 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::LogSumExp(), and MatrixBase< float >::LogSumExp().
|
static |
Definition at line 125 of file kaldi-math.h.
Referenced by VectorBase< float >::LogSumExp(), and MatrixBase< float >::LogSumExp().
| const int kNumStatesOffset = 1000 |
Definition at line 31 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
|
static |
Definition at line 39 of file context-dep.h.
Referenced by AccumulateTreeStats(), AutomaticallyObtainQuestions(), ContextDependency::Compute(), ContextDependency::EnumeratePairs(), GenRandStats(), GetFullBiphoneStubMap(), ContextDependency::GetPdfInfo(), GetStubMap(), GetToLengthMap(), KMeansClusterPhones(), main(), TreeRenderer::MakeEdgeLabel(), MakeEvent(), TreeRenderer::RenderNonLeaf(), TreeRenderer::RenderTable(), and TestGenRandStats().
|
static |
Definition at line 40 of file arpa-lm-compiler-test.cc.
Referenced by CoverageTest().
Definition at line 214 of file parse-options.cc.
| const int kTemporaryEpsilon = -2 |
Definition at line 30 of file word-align-lattice-lexicon.cc.
Referenced by WordAlignLatticeLexiconInfo::UpdateLexiconMap().
| const BaseFloat kWaveSampleMax = 32768.0 |
For historical reasons, we scale waveforms to the range (2^15-1)*[-1, 1], not the usual default DSP range [-1, 1].
Definition at line 62 of file wave-reader.h.
|
static |
Definition at line 48 of file kaldi-error.cc.
Referenced by MessageLogger::LogMessage(), and SetLogHandler().
| bool pitch_use_naive_search = false |
Definition at line 292 of file pitch-functions.cc.
Referenced by UnitTestDelay().
|
static |
Definition at line 47 of file kaldi-error.cc.
| char read_buffer[1025] |
Definition at line 357 of file online-audio-client.cc.
| const char* ws_delim = " \t\n\r" |
Definition at line 32 of file text-utils-test.cc.